|
Isotype (immunology)
In immunology, antibodies ( immunoglobulins (Ig)) are classified into several types called isotypes or classes. The variable (V) regions near the tip of the antibody can differ from molecule to molecule in countless ways, allowing it to specifically target an antigen (or more exactly, an epitope). In contrast, the constant (C) regions only occur in a few variants, which define the antibody's class. Antibodies of different classes activate distinct effector mechanisms in response to an antigen (triggering different elements of the innate immune system). They appear at different stages of an immune response, differ in structural features, and in their location around the body. Isotype expression reflects the maturation stage of a B cell. Naive B cells express IgM and IgD isotypes with unmutated variable genes, which are produced from the same initial transcript following alternative splicing. Expression of other antibody isotypes (in humans: IgG, IgA, and IgE) occurs via a process ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Activation-induced Cytidine Deaminase
Activation-induced cytidine deaminase, also known as AICDA, AID and single-stranded DNA cytosine deaminase, is a 24 kDa enzyme which in humans is encoded by the ''AICDA'' gene. It creates mutations in DNA by deamination of cytosine base, which turns it into uracil (which is recognized as a thymine). In other words, it changes a C:G base pair into a U:G mismatch. The cell's DNA replication machinery recognizes the U as a T, and hence C:G is converted to a T:A base pair. During germinal center development of B lymphocytes, AID also generates other types of mutations, such as C:G to A:T. The mechanism by which these other mutations are created is not well understood. It is a member of the APOBEC family. In B cells in the lymph nodes, AID causes mutations that produce antibody diversity, but that same mutation process leads to B cell lymphoma. Function This gene encodes a DNA-editing deaminase that is a member of the cytidine deaminase family. The protein is involved in somati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of South Carolina School Of Medicine
A university () is an institution of higher (or tertiary) education and research which awards academic degrees in several academic disciplines. ''University'' is derived from the Latin phrase ''universitas magistrorum et scholarium'', which roughly means "community of teachers and scholars". Universities typically offer both undergraduate and postgraduate programs. The first universities in Europe were established by Catholic Church monks. The University of Bologna (), Italy, which was founded in 1088, is the first university in the sense of: *being a high degree-awarding institute. *using the word ''universitas'' (which was coined at its foundation). *having independence from the ecclesiastic schools and issuing secular as well as non-secular degrees (with teaching conducted by both clergy and non-clergy): grammar, rhetoric, logic, theology, canon law, notarial law.Hunt Janin: "The university in medieval life, 1179–1499", McFarland, 2008, , p. 55f.de Ridder-Symoens, Hilde''A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Idiotype
In immunology, an idiotype is a shared characteristic between a group of immunoglobulin or T-cell receptor (TCR) molecules based upon the antigen binding specificity and therefore structure of their variable region. The variable region of antigen receptors of T cells (TCRs) and B cells (immunoglobulins) contain complementarity-determining regions (CDRs) with unique amino acid sequences. They define the surface and properties of the variable region, determining the antigen specificity and therefore the idiotope of the molecule. Immunoglobulins or TCRs with a shared idiotope are the same idiotype. Antibody idiotype is determined by: *Gene rearrangement *Junctional diversity *P-nucleotides (palindromic nucleotides at sites of single-strand breaks) *N-nucleotides *Somatic hypermutations Etymology and usage The word idiotype comes from two Greek roots, ''idio'' meaning 'private, distinctive, peculiar' and ''typos'' meaning 'mark.' Thus, idiotype describes the distinctive sequence and re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Immunoglobulin Light Chain
] The immunoglobulin light chain is the small Peptide, polypeptide subunit of an antibody (immunoglobulin). A typical antibody is composed of two immunoglobulin (Ig) heavy chains and two Ig light chains. In humans There are two types of light chain in humans: * kappa (κ) chain, encoded by the immunoglobulin kappa locus (IGK@) on chromosome 2 (locus: 2p11.2) * lambda (λ) chain, encoded by the immunoglobulin lambda locus (IGL@) on chromosome 22 (locus: 2q11.22) Antibodies are produced by B lymphocytes, each expressing only one class of light chain. Once set, light chain class remains fixed for the life of the B lymphocyte. In a healthy individual, the total kappa-to-lambda ratio is roughly 2:1 in serum (measuring intact whole antibodies) or 1:1.5 if measuring free light chains, with a highly divergent ratio indicative of neoplasm. The quotient of kappa divided by lambda, according to a novel polyclonal free light chain assay, ranges from 0.26 to 1.65. Both the kappa and t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Immunoglobulin G
Immunoglobulin G (Ig G) is a type of antibody. Representing approximately 75% of serum antibodies in humans, IgG is the most common type of antibody found in blood circulation. IgG molecules are created and released by plasma B cells. Each IgG antibody has two paratopes. Function Antibodies are major components of humoral immunity. IgG is the main type of antibody found in blood and extracellular fluid, allowing it to control infection of body tissues. By binding many kinds of pathogens such as viruses, bacteria, and fungi, IgG protects the body from infection. It does this through several mechanisms: * IgG-mediated binding of pathogens causes their immobilization and binding together via agglutination; IgG coating of pathogen surfaces (known as opsonization) allows their recognition and ingestion by phagocytic immune cells leading to the elimination of the pathogen itself; * IgG activates all the classical pathway of the complement system, a cascade of immune protein pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Immunoglobulin Heavy Chain
The immunoglobulin heavy chain (IgH) is the large polypeptide subunit of an antibody (immunoglobulin). In human genome, the IgH gene loci are on chromosome 14. A typical antibody is composed of two immunoglobulin (Ig) heavy chains and two Ig light chains. Several different types of heavy chain exist that define the class or isotype of an antibody. These heavy chain types vary between different animals. All heavy chains contain a series of immunoglobulin domains, usually with one variable domain (VH) that is important for binding antigen and several constant domains (CH1, CH2, etc.). Production of a viable heavy chain is a key step in B cell maturation. If the heavy chain is able to bind to a surrogate light chain and move to the plasma membrane, then the developing B cell can begin producing its light chain. The heavy chain doesn't always have to bind to a light chain. Pre-B lymphocytes can synthesize heavy chain in the absence of light chain, which then can allow the heavy ch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Human
Humans (''Homo sapiens'') are the most abundant and widespread species of primate, characterized by bipedalism and exceptional cognitive skills due to a large and complex brain. This has enabled the development of advanced tools, culture, and language. Humans are highly social and tend to live in complex social structures composed of many cooperating and competing groups, from families and kinship networks to political states. Social interactions between humans have established a wide variety of values, social norms, and rituals, which bolster human society. Its intelligence and its desire to understand and influence the environment and to explain and manipulate phenomena have motivated humanity's development of science, philosophy, mythology, religion, and other fields of study. Although some scientists equate the term ''humans'' with all members of the genus ''Homo'', in common usage, it generally refers to ''Homo sapiens'', the only extant member. Anatomically moder ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
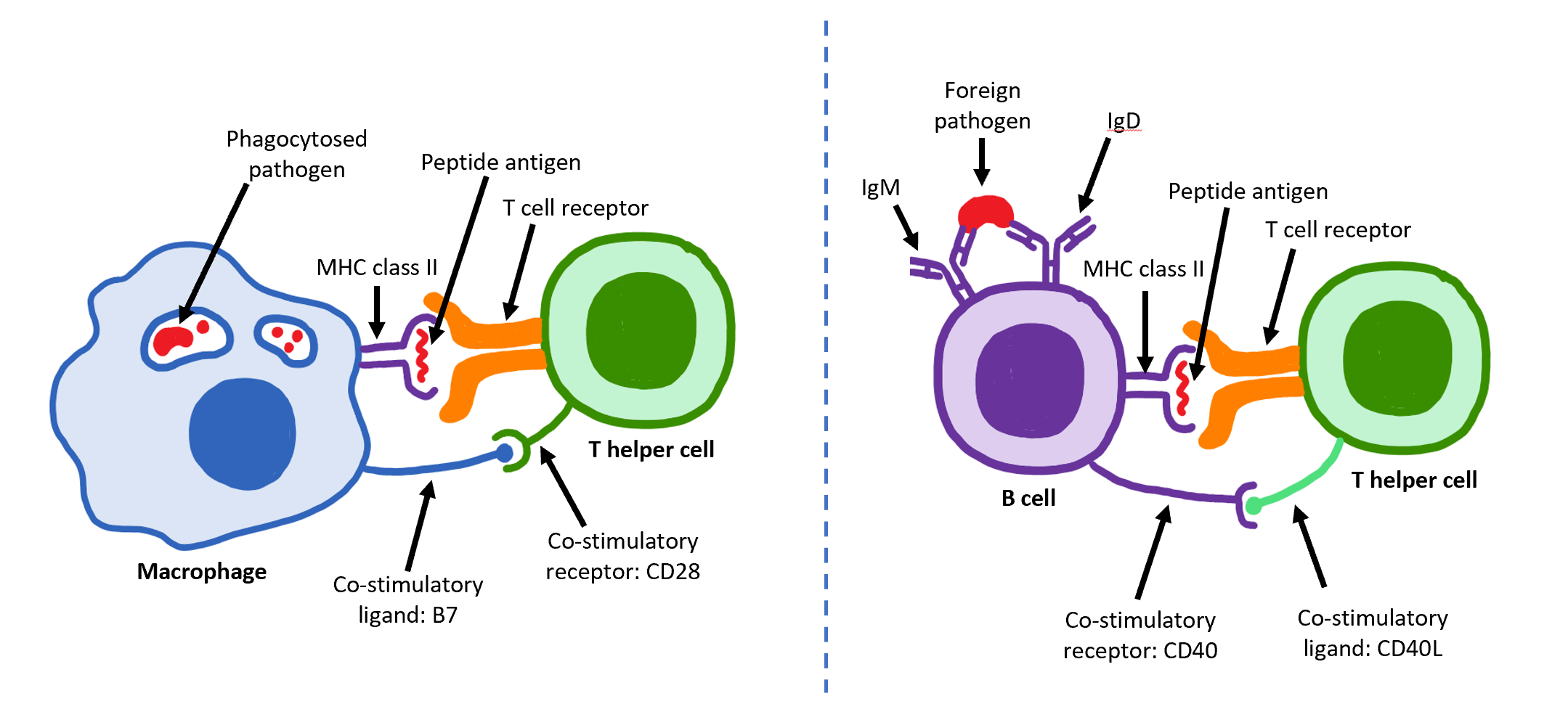
T Helper Cell
The T helper cells (Th cells), also known as CD4+ cells or CD4-positive cells, are a type of T cell that play an important role in the adaptive immune system. They aid the activity of other immune cells by releasing cytokines. They are considered essential in B cell antibody class switching, breaking cross-tolerance in dendritic cells, in the activation and growth of cytotoxic T cells, and in maximizing bactericidal activity of phagocytes such as macrophages and neutrophils. CD4+ cells are mature Th cells that express the surface protein CD4. Genetic variation in regulatory elements expressed by CD4+ cells determines susceptibility to a broad class of autoimmune diseases. Structure and function Th cells contain and release cytokines to aid other immune cells. Cytokines are small protein mediators that alter the behavior of target cells that express receptors for those cytokines. These cells help polarize the immune response depending on the nature of the immunological insult ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Immunoglobulin Class Switching
Immunoglobulin class switching, also known as isotype switching, isotypic commutation or class-switch recombination (CSR), is a biological mechanism that changes a B cell's production of immunoglobulin from one type to another, such as from the isotype IgM to the isotype IgG. During this process, the constant-region portion of the antibody heavy chain is changed, but the variable region of the heavy chain stays the same (the terms ''variable'' and ''constant'' refer to changes or lack thereof between antibodies that target different epitopes). Since the variable region does not change, class switching does not affect antigen specificity. Instead, the antibody retains affinity for the same antigens, but can interact with different effector molecules. Mechanism Class switching occurs after activation of a mature B cell via its membrane-bound antibody molecule (or B cell receptor) to generate the different classes of antibody, all with the same variable domains as the origin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Immunoglobulin Basic Unit
An antibody (Ab), also known as an immunoglobulin (Ig), is a large, Y-shaped protein used by the immune system to identify and neutralize foreign objects such as pathogenic bacteria and viruses. The antibody recognizes a unique molecule of the pathogen, called an antigen. Each tip of the "Y" of an antibody contains a paratope (analogous to a lock) that is specific for one particular epitope (analogous to a key) on an antigen, allowing these two structures to bind together with precision. Using this binding mechanism, an antibody can ''tag'' a microbe or an infected cell for attack by other parts of the immune system, or can neutralize it directly (for example, by blocking a part of a virus that is essential for its invasion). To allow the immune system to recognize millions of different antigens, the antigen-binding sites at both tips of the antibody come in an equally wide variety. In contrast, the remainder of the antibody is relatively constant. It only occurs in a few varian ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
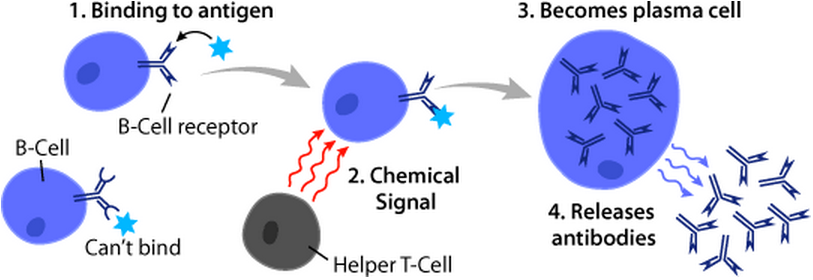
B Cell
B cells, also known as B lymphocytes, are a type of white blood cell of the lymphocyte subtype. They function in the humoral immunity component of the adaptive immune system. B cells produce antibody molecules which may be either secreted or inserted into the plasma membrane where they serve as a part of B-cell receptors. When a naïve or memory B cell is activated by an antigen, it proliferates and differentiates into an antibody-secreting effector cell, known as a plasmablast or plasma cell. Additionally, B cells present antigens (they are also classified as professional antigen-presenting cells (APCs)) and secrete cytokines. In mammals, B cells mature in the bone marrow, which is at the core of most bones. In birds, B cells mature in the bursa of Fabricius, a lymphoid organ where they were first discovered by Chang and Glick, which is why the 'B' stands for bursa and not bone marrow as commonly believed. B cells, unlike the other two classes of lymphocytes, T cells and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |