|
Imputed Rent
Imputed rent is the rental price an individual would pay for an asset they own. The concept applies to any capital good, but it is most commonly used in housing markets to measure the rent homeowners would pay for a housing unit equivalent to the one they own. Imputing housing rent is necessary to measure economic activity in national accounts. Because asset owners do not pay rent, owners' imputed rent must be measured indirectly. Imputed housing rent is the economic theory of imputation applied to real estate: that the value is more a matter of what the buyer is willing to pay than the cost the seller incurs to create it. In this case, market rents are used to estimate the value to the property owner. Thus, imputed rent offers a way to compare homeowners' and tenants' economic decisions. More formally, in owner-occupancy, the landlord–tenant relationship is short-circuited. Consider a model: two people, A and B, each of whom owns property. If A lives in B's property, and B li ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Accounts
National accounts or national account systems (NAS) are the implementation of complete and consistent accounting techniques for measuring the economic activity of a nation. These include detailed underlying measures that rely on double-entry accounting. By design, such accounting makes the totals on both sides of an account equal even though they each measure different characteristics, for example production and the income from it. As a method, the subject is termed national accounting or, more generally, social accounting.Nancy D. Ruggles, 1987. "social accounting," '' The New Palgrave: A Dictionary of Economics'', v. 4, pp. 377–82. Stated otherwise, national accounts as ''systems'' may be distinguished from the economic data associated with those systems. While sharing many common principles with business accounting, national accounts are based on economic concepts. One conceptual construct for representing flows of all economic transactions that take place in an economy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Theory Of Imputation
The theory of imputation is based on the so-called theory of factors of production proposed by the French economist Jean-Baptiste Say and elaborated by the American economist John Bates Clark in his work ''The Distribution of Wealth'' (1899; Russian translation, 1934). The proponents of the theory of imputation see its main task as elucidating which parts of wealth may be attributed (imputed) to labor and capital respectively. Principles In economics, the theory of imputation, first expounded by Carl Menger, maintains that factor prices are determined by output prices (i.e. the value of factors of production is the individual contribution of each in the final product, but its value is the value of the last contributed to the final product (the marginal utility before reaching the point Pareto optimal). Thus, Friedrich von Wieser identified a flaw in the theory of imputation as expounded by his teacher, Carl Menger: overvaluation may occur if one is confronted with economies where p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Real Estate
Real estate is property consisting of land and the buildings on it, along with its natural resources such as crops, minerals or water; immovable property of this nature; an interest vested in this (also) an item of real property, (more generally) buildings or housing in general."Real estate": Oxford English Dictionary online: Retrieved September 18, 2011 In terms of law, ''real'' is in relation to land property and is different from personal property while ''estate'' means the "interest" a person has in that land property. Real estate is different from personal property, which is not permanently attached to the land, such as vehicles, boats, jewelry, furniture, tools and the rolling stock of a farm. In the United States, the transfer, owning, or acquisition of real estate can be through business corporations, individuals, nonprofit corporations, fiduciaries, or any legal entity as seen within the law of each U.S. state. History of real estate The natural right of a person t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
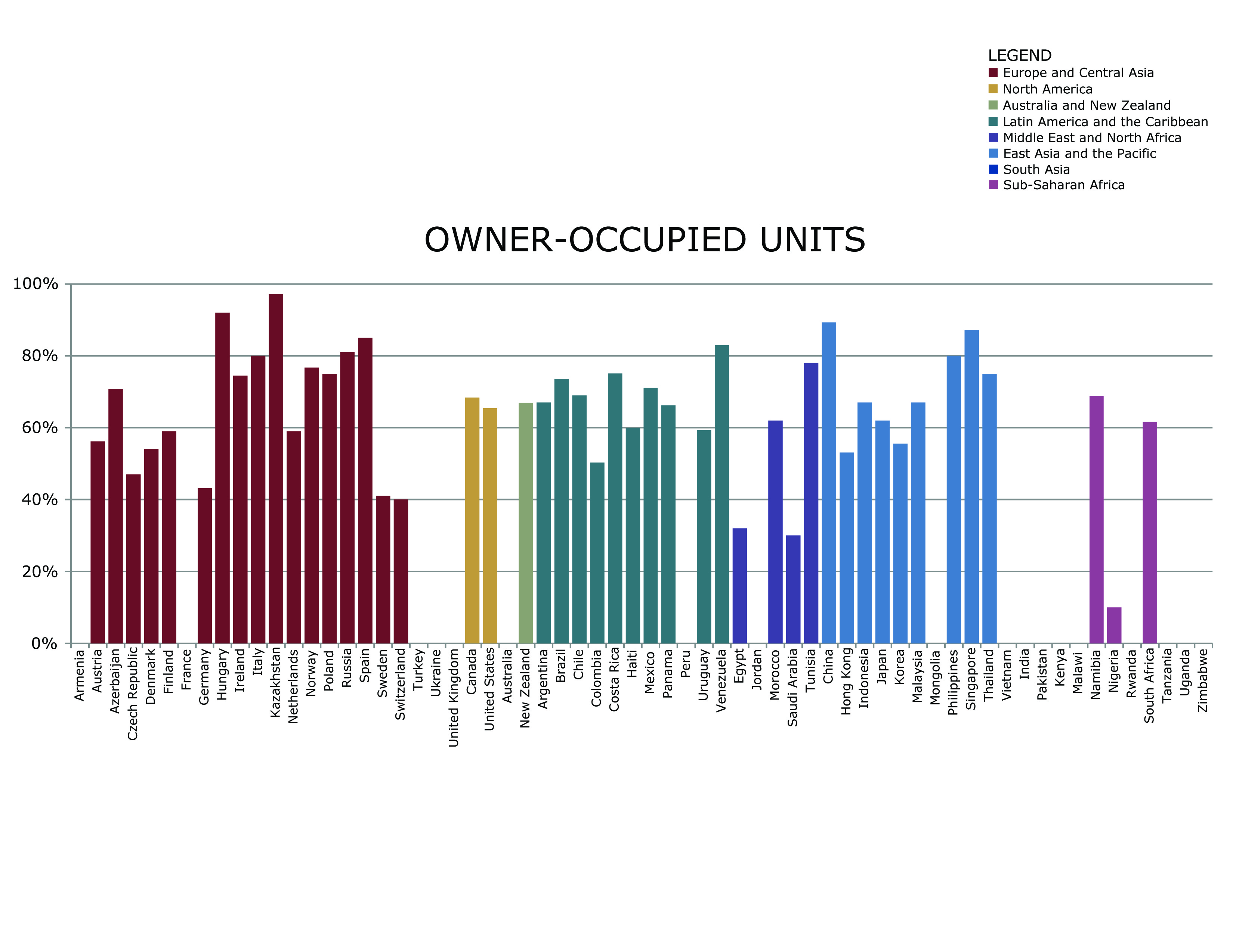
Owner-occupancy
Owner-occupancy or home-ownership is a form of housing tenure in which a person, called the owner-occupier, owner-occupant, or home owner, owns the home in which they live. The home can be a house, such as a single-family house, an apartment, condominium, or a housing cooperative. In addition to providing housing, owner-occupancy also functions as a real estate investment. Acquisition Some homes are constructed by the owners with the intent to occupy. Many are inherited. A large number are purchased, as new homes from a real estate developer or as an existing home from a previous landlord or owner-occupier. A house is usually the most expensive single purchase an individual or family makes, and often costs several times the annual household income. Given the high cost, most individuals do not have enough savings on hand to pay the entire amount outright. In developed countries, mortgage loans are available from financial institutions in return for interest. If the home ow ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Landlord
A landlord is the owner of a house, apartment, condominium, land, or real estate which is rented or leased to an individual or business, who is called a tenant (also a ''lessee'' or ''renter''). When a juristic person is in this position, the term landlord is used. Other terms include lessor and owner. The term landlady may be used for the female owners. The manager of a pub in the United Kingdom, strictly speaking a licensed victualler, is referred to as the landlord/landlady. In political economy it refers to the owner of natural resources alone (e.g., land, not buildings) from which an economic rent is the income received. History The concept of a landlord may be traced back to the feudal system of manoralism (seignorialism), where a landed estate is owned by a Lord of the Manor (mesne lords), usually members of the lower nobility which came to form the rank of knights in the high medieval period, holding their fief via subinfeudation, but in some cases the land may also ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leasehold Estate
A leasehold estate is an ownership of a temporary right to hold land or property in which a lessee or a tenant holds rights of real property by some form of title from a lessor or landlord. Although a tenant does hold rights to real property, a leasehold estate is typically considered personal property. Leasehold is a form of land tenure or property tenure where one party buys the right to occupy land or a building for a given length of time. As a lease is a legal estate, leasehold estate can be bought and sold on the open market. A leasehold thus differs from a freehold or fee simple where the ownership of a property is purchased outright and thereafter held for an indeterminate length of time, and also differs from a tenancy where a property is let (rented) on a periodic basis such as weekly or monthly. Terminology and types of leasehold vary from country to country. Sometimes, but not always, a residential tenancy under a lease agreement is colloquially known as renting. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Market (economics)
In economics, a market is a composition of systems, institutions, procedures, social relations or infrastructures whereby parties engage in exchange. While parties may exchange goods and services by barter, most markets rely on sellers offering their goods or services (including labour power) to buyers in exchange for money. It can be said that a market is the process by which the prices of goods and services are established. Markets facilitate trade and enable the distribution and allocation of resources in a society. Markets allow any tradeable item to be evaluated and priced. A market emerges more or less spontaneously or may be constructed deliberately by human interaction in order to enable the exchange of rights (cf. ownership) of services and goods. Markets generally supplant gift economies and are often held in place through rules and customs, such as a booth fee, competitive pricing, and source of goods for sale (local produce or stock registration). Markets can dif ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Measures Of National Income And Output
A variety of measures of national income and output are used in economics to estimate total economic activity in a country or region, including gross domestic product (GDP), gross national product (GNP), net national income (NNI), and adjusted national income (NNI adjusted for natural resource depletion – also called as NNI at factor cost). All are specially concerned with counting the total amount of goods and services produced within the economy and by various sectors. The boundary is usually defined by geography or citizenship, and it is also defined as the total income of the nation and also restrict the goods and services that are counted. For instance, some measures count only goods & services that are exchanged for money, excluding bartered goods, while other measures may attempt to include bartered goods by ''imputing'' monetary values to them. National accounts Arriving at a figure for the total production of goods and services in a large region like a country entails a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Income Tax
An income tax is a tax imposed on individuals or entities (taxpayers) in respect of the income or profits earned by them (commonly called taxable income). Income tax generally is computed as the product of a tax rate times the taxable income. Taxation rates may vary by type or characteristics of the taxpayer and the type of income. The tax rate may increase as taxable income increases (referred to as graduated or progressive tax rates). The tax imposed on companies is usually known as corporate tax and is commonly levied at a flat rate. Individual income is often taxed at progressive rates where the tax rate applied to each additional unit of income increases (e.g., the first $10,000 of income taxed at 0%, the next $10,000 taxed at 1%, etc.). Most jurisdictions exempt local charitable organizations from tax. Income from investments may be taxed at different (generally lower) rates than other types of income. Credits of various sorts may be allowed that reduce tax. Some jurisdicti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cross-National Equivalent File
{{Unreferenced, date=July 2022 The 'Cross-National Equivalent File'(CNEF)contains data from general population household-based panel surveys fielded in Australia, Canada, Germany, Great Britain, Japan, Korea, Russia, Switzerland and the United States. Each of these countries fields a longitudinal survey of households and their inhabitants. All of the surveys follow the set of people living in the set of households surveyed initially. With the exception of the Japan Household Panel Study, all of the surveys also follow the members of the original households, labeled as "original sample members" when they move away and form new households. Almost all of the surveys also follow people who joined a household of an "original sample member" (through marriage or cohabitation). Researchers at institutions in each country collaborate with CNEF to harmonize a subset of the data from each survey. The harmonized data get used, individually or as a set, by researchers who compare social and econo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Business Insider
''Insider'', previously named ''Business Insider'' (''BI''), is an American financial and business news website founded in 2007. Since 2015, a majority stake in ''Business Insider''s parent company Insider Inc. has been owned by the German publishing house Axel Springer. It operates several international editions, including one in the United Kingdom. ''Insider'' publishes original reporting and aggregates material from other outlets. , it maintained a liberal policy on the use of anonymous sources. It has also published native advertising and granted sponsors editorial control of its content. The outlet has been nominated for several awards, but is criticized for using factually incorrect clickbait headlines to attract viewership. In 2015, Axel Springer SE acquired 88 percent of the stake in Insider Inc. for $343 million (€306 million), implying a total valuation of $442 million. In February 2021, the brand was renamed simply ''Insider''. History ''Busi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Imputed Income
Imputed income is the accession to wealth that can be attributed, or imputed, to a person when they avoid paying for services by providing the services to themselves, or when the person avoids paying rent for durable goods by owning the durable goods, as in the case of imputed rent. Taxation of imputed income Many countries, such as the United States, tax imputed income only in certain limited situations. Imputed income is sometimes difficult to measure, and tax policies regarding imputed income can have political consequences. For taxpayers, not taxing imputed income creates a tax incentive in favor of owning over renting, and in favor of self-service over hiring. For the economy, not taxing imputed income directs economic activity away from activities associated with extreme and severe division of labor. Example: Durable property Home ownership is an example of an instance involving imputed income from durable property. If someone lives in their own property, they forgo the ren ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |