|
Internal Enemy
Internal enemy refers to individuals or groups within one country who are perceived as a threat to that country. The distinction between internal and external enemies is discussed in Plato's ''Republic''. Groups considered internal enemies by the countries in which they reside include Kurds in Turkey, Palestinians in Israel, Muslims in Western countries, and political dissidents under Latin American dictators. See also *Fifth column A fifth column is any group of people who undermine a larger group or nation from within, usually in favor of an enemy group or another nation. According to Harris Mylonas and Scott Radnitz, "fifth columns" are “domestic actors who work to un ... References Political terminology Political people Minorities Dissidents Exiled politicians {{poli-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plato
Plato ( ; grc-gre, Πλάτων ; 428/427 or 424/423 – 348/347 BC) was a Greek philosopher born in Athens during the Classical period in Ancient Greece. He founded the Platonist school of thought and the Academy, the first institution of higher learning on the European continent. Along with his teacher, Socrates, and his student, Aristotle, Plato is a central figure in the history of Ancient Greek philosophy and the Western and Middle Eastern philosophies descended from it. He has also shaped religion and spirituality. The so-called neoplatonism of his interpreter Plotinus greatly influenced both Christianity (through Church Fathers such as Augustine) and Islamic philosophy (through e.g. Al-Farabi). In modern times, Friedrich Nietzsche diagnosed Western culture as growing in the shadow of Plato (famously calling Christianity "Platonism for the masses"), while Alfred North Whitehead famously said: "the safest general characterization of the European philosophical tra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Republic (Plato)
The ''Republic'' ( grc-gre, Πολῑτείᾱ, Politeia; ) is a Socratic dialogue, authored by Plato around 375 BCE, concerning justice (), the order and character of the just city-state, and the just man. It is Plato's best-known work, and one of the world's most influential works of philosophy and political theory, both intellectually and historically. In the dialogue, Socrates discusses the meaning of justice and whether the just man is happier than the unjust man with various Athenians and foreigners.In ancient times, the book was alternately titled ''On Justice'' (not to be confused with the spurious dialogue of the same name). They consider the natures of existing regimes and then propose a series of different, hypothetical cities in comparison, culminating in Kallipolis (Καλλίπολις), a utopian city-state ruled by a philosopher-king. They also discuss ageing, love, theory of forms, the immortality of the soul, and the role of the philosopher and of poe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kurds In Turkey
The Kurds are the largest ethnic minority in Turkey. According to various estimates, they compose between 15% and 20% of the population of Turkey.; ; Sandra Mackey , “The reckoning: Iraq and the legacy of Saddam”, W.W. Norton and Company, 2002. Excerpt from pg 350: “As much as 25% of Turkey is Kurdish.” There are Kurds living in various provinces of Turkey, but they are primarily concentrated in the east and southeast of the country, within the region viewed by Kurds as Turkish Kurdistan. Officially in Eastern Anatolia and Southeastern Anatolia Regions. Massacres, such as the brutal suppression of the Sheikh Said Rebellion, the Dersim ethnocide, and the Zilan massacre, have periodically been committed against the Kurds since the establishment of the Republic of Turkey in 1923. The Turkish government categorized Kurds as "Mountain Turks" until 1991, and denied the existence of Kurds. The words "Kurds" or "Kurdistan" were banned in any language by the Turkish governmen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
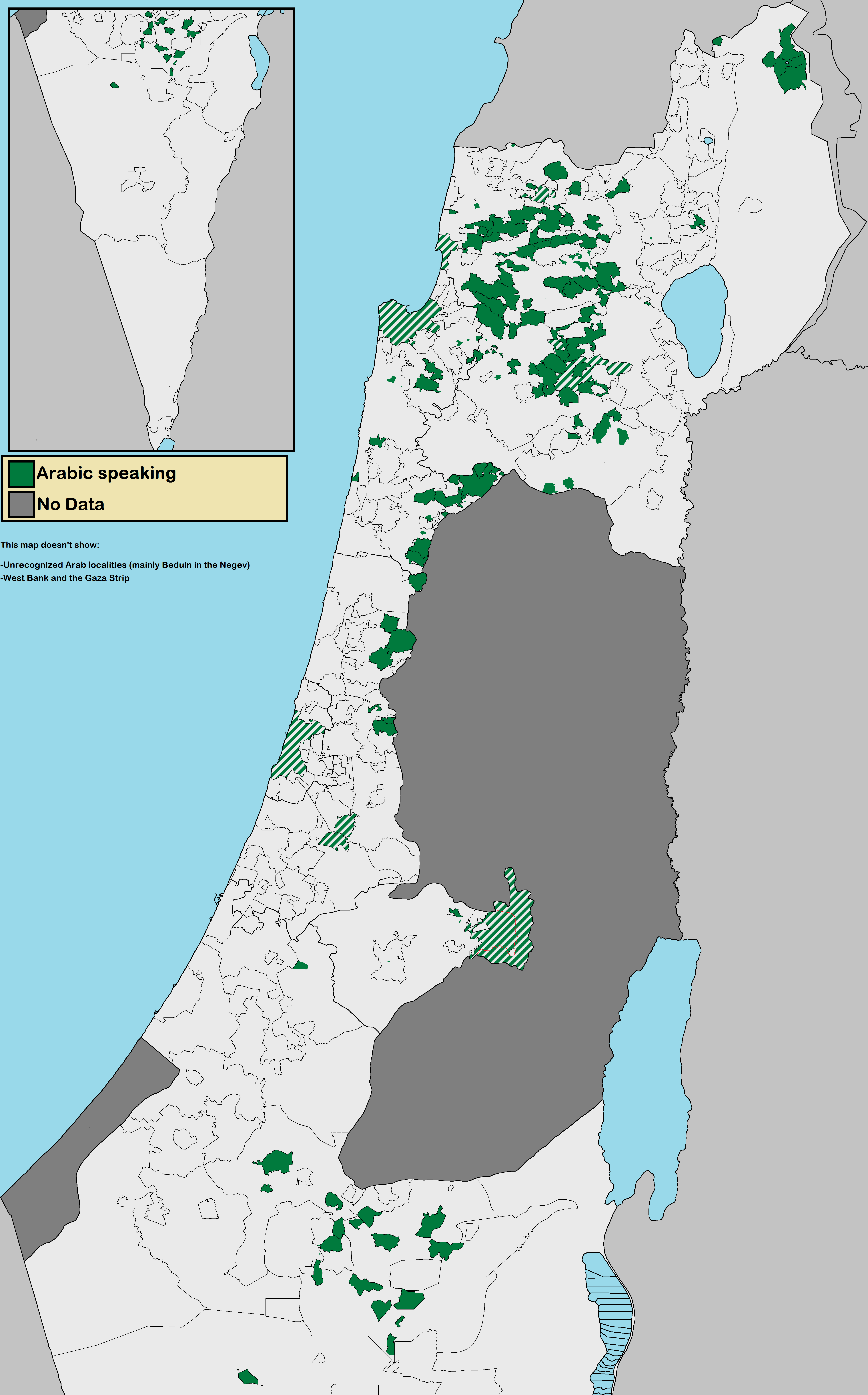
Palestinians In Israel
The Arab citizens of Israel are the largest ethnic minority in the country. They comprise a hybrid community of Israeli citizens with a heritage of Palestinian citizenship, mixed religions (Muslim, Christian or Druze), bilingual in Arabic and Hebrew, and with varying social identities. Self-identification as Palestinian citizens of Israel has sharpened in recent years, alongside distinct identities including Galilee and Negev Bedouin, the Druze people, and Arab Christians and Arab Muslims who do not identify as Palestinians. In Arabic, commonly used terms to refer to Israel's Arab population include 48-Arab ( ar, عرب 48, Arab Thamaniya Wa-Arba'in, label=none) and 48-Palestinian (). Since the Nakba, the Palestinians that have remained within Israel's 1948 borders have been colloquially known as "48-Arabs". In Israel itself, Arab citizens are commonly referred to as Israeli-Arabs or simply as ''Arabs''; international media often uses the term Arab-Israeli to distinguish A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
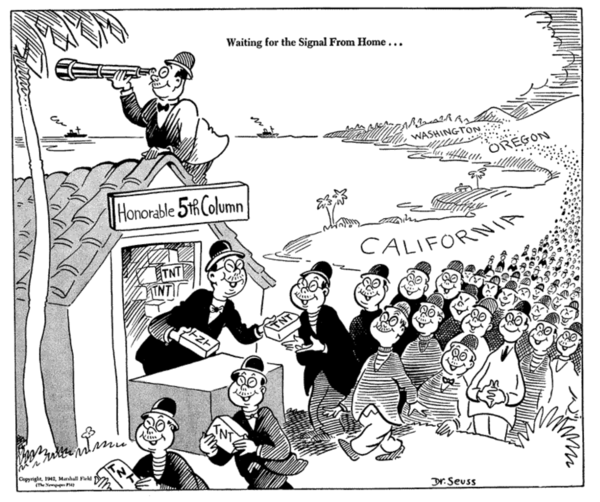
Fifth Column
A fifth column is any group of people who undermine a larger group or nation from within, usually in favor of an enemy group or another nation. According to Harris Mylonas and Scott Radnitz, "fifth columns" are “domestic actors who work to undermine the national interest, in cooperation with external rivals of the state." The activities of a fifth column can be overt or clandestine. Forces gathered in secret can mobilize openly to assist an external attack. This term is also extended to organised actions by military personnel. Clandestine fifth column activities can involve acts of sabotage, disinformation, espionage, and/or terrorism executed within defense lines by secret sympathizers with an external force. Origin The term "fifth column" originated in Spain (originally ''quinta columna'') during the early phase of the Spanish Civil War. It gained popularity in the Loyalist faction media in early October 1936 and immediately started to spread abroad. The exact origins of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Political Terminology
Politics (from , ) is the set of activities that are associated with making decisions in groups, or other forms of power relations among individuals, such as the distribution of resources or status. The branch of social science that studies politics and government is referred to as political science. It may be used positively in the context of a "political solution" which is compromising and nonviolent, or descriptively as "the art or science of government", but also often carries a negative connotation.. The concept has been defined in various ways, and different approaches have fundamentally differing views on whether it should be used extensively or limitedly, empirically or normatively, and on whether conflict or co-operation is more essential to it. A variety of methods are deployed in politics, which include promoting one's own political views among people, negotiation with other political subjects, making laws, and exercising internal and external force, including wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Political People
Politics (from , ) is the set of activities that are associated with making decisions in groups, or other forms of power relations among individuals, such as the distribution of resources or status. The branch of social science that studies politics and government is referred to as political science. It may be used positively in the context of a "political solution" which is compromising and nonviolent, or descriptively as "the art or science of government", but also often carries a negative connotation.. The concept has been defined in various ways, and different approaches have fundamentally differing views on whether it should be used extensively or limitedly, empirically or normatively, and on whether conflict or co-operation is more essential to it. A variety of methods are deployed in politics, which include promoting one's own political views among people, negotiation with other political subjects, making laws, and exercising internal and external force, including war ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dissidents
A dissident is a person who actively challenges an established political or religious system, doctrine, belief, policy, or institution. In a religious context, the word has been used since the 18th century, and in the political sense since the 20th century, coinciding with the rise of authoritarian governments in countries such as Fascist Italy, Nazi Germany, Imperial Japan, Francoist Spain, the Soviet Union (and later Russia), Saudi Arabia, North Korea, Iran, China, and Turkmenistan. In the Western world, there are historical examples of people who have been considered and have considered themselves dissidents, such as the Dutch philosopher Baruch Spinoza. In totalitarian countries, dissidents are often incarcerated or executed without explicit political accusations, or due to infringements of the very same laws they are opposing, or because they are supporting civil liberties such as freedom of speech. Eastern bloc The term ''dissident'' was used in the Eastern bloc, particular ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |