|
Interplanetary Magnetic Field
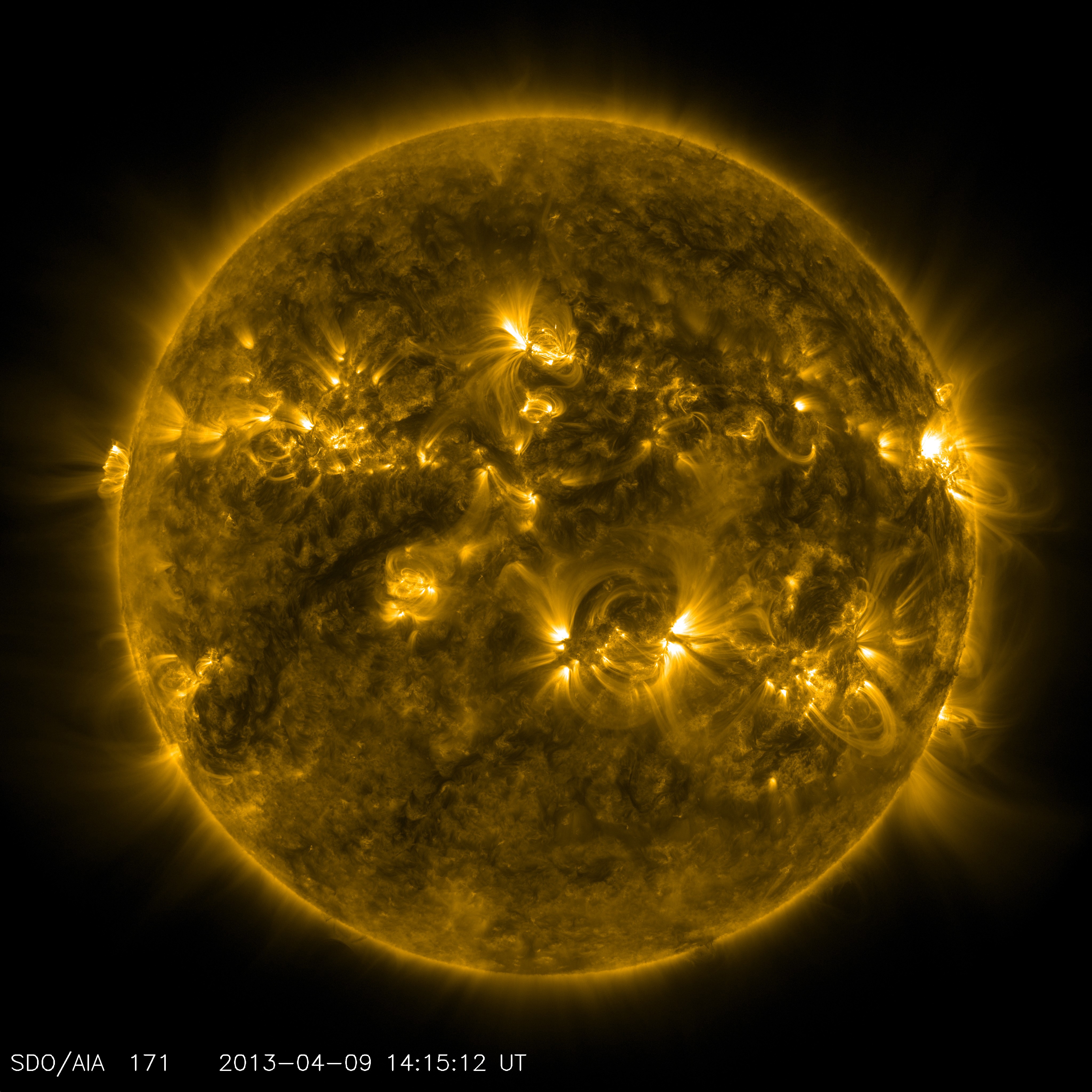
The interplanetary magnetic field (IMF), also commonly referred to as the heliospheric magnetic field (HMF), is the component of the solar magnetic field that is dragged out from the solar corona by the solar wind flow to fill the Solar System. Coronal and solar wind plasma The coronal and solar wind plasmas are highly electrically conductive, meaning the magnetic field lines and the plasma flows are effectively "frozen" together and the magnetic field cannot diffuse through the plasma on time scales of interest. In the solar corona, the magnetic pressure greatly exceeds the plasma pressure and thus the plasma is primarily structured and confined by the magnetic field. However, with increasing altitude through the corona, the solar wind accelerates as it extracts energy from the magnetic field through the Lorentz force interaction, resulting in the flow momentum exceeding the restraining magnetic tension force and the coronal magnetic field is dragged out by the solar win ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heliosphere
The heliosphere is the magnetosphere, astrosphere, and outermost atmospheric layer of the Sun. It takes the shape of a vast, tailed bubble-like region of space. In plasma physics terms, it is the cavity formed by the Sun in the surrounding interstellar medium. The "bubble" of the heliosphere is continuously "inflated" by plasma originating from the Sun, known as the solar wind. Outside the heliosphere, this solar plasma gives way to the interstellar plasma permeating the Milky Way. As part of the interplanetary magnetic field, the heliosphere shields the Solar System from significant amounts of cosmic ionizing radiation; uncharged gamma rays are, however, not affected. Its name was likely coined by Alexander J. Dessler, who is credited with the first use of the word in the scientific literature in 1967. The scientific study of the heliosphere is heliophysics, which includes space weather and space climate. Flowing unimpeded through the Solar System for billions of kilo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Space Weather
Space weather is a branch of space physics and aeronomy, or heliophysics, concerned with the varying conditions within the Solar System and its heliosphere. This includes the effects of the solar wind, especially on the Earth's magnetosphere, ionosphere, thermosphere, and exosphere. Though physically distinct, space weather is analogous to the terrestrial weather of Earth's atmosphere of Earth, atmosphere (troposphere and stratosphere). The term "space weather" was first used in the 1950s and popularized in the 1990s. Later, it prompted research into "space climate", the large-scale and long-term patterns of space weather. History For many centuries, the effects of space weather were noticed, but not understood. Displays of aurora (astronomy), auroral light have long been observed at high latitudes. Beginnings In 1724, George Graham (clockmaker), George Graham reported that the needle of a magnetic compass was regularly deflected from magnetic north over the course of each day. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MHD Dynamo
A magnetohydrodynamic generator (MHD generator) is a magnetohydrodynamic converter that transforms thermal energy and kinetic energy directly into electricity. An MHD generator, like a conventional generator, relies on moving a conductor through a magnetic field to generate electric current. The MHD generator uses hot conductive ionized gas (a plasma) as the moving conductor. The mechanical dynamo, in contrast, uses the motion of mechanical devices to accomplish this. MHD generators are different from traditional electric generators in that they operate without moving parts (e.g. no turbines), so there is no limit on the upper temperature at which they can operate. They have the highest known theoretical thermodynamic efficiency of any electrical generation method. MHD has been developed for use in combined cycle power plants to increase the efficiency of electric generation, especially when burning coal or natural gas. The hot exhaust gas from an MHD generator can heat the boi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magnetohydrodynamic
In physics and engineering, magnetohydrodynamics (MHD; also called magneto-fluid dynamics or hydromagnetics) is a model of electrically conducting fluids that treats all interpenetrating particle species together as a single continuous medium. It is primarily concerned with the low-frequency, large-scale, magnetic behavior in plasmas and liquid metals and has applications in multiple fields including space physics, geophysics, astrophysics, and engineering. The word ''magnetohydrodynamics'' is derived from ' meaning magnetic field, ' meaning water, and ' meaning movement. The field of MHD was initiated by Hannes Alfvén, for which he received the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1970. History The MHD description of electrically conducting fluids was first developed by Hannes Alfvén in a 1942 paper published in ''Nature'' titled "Existence of Electromagnetic–Hydrodynamic Waves" which outlined his discovery of what are now referred to as ''Alfvén waves''. A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tesla (unit)
The tesla (symbol: T) is the unit of magnetic flux density (also called magnetic B-field strength) in the International System of Units (SI). One tesla is equal to one weber per square metre. The unit was announced during the General Conference on Weights and Measures in 1960 and is named in honour of Serbian-American electrical and mechanical engineer Nikola Tesla, upon the proposal of the Slovenian electrical engineer France Avčin. Definition A particle, carrying a charge of one coulomb (C), and moving perpendicularly through a magnetic field of one tesla, at a speed of one metre per second (m/s), experiences a force with magnitude one newton (N), according to the Lorentz force law. That is, \mathrm. As an SI derived unit, the tesla can also be expressed in terms of other units. For example, a magnetic flux of 1 weber (Wb) through a surface of one square meter is equal to a magnetic flux density of 1 tesla.''The International System of Units (SI), 8th edition' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Interplanetary Medium
The interplanetary medium (IPM) or interplanetary space consists of the mass and energy which fills the Solar System, and through which all the larger Solar System bodies, such as planets, dwarf planet A dwarf planet is a small planetary-mass object that is in direct orbit around the Sun, massive enough to be hydrostatic equilibrium, gravitationally rounded, but insufficient to achieve clearing the neighbourhood, orbital dominance like the ...s, asteroids, and comets, move. The IPM stops at the Heliopause (astronomy), heliopause, outside of which the interstellar medium begins. Before 1950, interplanetary space was widely considered to either be an empty vacuum, or consisting of "Aether theories, aether". Composition and physical characteristics The interplanetary medium includes Interplanetary dust cloud, interplanetary dust, cosmic rays, and hot Plasma (physics), plasma from the solar wind. The density of the interplanetary medium is very low, decreasing in inverse pro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ballerina Skirt
A ballerina skirt, also referred to as a Juliet skirt or a romance skirt, is a full skirt that is worn by ballet dancers and is composed of multiple layers of fabric. Ballet dancers wear the longer version of the skirt, while for fashion purposes the skirt is worn shorter, like a mini skirt for better dancing, the cocktail version. The standard ballerina attire is composed of fabric with a wire, in order for tulle to be visualized as stiff when it is around their waists. The Juliet styled skirt is free-flowing and covers the majority of their legs to place a high emphasis on the performer's legs. The ballerina skirt is typically made up of five to twelve layers of tulle fabric. A ballerina skirt is portrayed as feminine and elegant, as well as being associated with the traditional attire for classical ballet performances. There are several different types of the ballerina skirts are used when performing. Those include: romantic, classic, pancake, balanchine and platter skirts. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
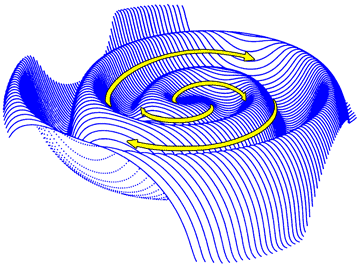
Heliospheric Current Sheet
The heliospheric current sheet, or interplanetary current sheet, is a surface separating regions of the heliosphere where the interplanetary magnetic field points toward and away from the Sun. A small electrical current with a current density of about 10−10 A/m2 flows within this surface, forming a current sheet confined to this surface.Israelevich, P. L., ''et al.'',MHD simulation of the three-dimensional structure of the heliospheric current sheet" (2001) ''Astronomy and Astrophysics'', v.376, p.288–291 The shape of the current sheet results from the influence of the Sun's rotating magnetic field on the plasma in the interplanetary medium. The thickness of the current sheet is about near the orbit of the Earth. Characteristics Ballerina's skirt shape As the Sun rotates, its magnetic field twists into an Archimedean spiral, as it extends through the Solar System. This phenomenon is often called the Parker spiral, after Eugene Parker's workParker, E. N.,Dynamics of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electric Current
An electric current is a flow of charged particles, such as electrons or ions, moving through an electrical conductor or space. It is defined as the net rate of flow of electric charge through a surface. The moving particles are called charge carriers, which may be one of several types of particles, depending on the Electrical conductor, conductor. In electric circuits the charge carriers are often electrons moving through a wire. In semiconductors they can be electrons or Electron hole, holes. In an Electrolyte#Electrochemistry, electrolyte the charge carriers are ions, while in Plasma (physics), plasma, an Ionization, ionized gas, they are ions and electrons. In the International System of Units (SI), electric current is expressed in Unit of measurement, units of ampere (sometimes called an "amp", symbol A), which is equivalent to one coulomb per second. The ampere is an SI base unit and electric current is a ISQ base quantity, base quantity in the International System of Qua ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Current Sheet
A current sheet is an electric current that is confined to a surface, rather than being spread through a volume of space. Current sheets feature in magnetohydrodynamics (MHD), a model of electrically conductive fluids: if there is an electric current through part of the volume of such a fluid, magnetic forces tend to expel it from the fluid, compressing the current into thin layers that pass through the volume. The largest occurring current sheet in the Solar System is the so-called heliospheric current sheet, which is about 10,000 km thick, and extends from the Sun and out beyond the orbit of Pluto. In astrophysical plasmas such as the solar corona, current sheets theoretically might have an aspect ratio (breadth divided by thickness) as high as 100,000:1. By contrast, the pages of most books have an aspect ratio close to 2000:1. Because current sheets are so thin in comparison to their size, they are often treated as if they have zero thickness; this is a result of the s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |