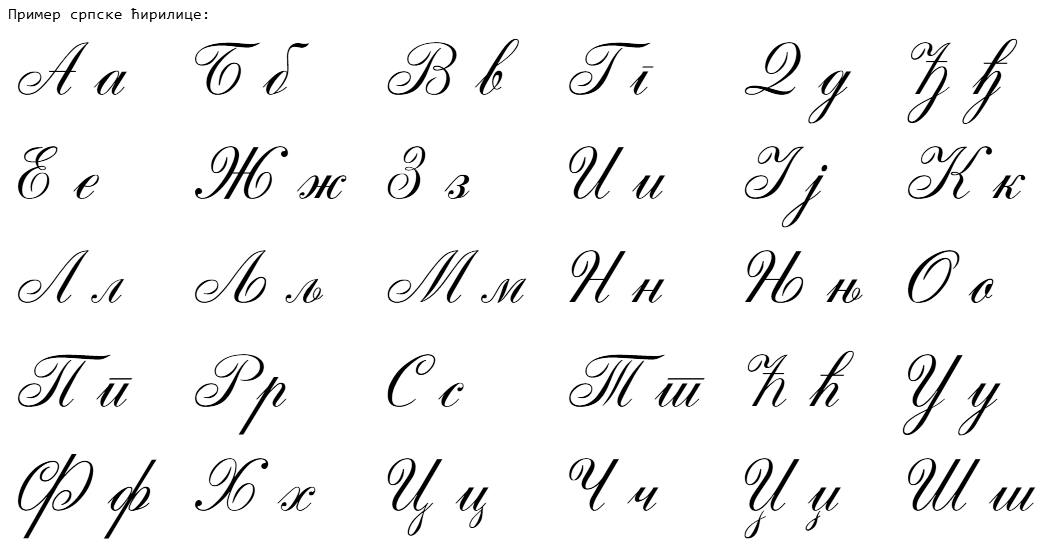|
I (Cyrillic)
И и (И и; italics: ) is a letter used in almost all Cyrillic alphabets with the exception of Belarusian. It commonly represents the close front unrounded vowel , like the pronunciation of in "machine", or the near-close near-front unrounded vowel , like the pronunciation of in "bin". History Because the Cyrillic letter І was derived from the Greek letter Eta (Η η), the Cyrillic had the shape of up to the 13th century. The name of the Cyrillic letter І in the Early Cyrillic alphabet was (''iže''), meaning "which". In the Cyrillic numeral system, the Cyrillic letter І had a value of 8, corresponding to the Greek letter Eta. In the Early Cyrillic alphabet, there was little or no distinction between the letter and the letter , the latter of which was derived from the Greek letter Iota (Ι ι). Both remained in the alphabetical repertoire because they represented different numbers in the Cyrillic numeral system: eight and ten. In New Church Slavonic, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dotted I (Cyrillic)
The dotted i (І і; italics: ''''), also called decimal i (и десятеричное, after its former numeric value), is a letter of the Cyrillic script. It commonly represents the close front unrounded vowel , like the pronunciation of ⟨i⟩ in English "machine". It is used in the orthographies of Belarusian, Kazakh, Khakas, Komi, Carpathian Rusyn and Ukrainian and quite often, but not always, is the equivalent of the Cyrillic letter i (И и) as used in Russian and other languages. The letter was also used in Russian before 1918. In Ukrainian, І is the twelfth letter of the alphabet and represents the sound i.html"_;"title="Close_front_unrounded_vowel.html"_;"title="nowiki/>Close_front_unrounded_vowel">i">Close_front_unrounded_vowel.html"_;"title="nowiki/>Close_front_unrounded_vowel">iin_writing._Ukrainian_uses_и_to_represent_the_sound_[Near-close_near-front_unrounded_vowel.html" ;"title="Close_front_unrounded_vowel">i.html" ;"title="Close_front_unrou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Palatalization (phonetics)
In phonetics, palatalization (, also ) or palatization is a way of pronouncing a consonant in which part of the tongue is moved close to the hard palate. Consonants pronounced this way are said to be palatalized and are transcribed in the International Phonetic Alphabet by affixing the letter ⟨ʲ⟩ to the base consonant. Palatalization cannot minimally distinguish words in most dialects of English, but it may do so in languages such as Russian, Mandarin, and Irish. Types In technical terms, palatalization refers to the secondary articulation of consonants by which the body of the tongue is raised toward the hard palate and the alveolar ridge during the articulation of the consonant. Such consonants are phonetically palatalized. "Pure" palatalization is a modification to the articulation of a consonant, where the middle of the tongue is raised, and nothing else. It may produce a laminal articulation of otherwise apical consonants such as and . Phonetically palatalized consona ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Serbian Cyrillic Alphabet
The Serbian Cyrillic alphabet ( sr, / , ) is a variation of the Cyrillic script used to write the Serbian language, updated in 1818 by Serbian linguist Vuk Stefanović Karadžić, Vuk Karadžić. It is one of the two alphabets used to write standard modern Serbian language, Serbian, the other being Gaj's Latin alphabet. Karadžić based his alphabet on the previous Slavonic-Serbian script, following the principle of "write as you speak and read as it is written", removing obsolete letters and letters representing iotified vowels, introducing from the Latin alphabet instead, and adding several consonant letters for sounds specific to Serbian phonology. During the same period, linguists led by Ljudevit Gaj adapted the Latin alphabet, in use in western South Slavic areas, using the same principles. As a result of this joint effort, Serbian Cyrillic and Gaj's Latin alphabets for Serbian-Croatian have a complete one-to-one congruence, with the Latin Digraph (orthography), digraph ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ukrainian Phonology
This article deals with the phonology of the standard Ukrainian language. Stress Stress is phonemic in Ukrainian. With most Ukrainian nouns, the stress falls on either the final vowel of the stem or the initial vowel of the inflection. In a few nouns the stress may be further forward. The position is generally fixed for the various cases of the noun (though inflection stress shifts to the last vowel of the stem if the inflection is a zero suffix), but may change with number (stem stress in both singular and plural, e.g. теа́тр ~ теа́три 'theater'; stem stress in the singular and inflection stress in the plural, e.g. жі́нка ~ жінки́ 'woman'; and so on for all permutations.) The pattern with adjectives is similar to that of nouns, but does not differ between singular and plural (all stem stress or all inflection stress). In some inflection-stressed adjectives, stress shifts to the stem in the comparative. With most verbs, stress falls on a syllable in th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phoneme
In phonology and linguistics, a phoneme () is a unit of sound that can distinguish one word from another in a particular language. For example, in most dialects of English, with the notable exception of the West Midlands and the north-west of England, the sound patterns (''sin'') and (''sing'') are two separate words that are distinguished by the substitution of one phoneme, , for another phoneme, . Two words like this that differ in meaning through the contrast of a single phoneme form a ''minimal pair''. If, in another language, any two sequences differing only by pronunciation of the final sounds or are perceived as being the same in meaning, then these two sounds are interpreted as phonetic variants of a single phoneme in that language. Phonemes that are established by the use of minimal pairs, such as ''tap'' vs ''tab'' or ''pat'' vs ''bat'', are written between slashes: , . To show pronunciation, linguists use square brackets: (indicating an aspirated ''p'' in ''p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ukrainian Alphabet
The Ukrainian alphabet ( uk, абе́тка, áзбука алфа́ві́т, abetka, azbuka alfavit) is the set of letters used to write Ukrainian, which is the official language of Ukraine. It is one of several national variations of the Cyrillic script. It comes from the Cyrillic script, which was devised in the 9th century for the first Slavic literary language, called Old Slavonic. Since the 10th century, it became used in the Kyivan Rus' for Old East Slavic, from which the Belarusian, Russian, Rusyn, and Ukrainian alphabets later evolved. The modern Ukrainian alphabet has 33 letters in total: 20 consonants, 2 semivowels, 10 vowels and 1 palatalization sign. Sometimes the apostrophe (') is also included, which has a phonetic meaning and is a mandatory sign in writing, but is not considered as a letter and is not included in the alphabet. In Ukrainian, it is called (; tr. ''ukrayins'ka abetka''), from the initial letters '' а'' (tr. ''a'') and '' б'' (tr. ''b''); ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ukrainian I
The dotted i (І і; italics: ''''), also called decimal i (и десятеричное, after its former numeric value), is a letter of the Cyrillic script. It commonly represents the close front unrounded vowel , like the pronunciation of ⟨i⟩ in English "machine". It is used in the orthographies of Belarusian, Kazakh, Khakas, Komi, Carpathian Rusyn and Ukrainian and quite often, but not always, is the equivalent of the Cyrillic letter i (И и) as used in Russian and other languages. The letter was also used in Russian before 1918. In Ukrainian, І is the twelfth letter of the alphabet and represents the sound i.html"_;"title="Close_front_unrounded_vowel.html"_;"title="nowiki/>Close_front_unrounded_vowel">i">Close_front_unrounded_vowel.html"_;"title="nowiki/>Close_front_unrounded_vowel">iin_writing._Ukrainian_uses_и_to_represent_the_sound_[Near-close_near-front_unrounded_vowel.html" ;"title="Close_front_unrounded_vowel">i.html" ;"title="Close_front_unrou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kazakh Language
The Kazakh or simply Qazaq (Latin: or , Cyrillic: or , Arabic Script: or , , ) is a Turkic language of the Kipchak branch spoken in Central Asia by Kazakhs. It is closely related to Nogai, Kyrgyz and Karakalpak. It is the official language of Kazakhstan and a significant minority language in the Ili Kazakh Autonomous Prefecture in Xinjiang, north-western China and in the Bayan-Ölgii Province of western Mongolia. The language is also spoken by many ethnic Kazakhs throughout the former Soviet Union (some 472,000 in Russia according to the 2010 Russian Census), Germany, and Turkey. Like other Turkic languages, Kazakh is an agglutinative language and employs vowel harmony. '' Ethnologue'' recognizes three mutually intelligible dialect groups, Northeastern Kazakh, the most widely spoken variety which also serves as the basis for the standard language, Southern Kazakh and Western Kazakh. The language share a degree of mutual intelligiblity with closely related Karakalpak ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
I With Grave (Cyrillic)
I with grave (Ѝ ѝ; italics: ) is a character representing a stressed variant of the regular letter in some Cyrillic alphabets, but none of them, whether modern or archaic, includes it as a separate letter. South Slavic languages Bulgarian and Macedonian Most regularly is used in Bulgarian and Macedonian languages to distinguish the short form of the indirect object ("her") from the conjunction ("and", "also") or, less frequently, to prevent ambiguity in other similar cases. If it is not available, the character is often replaced by an ordinary (not recommended but still orthographically correct) or in Bulgarian by the letter (formally considered a spelling error). Church Slavonic Since the 17th century in the modern Russian recension of Church Slavonic, and any other vowel with a grave accent is just an orthographic variant of the same letter with an acute accent when it is used as the last letter of a word. Serbian (as well as other vowels with an acute, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bulgarian Alphabet
The Bulgarian Cyrillic alphabet is used to write the Bulgarian language. The Cyrillic alphabet was originally developed in the First Bulgarian Empire during the 9th – 10th century AD at the Preslav Literary School. It has been used in Bulgaria (with modifications and exclusion of certain archaic letters via spelling reforms) continuously since then, superseding the previously used Glagolitic alphabet, which was also invented and used there before the Cyrillic script overtook its use as a written script for the Bulgarian language. The Cyrillic alphabet was used in the then much bigger territory of Bulgaria (including most of today's Serbia), North Macedonia, Kosovo, Albania, Northern Greece (Macedonia region), Romania and Moldova, officially from 893. It was also transferred from Bulgaria and adopted by the East Slavic languages in Kievan Rus' and evolved into the Belarusian, Russian and Ukrainian alphabets and the alphabets of many other Slavic (and later non-Slavic) languages. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ya (Cyrillic)
Ya or Ja (Я я; italics: ) is a letter of the Cyrillic script, the civil script variant of Old Cyrillic Little Yus () or maybe even ' Ꙗ'. Among modern Slavic languages, it is used in the East Slavic languages and Bulgarian. It is also used in the Cyrillic alphabets used by Mongolian and many Uralic, Caucasian and Turkic languages of the former Soviet Union. Pronunciation The iotated vowel is pronounced in initial or post-vocalic positions, like the English pronunciation of in "yard". When follows a soft consonant, no sound occurs between the consonant and the vowel. The exact pronunciation of the vowel sound of depends also on the following sound by allophony in the Slavic languages. Before a soft consonant, it is , like in the English "cat". If a hard consonant follows or none, the result is an open vowel, usually []. In non-stressed positionsm, the vowel reduction depends on the language and the dialect. The standard vowel reduction in Russian, Russian lan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yu (Cyrillic)
Yu or Ju (Ю ю; italics: ) is a letter of the Cyrillic script used in East Slavic and Bulgarian alphabets. In English, Yu is commonly romanized as (or ). In turn, is used, where is available, in transcriptions of English letter (in open syllables), and also of the digraph. The sound , like in French and in German, may also be approximated by the letter . Pronunciation It is a so-called iotated vowel, pronounced in isolation as , like the pronunciation of in "human". After a consonant, no distinct sound is pronounced, but the consonant is softened. The exact pronunciation of the vowel sound of in Russian depends also on the succeeding sound because of allophony. Before a soft consonant, it is , the close central rounded vowel, as in 'rude'. Before a hard consonant or at the end of a word, the result is a back vowel , as in "new". History Apart from the form ''I-O'', in early Slavonic manuscripts the letter appears also in a mirrored form ''O-I'' (). It is the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |