|
Interactive Data Visualization
Data and information visualization (data viz/vis or info viz/vis) is the practice of designing and creating graphic or visual representations of a large amount of complex quantitative and qualitative data and information with the help of static, dynamic or interactive visual items. Typically based on data and information collected from a certain domain of expertise, these visualizations are intended for a broader audience to help them visually explore and discover, quickly understand, interpret and gain important insights into otherwise difficult-to-identify structures, relationships, correlations, local and global patterns, trends, variations, constancy, clusters, outliers and unusual groupings within data (''exploratory visualization''). When intended for the general public (mass communication) to convey a concise version of known, specific information in a clear and engaging manner (''presentational'' or ''explanatory visualization''), it is typically called information graph ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Minard
Minard may refer to: Places: *Minard, Argyll, Scotland, United Kingdom **Minard Castle a castle in Argyll *Minard Castle (County Kerry) a castle in County Kerry, Ireland People with the surname: *Charles Joseph Minard (1781–1870), French civil engineer and noted pioneer in infographics *Chris Minard (born 1981), Canadian ice hockey player *David Minard (1913–2005), American physiologist *Joseph M. Minard (1932–2022), American politician from West Virginia *Lawrence Minard (1949–2001), American journalist See also *Menard (other) {{disambiguation, surname ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
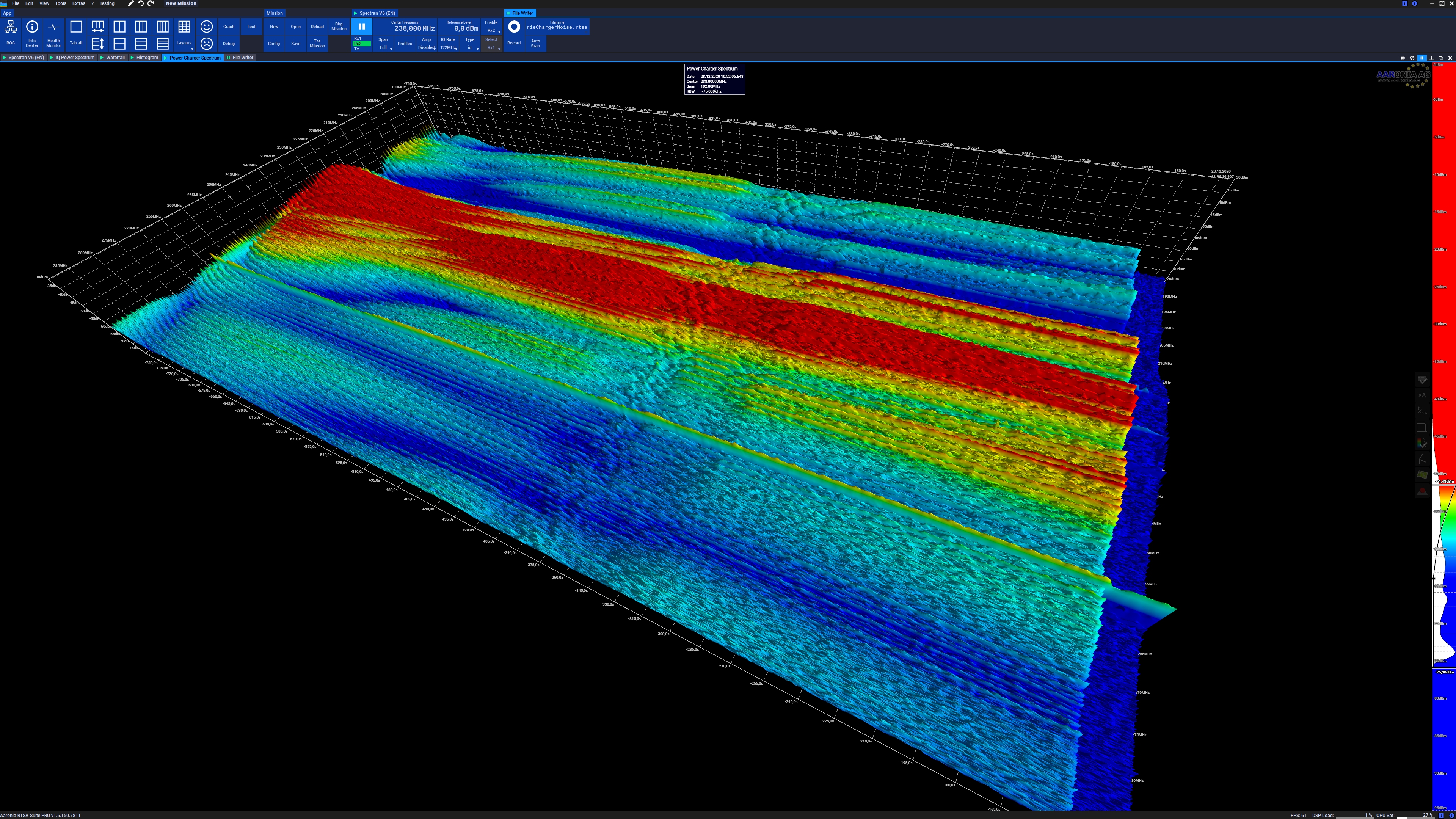
Spectrogram
A spectrogram is a visual representation of the spectrum of frequencies of a signal as it varies with time. When applied to an audio signal, spectrograms are sometimes called sonographs, voiceprints, or voicegrams. When the data are represented in a 3D plot they may be called '' waterfall displays''. Spectrograms are used extensively in the fields of music, linguistics, sonar, radar, speech processing, seismology, ornithology, and others. Spectrograms of audio can be used to identify spoken words phonetically, and to analyse the various calls of animals. A spectrogram can be generated by an optical spectrometer, a bank of band-pass filters, by Fourier transform or by a wavelet transform (in which case it is also known as a scaleogram or scalogram). A spectrogram is usually depicted as a heat map, i.e., as an image with the intensity shown by varying the colour or brightness. Format A common format is a graph with two geometric dimensions: one axis represents time ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heat Map
A heat map (or heatmap) is a 2-dimensional data visualization technique that represents the magnitude of individual values within a dataset as a color. The variation in color may be by hue or intensity. In some applications such as crime analytics or website click-tracking, color is used to represent the ''density'' of data points rather than a value associated with each point. "Heat map" is a relatively new term, but the practice of shading matrices has existed for over a century. History Heat maps originated in 2D displays of the values in a data matrix. Larger values were represented by small dark gray or black squares (pixels) and smaller values by lighter squares. The earliest known example dates to 1873, when Toussaint Loua used a hand-drawn and colored shaded matrix to visualize social statistics across the districts of Paris. The idea of reordering rows and columns to reveal structure in a data matrix, known as seriation, was introduced by Flinders Petrie in 1899. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Isopleth Map
A contour line (also isoline, isopleth, isoquant or isarithm) of a function of two variables is a curve along which the function has a constant value, so that the curve joins points of equal value. It is a plane section of the three-dimensional graph of the function f(x,y) parallel to the (x,y)-plane. More generally, a contour line for a function of two variables is a curve connecting points where the function has the same particular value. In cartography, a contour line (often just called a "contour") joins points of equal elevation (height) above a given level, such as mean sea level. A contour map is a map illustrated with contour lines, for example a topographic map, which thus shows valleys and hills, and the steepness or gentleness of slopes. The contour interval of a contour map is the difference in elevation between successive contour lines. The gradient of the function is always perpendicular to the contour lines. When the lines are close together the magnitu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Choropleth Map
A choropleth map () is a type of statistical thematic map that uses pseudocolor, meaning color corresponding with an aggregate summary of a geographic characteristic within spatial enumeration units, such as population density or per-capita income. Choropleth maps provide an easy way to visualize how a variable varies across a geographic area or show the level of variability within a region. A heat map or isarithmic map is similar but uses regions drawn according to the pattern of the variable, rather than the ''a priori'' geographic areas of choropleth maps. The choropleth is likely the most common type of thematic map because published statistical data (from government or other sources) is generally aggregated into well-known geographic units, such as countries, states, provinces, and counties, and thus they are relatively easy to create using Geographic information system, GIS, spreadsheets, or other software tools. History The earliest known choropleth map was created i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
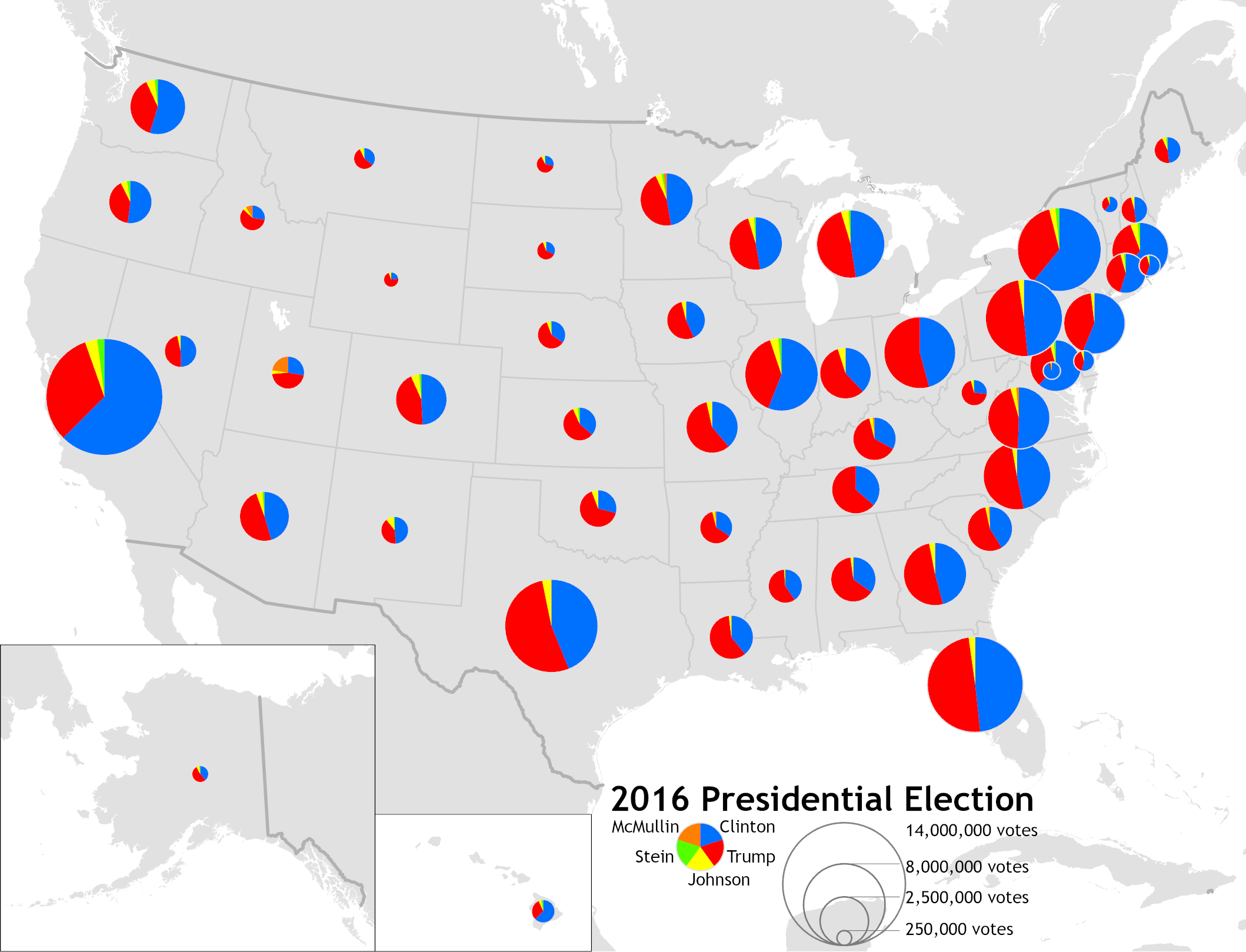
Proportional Symbol Map
A proportional symbol map or proportional point symbol map is a type of thematic map that uses map symbols that Visual variable, vary in size to represent a quantitative variable. For example, circles may be used to show the location of cities within the map, with the size of each circle sized proportionally to the population of the city. Typically, the size of each symbol is calculated so that its area is mathematically proportional to the variable, but more indirect methods (e.g., categorizing symbols as "small," "medium," and "large") are also used. While all dimensions of geometric primitives (i.e., points, lines, and regions) on a map can be resized according to a variable, this term is generally only applied to point symbols, and different design techniques are used for other dimensionalities. A cartogram is a map that distorts region size proportionally, while a flow map represents lines, often using the width of the Map symbol, symbol (a form of size) to represent a quantit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Box-and-whisker Plot
In descriptive statistics, a box plot or boxplot is a method for demonstrating graphically the locality, spread and skewness groups of numerical data through their quartiles. In addition to the box on a box plot, there can be lines (which are called ''whiskers'') extending from the box indicating variability outside the upper and lower quartiles, thus, the plot is also called the box-and-whisker plot and the box-and-whisker diagram. Outliers that differ significantly from the rest of the dataset may be plotted as individual points beyond the whiskers on the box-plot. Box plots are non-parametric: they display variation in samples of a statistical population without making any assumptions of the underlying statistical distribution (though Tukey's boxplot assumes symmetry for the whiskers and normality for their length). The spacings in each subsection of the box-plot indicate the degree of dispersion (spread) and skewness of the data, which are usually described using the five-n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Distribution Plot
Distribution may refer to: Mathematics *Distribution (mathematics), generalized functions used to formulate solutions of partial differential equations *Probability distribution, the probability of a particular value or value range of a variable **Cumulative distribution function, in which the probability of being no greater than a particular value is a function of that value *Frequency distribution, a list of the values recorded in a sample * Inner distribution, and outer distribution, in coding theory *Distribution (differential geometry), a subset of the tangent bundle of a manifold * Distributed parameter system, systems that have an infinite-dimensional state-space * Distribution of terms, a situation in which all members of a category are accounted for *Distributivity, a property of binary operations that generalises the distributive law from elementary algebra *Distribution (number theory) *Distribution problems, a common type of problems in combinatorics where the goa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scatter Plot
A scatter plot, also called a scatterplot, scatter graph, scatter chart, scattergram, or scatter diagram, is a type of plot or mathematical diagram using Cartesian coordinates to display values for typically two variables for a set of data. If the points are coded (color/shape/size), one additional variable can be displayed. The data are displayed as a collection of points, each having the value of one variable determining the position on the horizontal axis and the value of the other variable determining the position on the vertical axis. History According to Michael Friendly and Daniel Denis, the defining characteristic distinguishing scatter plots from line charts is the representation of specific observations of bivariate data where one variable is plotted on the horizontal axis and the other on the vertical axis. The two variables are often abstracted from a physical representation like the spread of bullets on a target or a geographic or celestial projection. Wh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plot (graphics)
A plot is a graphical technique for representing a data set, usually as a Graph of a function, graph showing the relationship between two or more variables. The plot can be drawn by hand or by a computer. In the past, sometimes mechanical or electronic plotters were used. Graphs are a visual representation of the relationship between variables, which are very useful for humans who can then quickly derive an understanding which may not have come from lists of values. Given a scale or ruler, graphs can also be used to read off the value of an unknown variable plotted as a function of a known one, but this can also be done with data presented in tabular form. Graphs of functions are used in mathematics, sciences, engineering, technology, finance, and other areas. Overview Plots play an important role in statistics and data analysis. The procedures here can broadly be split into two parts: quantitative and graphical. Quantitative techniques are a set of statistical procedures that yi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diagram
A diagram is a symbolic Depiction, representation of information using Visualization (graphics), visualization techniques. Diagrams have been used since prehistoric times on Cave painting, walls of caves, but became more prevalent during the Age of Enlightenment, Enlightenment. Sometimes, the technique uses a Three-dimensional space, three-dimensional visualization which is then graphical projection, projected onto a two-dimensional surface. The word ''graphics, graph'' is sometimes used as a synonym for diagram. Overview The term "diagram" in its commonly used sense can have a general or specific meaning: * ''visual information device'' : Like the term "illustration", "diagram" is used as a collective term standing for the whole class of technical genres, including graphics, graphs, technical drawings and tables. * ''specific kind of visual display'' : This is the genre that shows qualitative data with shapes that are connected by lines, arrows, or other visual links. In scie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bullet Graph
A bullet graph is a variation of a bar graph developed by Stephen Few. Seemingly inspired by the traditional thermometer charts and progress bars found in many dashboards, the bullet graph serves as a replacement for dashboard gauges and meters. Bullet graphs were developed to overcome the fundamental issues of gauges and meters: they typically display too little information, require too much space, and are cluttered with useless and distracting decorations. The bullet graph features a single, primary measure (for example, current year-to-date revenue), compares that measure to one or more other measures to enrich its meaning (for example, compared to a target), and displays it in the context of qualitative ranges of performance, such as poor, satisfactory, and good. The qualitative ranges are displayed as varying intensities of a single hue to make them discernible by those who are color blind and to restrict the use of colors on the dashboard to a minimum. Bullet graphs can be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |