|
Index (typography)
The manicule, , is a typographic mark with the appearance of a hand with its index finger extending in a pointing gesture. Originally used for handwritten marginal notes, it later came to be used in printed works to draw the reader's attention to important text. Though once widespread, it is rarely used today, except as an occasional archaic novelty. Terminology For most of its history, the mark has been inconsistently referred to by a variety of names. William H. Sherman, in the first dedicated study of the mark, uses the term ''manicule'' (from the Latin root ''manicula'', meaning "little hand"), but also identifies 15 further names which have been used: * hand * pointing hand * hand director * pointer * digit * fist * mutton fist * bishop's fist * index * * indicator * indicule * maniple * pilcrow The last three Sherman labels erroneous, with ''indicule'' and ''maniple'' being mishearings or conflations, and ''pilcrow'' properly referring to the paragraph mark, . History ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Typography
Typography is the art and technique of arranging type to make written language legible, readable and appealing when displayed. The arrangement of type involves selecting typefaces, point sizes, line lengths, line-spacing ( leading), and letter-spacing (tracking), as well as adjusting the space between pairs of letters (kerning). The term ''typography'' is also applied to the style, arrangement, and appearance of the letters, numbers, and symbols created by the process. Type design is a closely related craft, sometimes considered part of typography; most typographers do not design typefaces, and some type designers do not consider themselves typographers. Typography also may be used as an ornamental and decorative device, unrelated to the communication of information. Typography is the work of typesetters (also known as compositors), typographers, graphic designers, art directors, manga artists, comic book artists, and, now, anyone who arranges words, letters, numbers ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Return Address
In postal mail, a return address is an explicit inclusion of the address of the person sending the message. It provides the recipient (and sometimes authorized intermediaries) with a means to determine how to respond to the sender of the message if needed. The return address should include an address or P.O. box details in the same way as the delivery address should. In countries like the United States, the return address is located in the upper left-hand corner of the envelope, card, or label. In the United Kingdom, the return address is usually placed on the reverse of the envelope, after the words "Return address". Businesses often use envelopes preprinted with a return address. Many individuals have sheets of adhesive labels preprinted with their home address to affix to their correspondence. Charities sometimes include such sheets in mailshots. Rolls of return address labels can be purchased from companies that sell personalized labels to provide individuals an easy way to p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thomas Pynchon
Thomas Ruggles Pynchon Jr. ( , ; born May 8, 1937) is an American novelist noted for his dense and complex novels. His fiction and non-fiction writings encompass a vast array of subject matter, genres and themes, including history, music, science, and mathematics. For ''Gravity's Rainbow'', Pynchon won the 1973 U.S. National Book Award for Fiction."National Book Awards – 1974" . Retrieved 2012-03-29. (With essays by Casey Hicks and Chad Post from the Awards 60-year anniversary blog. The mock acceptance speech by Irwin Corey is not reprinted by NBF.) Hailing from |
Stream Of Consciousness (narrative Mode)
In literary criticism, stream of consciousness is a narrative mode or method that attempts "to depict the multitudinous thoughts and feelings which pass through the mind" of a narrator. The term was coined by Daniel Oliver in 1840 in ''First Lines of Physiology: Designed for the Use of Students of Medicine,'' when he wrote, Better known, perhaps, is the 1855 usage by Alexander Bain in the first edition of ''The Senses and the Intellect'', when he wrote, "The concurrence of Sensations in one common stream of consciousness–on the same cerebral highway–enables those of different senses to be associated as readily as the sensations of the same sense". But it is commonly credited to William James who used it in 1890 in his ''The Principles of Psychology''. In 1918, the novelist May Sinclair (1863–1946) first applied the term stream of consciousness, in a literary context, when discussing Dorothy Richardson's novels. '' Pointed Roofs'' (1915), the first work in Richardson's ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Breakfast Of Champions
''Breakfast of Champions, or Goodbye Blue Monday'' is a 1973 novel by the American author Kurt Vonnegut. His seventh novel, it is set predominantly in the fictional town of Midland City, Ohio, and focuses on two characters: Dwayne Hoover, a Midland resident, Pontiac dealer and affluent figure in the city, and Kilgore Trout, a widely published but mostly unknown science fiction author. ''Breakfast of Champions'' deals with themes of free will, suicide, and race relations, among others. The novel is full of drawings by the author, substituting descriptive language with depictions requiring no translation. Plot ''Breakfast of Champions'' tells the story of the events that lead up to the meeting of Kilgore Trout and Dwayne Hoover, the meeting itself, and the immediate aftermath. Trout is a struggling science fiction writer who, after their fateful meeting, becomes successful and wins a Nobel Prize; Hoover is a wealthy businessman who is going insane, sent over the brink by his enco ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kurt Vonnegut
Kurt Vonnegut Jr. (November 11, 1922 – April 11, 2007) was an American writer known for his satirical and darkly humorous novels. In a career spanning over 50 years, he published fourteen novels, three short-story collections, five plays, and five nonfiction works; further collections have been published after his death. Born and raised in Indianapolis, Vonnegut attended Cornell University but withdrew in January 1943 and enlisted in the US Army. As part of his training, he studied mechanical engineering at the Carnegie Institute of Technology (now Carnegie Mellon University) and the University of Tennessee. He was then deployed to Europe to fight in World War II and was captured by the Germans during the Battle of the Bulge. He was interned in Dresden, where he survived the Allied bombing of the city in a meat locker of the slaughterhouse where he was imprisoned. After the war, he married Jane Marie Cox, with whom he had three children. He adopted his nephews after his siste ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
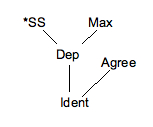
Optimality Theory
In linguistics, Optimality Theory (frequently abbreviated OT) is a linguistic model proposing that the observed forms of language arise from the optimal satisfaction of conflicting constraints. OT differs from other approaches to phonological analysis, such as autosegmental phonology and linear phonology (SPE), which typically use rules rather than constraints. OT models grammars as systems that provide mappings from inputs to outputs; typically, the inputs are conceived of as underlying representations, and the outputs as their surface realizations. It is an approach within the larger framework of generative grammar. In linguistics, Optimality Theory has its origin in a talk given by Alan Prince and Paul Smolensky in 1991 which was later developed in a book manuscript by the same authors in 1993. Overview There are three basic components of the theory: * Generator () takes an input, and generates the list of possible outputs, or candidates, * Constraint component () provides ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cross-reference
The term cross-reference (abbreviation: xref) can refer to either: * An instance within a document which refers to related information elsewhere in the same document. In both printed and online dictionaries cross-references are important because they form a network structure of relations existing between different parts of data, dictionary-internal as well as dictionary external. * In an index, a cross-reference is often denoted by ''See also''. For example, under the term ''Albert Einstein'' in the index of a book about Nobel Laureates, there may be the cross-reference ''See also: Einstein, Albert''. * In hypertext, cross-referencing is maintained to a document with either in-context (XRIC) or out-of-context (''XROC'') cross-referencing. These are similar to KWIC and KWOC. * In programming, "cross-referencing" means the listing of every file name and line number where a given named identifier occurs within the program's source tree. * In a relational database management sy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Section Divider
In books and documents, a section is a subdivision, especially of a chapter. Sections are visually separated from each other with a section break, typically consisting of extra space between the sections, and sometimes also by a section heading for the latter section. They are a concern in the process of typography and pagination, where it may be desirable to have a page break follow a section break for the sake of aesthetics or readability. In fiction, sections often represent scenes, and accordingly the space separating them is sometimes also called a scene break. Section form and numbering In written narrative such as fiction, sections are not usually numbered or named. Section breaks are used to signal various changes in a story, including changes in time, location, point-of-view character, mood, tone, emotion, and pace. As a fiction-writing mode, the section break can be considered a transition, similar to a chapter break. Some documents, especially legal document ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Asterisks
The asterisk ( ), from Late Latin , from Ancient Greek , ''asteriskos'', "little star", is a typographical symbol. It is so called because it resembles a conventional image of a heraldic star. Computer scientists and mathematicians often vocalize it as star (as, for example, in ''the A* search algorithm'' or ''C*-algebra''). In English, an asterisk is usually five- or six-pointed in sans-serif typefaces, six-pointed in serif typefaces, and six- or eight-pointed when handwritten. Its most common use is to call out a footnote. It is also often used to censor offensive words. In computer science, the asterisk is commonly used as a wildcard character, or to denote pointers, repetition, or multiplication. History The asterisk has already been used as a symbol in ice age cave paintings. There is also a two thousand-year-old character used by Aristarchus of Samothrace called the , , which he used when proofreading Homeric poetry to mark lines that were duplicated. Origen is know ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fleuron (typography)
A fleuron (;), also known as printers' flower, is a typographic element, or glyph, used either as a punctuation mark or as an ornament for typographic compositions. Fleurons are stylized forms of flowers or leaves; the term derives from the fro, floron ("flower"). Robert Bringhurst in ''The Elements of Typographic Style'' calls the forms "horticultural dingbats". A commonly-encountered fleuron is the , the floral heart or (ivy leaf). It is also known as an aldus leaf (after Italian Renaissance printer Aldus Manutius). History Flower decorations are among the oldest typographic ornaments. A fleuron can also be used to fill the white space that results from the indentation of the first line of a paragraph, on a line by itself to divide paragraphs in a highly stylized way, to divide lists, or for pure ornamentation. The fleuron (as a formal glyph) is an sixteenth century introduction. Fleurons were crafted the same way as other typographic elements were: as individual metal s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sententiae
''Sententiae'', the nominative plural of the Latin word ''sententia'', are brief moral sayings, such as proverbs, adages, aphorisms, maxims, or apophthegms taken from ancient or popular or other sources, often quoted without context. ''Sententia'', the nominative singular, also called a "sentence", is a kind of rhetorical proof. Through the invocation of a proverb, quotation, or witty turn of phrase during a presentation or conversation one may be able to gain the assent of the listener, who will hear a kind of non-logical, but agreed-upon truth in what one is saying. An example of this is the phrase "age is better with wine" playing off of the adage "wine is better with age". The same saying is present in . History The use of ''sententiae'' has been explained by Aristotle (when he discusses the γνώμη ''gnomê'', or sententious maxim, as a form of enthymeme), Quintilian, and other classical authorities. Early modern English writers, heavily influenced by various humanist ed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |