|
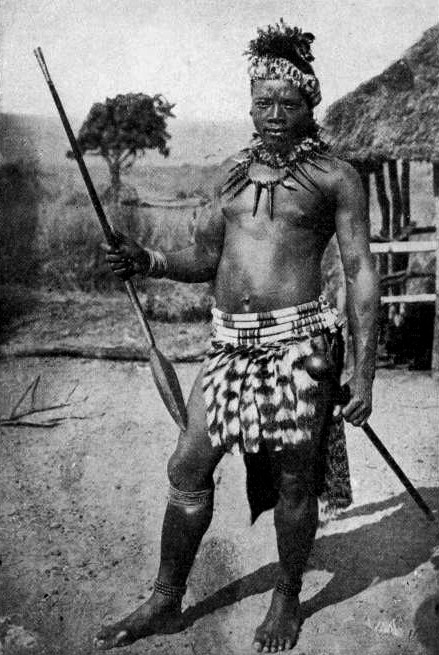
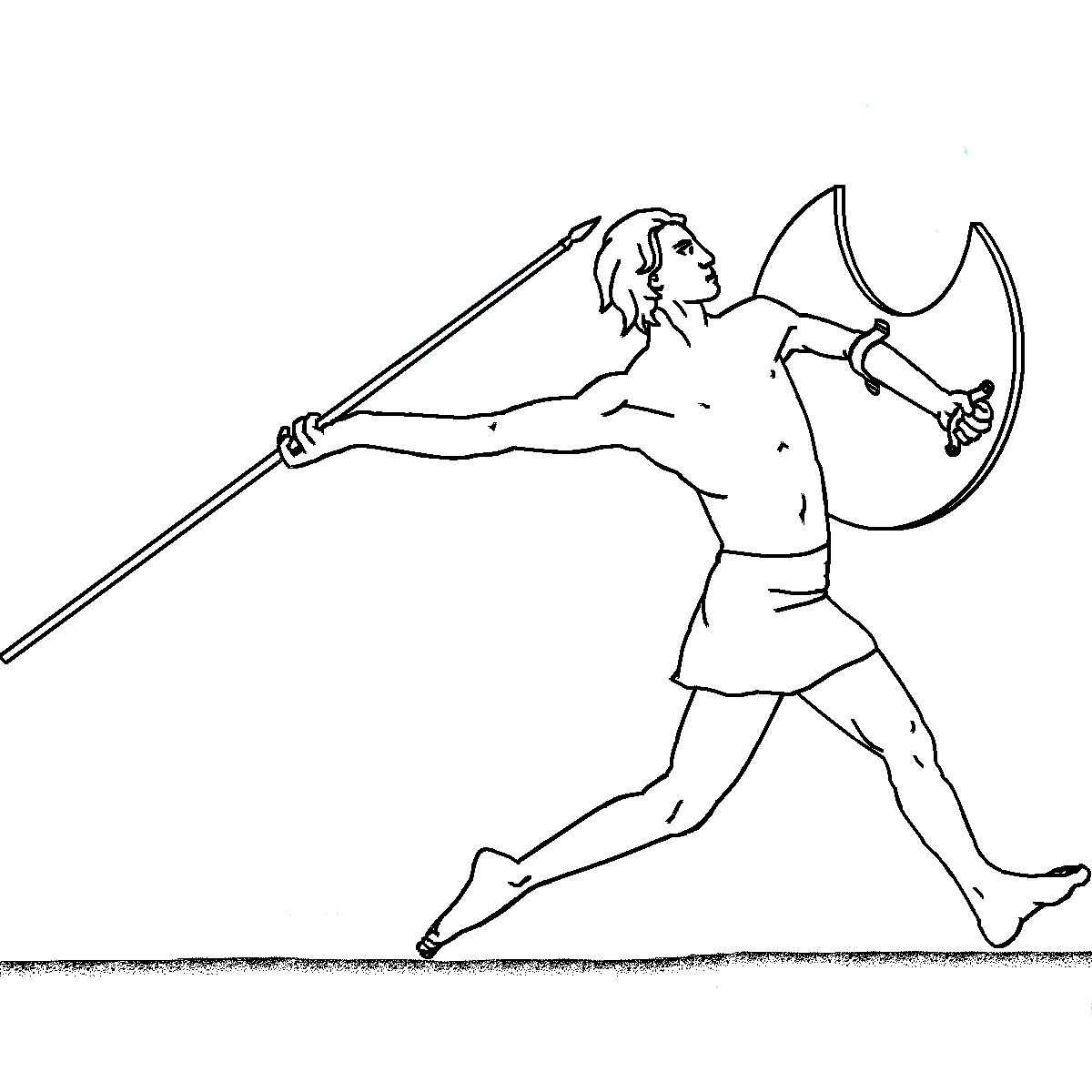
Iklwa
An assegai or assagai (Arabic ''az-zaġāyah'', Berber ''zaġāya'' "spear", Old French ''azagaie'', Spanish ''azagaya'', Italian ''zagaglia'', Middle English ''lancegay'') is a pole weapon used for throwing, usually a light spear or javelin made up of a wooden handle and an iron tip. Area of use The use of various types of the assegai was widespread all over Africa and it was the most common weapon used before the introduction of firearms. The Zulu, Xhosa and other Nguni tribes of South Africa were renowned for their use of the assegai. ''Iklwa'' Shaka of the Zulu invented a shorter stabbing spear with a two-foot (0.61 m) shaft and a larger, broader blade one foot (0.3 m) long. This weapon is otherwise known as the ''iklwa'' or ''ixwa'', after the sound that was heard as it was withdrawn from the victim's wound. The traditional spear was not abandoned, but was used to range attack enemy formations before closing in for close quarters battle with the iklwa. This ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zulu Warrior
is a Zulu language, Zulu word meaning war or combat and by association any body of men gathered for war, for example is a term denoting an army. were formed from regiments () from (large militarised homesteads). In English is often used to refer to a regiment, which is called an in or the army. Its beginnings lie far back in historic local warfare customs, when groups of armed men called battled. They were systematised radically by the king Shaka, who was then only the exiled illegitimate son of king Senzangakhona kaJama, but already showing much prowess as a general in the army () of Mthethwa Paramountcy, Mthethwa king Dingiswayo in the Ndwandwe–Zulu War of 1817–1819. Genesis of the impi The Zulu impi is popularly identified with the ascent of Shaka Zulu, Shaka, ruler of the relatively small Zulu tribe before its explosion across the landscape of southern Africa, but its earliest shape as an instrument of statecraft lies in the innovations of the Mthethwa Param ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shaka
Shaka kaSenzangakhona ( – 22 September 1828), also known as Shaka Zulu () and Sigidi kaSenzangakhona, was the king of the Zulu Kingdom from 1816 to 1828. One of the most influential monarchs of the Zulu, he ordered wide-reaching reforms that re-organized the military into a formidable force. King Shaka was born in the lunar month of ''uNtulikazi'' (July) in the year of 1787 near present-day Melmoth, KwaZulu-Natal Province, the son of the Zulu King Senzangakhona kaJama. Spurned as an illegitimate son, Shaka spent his childhood in his mother's settlements, where he was initiated into an '' ibutho lempi'' (fighting unit), serving as a warrior under Inkosi Dingiswayo. King Shaka further refined the ''ibutho'' military system and, with the Mthethwa Paramountcy's support over the next several years, forged alliances with his smaller neighbours to counter Ndwandwe raids from the north. The initial Zulu maneuvers were primarily defensive, as King Shaka preferred to apply pressure d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spear
A spear is a pole weapon consisting of a shaft, usually of wood, with a pointed head. The head may be simply the sharpened end of the shaft itself, as is the case with fire hardened spears, or it may be made of a more durable material fastened to the shaft, such as bone, flint, obsidian, iron, steel, or bronze. The most common design for hunting or combat spears since ancient times has incorporated a metal spearhead shaped like a triangle, lozenge, or leaf. The heads of fishing spears usually feature barbs or serrated edges. The word '' spear'' comes from the Old English '' spere'', from the Proto-Germanic ''speri'', from a Proto-Indo-European root ''*sper-'' "spear, pole". Spears can be divided into two broad categories: those designed for thrusting as a melee weapon and those designed for throwing as a ranged weapon (usually referred to as javelins or darts). The spear has been used throughout human history both as a hunting and fishing tool and as a weapon. Along ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Javelins
A javelin is a light spear designed primarily to be thrown, historically as a ranged weapon, but today predominantly for sport. The javelin is almost always thrown by hand, unlike the sling, bow, and crossbow, which launch projectiles with the aid of a hand-held mechanism. However, devices do exist to assist the javelin thrower in achieving greater distance, such as spear-throwers or the amentum. A warrior or soldier armed primarily with one or more javelins is a javelineer. The word javelin comes from Middle English and it derives from Old French ''javelin'', a diminutive of ''javelot'', which meant spear. The word ''javelot'' probably originated from one of the Celtic languages. Prehistory There is archaeological evidence that javelins and throwing sticks were already in use by the last phase of the Lower Paleolithic. Seven spear-like objects were found in a coal mine in the city of Schöningen, Germany. Stratigraphic dating indicates that the weapons are about 400,000 ye ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shield
A shield is a piece of personal armour held in the hand, which may or may not be strapped to the wrist or forearm. Shields are used to intercept specific attacks, whether from close-ranged weaponry or projectiles such as arrows, by means of active blocks, as well as to provide passive protection by closing one or more lines of engagement during combat. Shields vary greatly in size and shape, ranging from large panels that protect the user's whole body to small models (such as the buckler) that were intended for hand-to-hand-combat use. Shields also vary a great deal in thickness; whereas some shields were made of relatively deep, absorbent, wooden planking to protect soldiers from the impact of spears and crossbow bolts, others were thinner and lighter and designed mainly for deflecting blade strikes (like the roromaraugi or qauata). Finally, shields vary greatly in shape, ranging in roundness to angularity, proportional length and width, symmetry and edge pattern; different s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Throwing Spears
A javelin is a light spear designed primarily to be thrown, historically as a ranged weapon, but today predominantly for sport. The javelin is almost always thrown by hand, unlike the sling, bow, and crossbow, which launch projectiles with the aid of a hand-held mechanism. However, devices do exist to assist the javelin thrower in achieving greater distance, such as spear-throwers or the amentum. A warrior or soldier armed primarily with one or more javelins is a javelineer. The word javelin comes from Middle English and it derives from Old French ''javelin'', a diminutive of ''javelot'', which meant spear. The word ''javelot'' probably originated from one of the Celtic languages. Prehistory There is archaeological evidence that javelins and throwing sticks were already in use by the last phase of the Lower Paleolithic. Seven spear-like objects were found in a coal mine in the city of Schöningen, Germany. Stratigraphic dating indicates that the weapons are about 400,000 year ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Javelin
A javelin is a light spear designed primarily to be thrown, historically as a ranged weapon, but today predominantly for sport. The javelin is almost always thrown by hand, unlike the sling, bow, and crossbow, which launch projectiles with the aid of a hand-held mechanism. However, devices do exist to assist the javelin thrower in achieving greater distance, such as spear-throwers or the amentum. A warrior or soldier armed primarily with one or more javelins is a javelineer. The word javelin comes from Middle English and it derives from Old French ''javelin'', a diminutive of ''javelot'', which meant spear. The word ''javelot'' probably originated from one of the Celtic languages. Prehistory There is archaeological evidence that javelins and throwing sticks were already in use by the last phase of the Lower Paleolithic. Seven spear-like objects were found in a coal mine in the city of Schöningen, Germany. Stratigraphy, Stratigraphic dating indicates that the weapons are abo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Almogavars
Almogavars ( es, almogávares, an, almugávares, ca, almogàvers and pt, almogávares ar, Al-Mugavari) is the name of a class of light infantry soldier originated in the Crown of Aragon used in the later phases of the Reconquista, during the 13th and 14th centuries. Almogavars were lightly clad, quick-moving frontiersmen and foot-soldiers. They hailed from the Kingdom of Aragon, the Principality of Catalonia, the Kingdom of Valencia, the Crown of Castile and the Kingdom of Portugal. In the Crown of Castile, the inner organization was managed by King Alfonso X of Castile in the Siete Partidas. At first these troops were formed by farmers and shepherds originating from the countryside, woods and frontier mountain areas. Later, they were employed as mercenary, mercenaries in Italy, Latin Greece and the Levant. Etymology There are several theories as to where this name comes from ar, المغوار; pl. ar, المغاوير, ''al-mughāwir'', lit=Raiders, or ''al-mukhābir'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Amalinde
The Battle of Amalinde was an armed confrontation between two Xhosa chiefs of the Rharhabe House, which took place in October 1818 just outside of what is today King Williams Town, in the Eastern Cape region of South Africa. on the eve of the fifth Xhosa War. Chief Ngqika had close ties with the British, while his uncle, Chief Ndlambe, had no such agreements and painted Ngqika as someone selling out his people in return for personal gain. Chief Ndlambe was assisted in the battle by the senior, King Hintsa and his Gcaleka warriors. When chief Ngqika was defeated in the battle, he retreated and appealed to the British for protection. A British-led force commanded by Colonel Thomas Brereton then seized 23,000 head of cattle from Ndlambe's people in retaliation, leading to the battle of Grahamstown. Background and causes The two contending AmaXhosa chiefs of the Rharhabe House were Chief Ngqika and his paternal uncle, Chief Ndlambe. Ngqika's father, Mlawu, died when Ngqika was too y ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pilum
The ''pilum'' (; plural ''pila'') was a javelin commonly used by the Roman army in ancient times. It was generally about long overall, consisting of an iron shank about in diameter and long with a pyramidal head, attached to a wooden shaft by either a socket or a flat tang. Design A ''pilum'' had a total weight of between , with the versions produced during the earlier Republic being slightly heavier than those produced in the later Empire. The weapon had a hard pyramidal tip, but the shank was sometimes made of softer iron. The softness could cause the shank to bend after impact and so render the weapon useless to the enemy. Some believe that the ''pilum'' was not meant to bend after impact but that bending came from improper handling/removal of the weapon when it became stuck in an object. If a ''pilum'' struck a shield it might embed itself, the bending of the shank would force the enemy to discard his shield as unusable without removing the ''pilum'', which would be t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Falarica
Falarica, also Phalarica, was an ancient Iberian ranged pole weapon that was sometimes used as an incendiary weapon. Design The Falarica was a heavy javelin with a long, thin iron head of about 90 centimeters in length attached to a wooden shaft of about equal length. The iron head had a narrow sharp tip, which made the falarica an excellent armour-piercing weapon. The Iberians used to bind combustible material to the metal shaft of the weapon and use the falarica as an incendiary projectile. The incendiary javelin would hit the shields or siege works of the enemy often setting them ablaze. The falarica could also be launched by the use of spear throwers or siege engines to increase its range and velocity. the besieged were protected and the enemy kept away from the gates by the falarica, which many arms at once were wont to poise... when hurled like a thunderbolt from the topmost walls of the citadel, it clove the furrowed air with a flickering flame, even as a fiery meteor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rarabe KaPhalo
Rarabe ka Phalo (about 1722 - 1787) was a Xhosa Prince and the founder of the Right Hand House of the Xhosa Xhosa may refer to: * Xhosa people, a nation, and ethnic group, who live in south-central and southeasterly region of South Africa * Xhosa language, one of the 11 official languages of South Africa, principally spoken by the Xhosa people See als ... nation. Rarabe was the eldest son and right hand son of King Phalo ka Tshiwo. Rharhabe died near present-day Dohne in the Eastern Cape province. Family He fathered the following known children ( Mlawu ka Rarabe (Great son), Ndlambe ka Rarabe, Sigcawu ka Rarabe, Cebo ka Rarabe (Right Hand son), Hlahla ka Rarabe, Nzwane ka Rarabe, Mnyaluza ka Rarabe, Ntsusa ka Rarabe (a daughter) and Nukwa ka Rarabe. Death Rharhabe-Qwathi War Rharhabe's daughter Ntsusa married the Qwathi chief Mdandala, who as dowry(lobola) sent a miserable hundred head of cattle to Rharhabe. This was seen by Rharhabe as a great insult for some ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |