|
Intellectual Disability Sport Classification
Intellectual disability sport classification is a Disability sport classification, classification system used for disability sport that allows people with intellectual disabilities to fairly compete with and against other people with intellectual disabilities. Separate classification systems exist for the elite athlete with a disability side affiliated with the Paralympic movement anVirtus(formerly known as the International Sports Federation for Persons with Intellectual Disability INAS), and the sports for all model affiliated with Special Olympics. People with intellectual disabilities have issues with conceptual skills, social skills and practical skills. They have IQs of 75 points or lower, limitations in adaptive behaviour and their disability manifested and was documented prior to turning 18 years of age. ID sport classification started in earnest internationally in 1985 following the creation of INAS. INAS went on to be a founding member of the International Paralympic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Disability Sport Classification
Disability sports classification is a system that allows for fair competition between people with different types of disabilities. Historically, the process has been overseen by 2 groups: specific disability type sport organizations that cover multiple sports, and specific sport organizations that cover multiple disability types including amputations, cerebral palsy, deafness, intellectual impairments, les autres and short stature, vision impairments, spinal cord injuries, and other disabilities not covered by these groups. Within specific disability types, some of the major organizations have been: CPISRA for cerebral palsy and head injuries, ISMWSF for spinal cord injuries, ISOD for orthopaedic conditions and amputees, INAS for people with intellectual disabilities, and IBSA for blind and vision impaired athletes. Amputee sports classification is a disability specific sport classification used for disability sports to facilitate fair competition among people with different types ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apert Syndrome
Apert syndrome is a form of acrocephalosyndactyly, a congenital disorder characterized by malformations of the skull, face, hands and feet. It is classified as a branchial arch syndrome, affecting the first branchial (or pharyngeal) arch, the precursor of the maxilla and mandible. Disturbances in the development of the branchial arches in fetal development create lasting and widespread effects. In 1906, Eugène Apert, a French physician, described nine people sharing similar attributes and characteristics. Linguistically, in the term "acrocephalosyndactyly", ''acro'' is Greek for "peak", referring to the "peaked" head that is common in the syndrome; ''cephalo'', also from Greek, is a combining form meaning "head"; ''syndactyly'' refers to webbing of fingers and toes. In embryology, the hands and feet have selective cells that die in a process called selective cell death, or apoptosis, causing separation of the digits. In the case of acrocephalosyndactyly, selective cell death ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
S14 (classification)
S14, SB14, SM14 are disability swimming classifications used for categorising swimmers based on their level of disability. Definition This classification is for people with intellectual disabilities. History The classification was created by the International Paralympic Committee and has roots in a 2003 attempt to address "the overall objective to support and co-ordinate the ongoing development of accurate, reliable, consistent and credible sport focused classification systems and their implementation." For the 2016 Summer Paralympics in Rio, the International Paralympic Committee had a zero classification at the Games policy. This policy was put into place in 2014, with the goal of avoiding last minute changes in classes that would negatively impact athlete training preparations. All competitors needed to be internationally classified with their classification status confirmed prior to the Games, with exceptions to this policy being dealt with on a case-by-case basis. Competi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
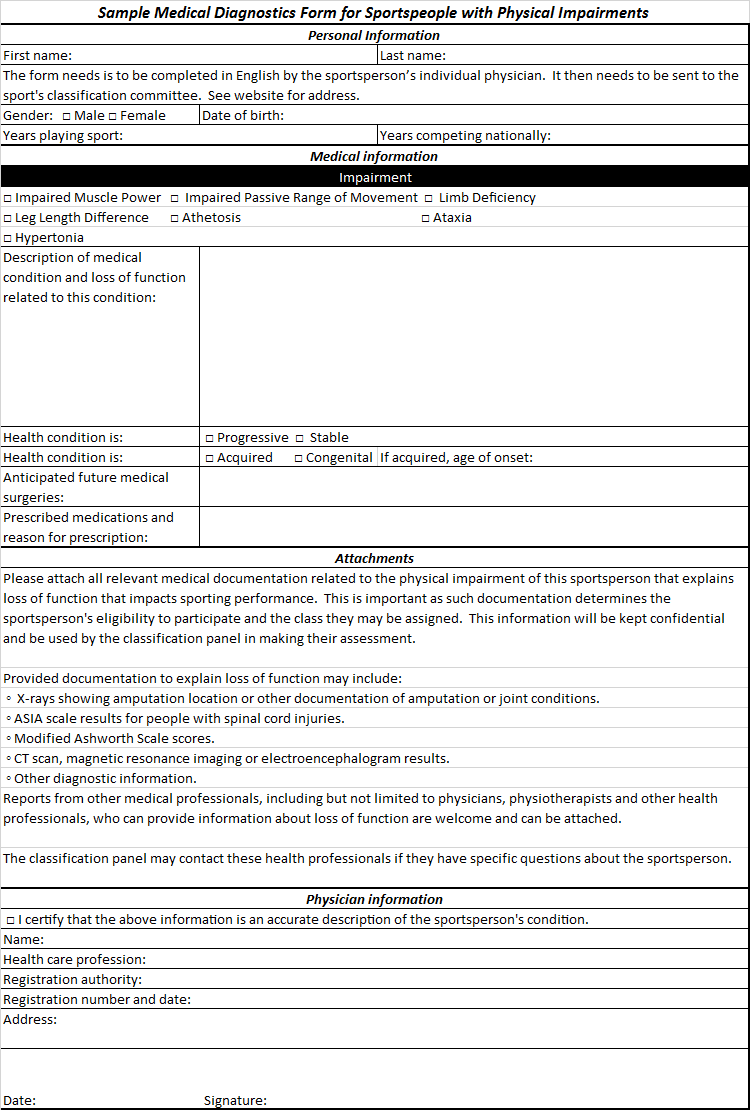
Para-equestrian Classification
Para-equestrian classification is a system for para-equestrian sport is a graded system based on the degree of physical or visual disability and handled at the international level by the FEI. The sport has eligible classifications for people with physical and vision disabilities. Groups of eligible riders include The sport is open to competitors with impaired muscle power, athetosis, impaired passive range of movement, hypertonia, limb deficiency, ataxia, leg length difference, short stature, and vision impairment. They are grouped into five different classes to allow fair competition. These classes are Grade I, Grade II, Grade III, Grade IV, and Grade V(Grade Names Changed as of Jan 2017) . The para-equestrian classification does not consider the gender of the rider, as equestrines compete in mixed gender competitions. History of classification In 1983, classification for cerebral palsy competitors in this sport was done by the Cerebral Palsy-International Sports and Recr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ID (classification)
ID is an adaptive rowing classification. The classifications were developed and current as of March 2011. Definition Rowing Australia defines this classification as "Rowers with an intellectual disability owers with an intellectual disability are not eligible to compete at the Paralympics at the time of publication (March 2011) Events Rowers in this classification compete in single and double sculls for club, state and national competitions. In international competitions, they compete in a mixed coxed four. Becoming classified Classification is handled by FISA – International Rowing Federation. Australians seeking classification through Rowing Australia need to provide several documents to a classifier at the time of application, including an AUSRAPID accreditation card, or International Sports Federation for Persons with an Intellectual Impairment (INAS-FID) ID card. At the Paralympic Games For the 2016 Summer Paralympics in Rio, the International Paralympic Committee ha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
141100 - ID Basketball Nicholas Maroney Ball - 3b - 2000 Sydney Match Photo
Year 1411 ( MCDXI) was a common year starting on Thursday (link will display the full calendar) of the Julian calendar. Events January–December * February 1 – The First Peace of Thorn is signed at Thorn in the Monastic State of the Teutonic Knights, ending the Polish–Lithuanian–Teutonic War. * February 17 – Ottoman Interregnum: Süleyman Çelebi is killed after being forced to flee his capital, Edirne, by his brother Musa Çelebi. Rule of the Ottoman domains in Europe (Rumelia) passes to Musa. * July 6 – Ming dynasty Admiral Zheng He returns to Nanjing after his second voyage, and presents the Sinhalese king, captured during the Ming–Kotte War, to the Yongle Emperor. * July 24 – Battle of Harlaw in Scotland: Domhnall of Islay, Lord of the Isles, and an army commanded by Alexander Stewart, Earl of Mar battle to a bloody draw. * September 3 – The Treaty of Selymbria is concluded between the Ottoman Empire and the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atlantoaxial Instability
In anatomy, the transverse ligament of the atlas is a ligament which arches across the ring of the atlas (the topmost cervical vertebra, which directly supports the skull), and keeps the odontoid process in contact with the atlas. Anatomy It is concave in front, convex behind, broader and thicker in the middle than at the ends, and firmly attached on either side to a small tubercle on the medial surface of the lateral mass of the atlas.Gray's anatomy, 1918 As it crosses the odontoid process, a small fasciculus (''crus superius'') is prolonged upward, and another (''crus inferius'') downward, from the superficial or posterior fibers of the ligament. The former is attached to the basilar part of the occipital bone, in close relation with the membrana tectoria; the latter is fixed to the posterior surface of the body of the axis; hence, the whole ligament is named the cruciate ligament of the atlas. The transverse ligament divides the ring of the atlas into two unequal parts: of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ligamentous Laxity
Ligamentous laxity, or ligament laxity, is a cause of chronic body pain characterized by loose ligaments. When this condition affects joints in the entire body, it is called ''generalized joint hypermobility'', which occurs in about ten percent of the population, and may be genetic. Loose ligaments can appear in a variety of ways and levels of severity. It also does not always affect the entire body. One could have loose ligaments of the feet, but not of the arms. Someone with ligamentous laxity, by definition, has loose ligaments. Unlike other, more pervasive diseases, the diagnosis does not require the presence of loose tendons, muscles or blood vessels, hyperlax skin or other connective tissue problems. In heritable connective tissue disorders associated with joint hypermobility (such as Marfan syndrome and Ehlers–Danlos syndrome types I–III, VII, and XI), the joint laxity usually is apparent before adulthood. However, age of onset and extent of joint laxity are variable ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Special Olympics USA
Special Olympics USA is a sports organization for children and adults with intellectual disabilities in the United States. It is part of the global Special Olympics movement. Special Olympics was founded in 1968 with the main goal of accepting and welcoming individuals as they are. Special Olympics provides year-round training in Olympic based sports and is based in 204 countries. Special Olympics USA Games The Special Olympics USA Games is a national Special Olympics event held every four years in the United States.Special Olympics 2010 USA National Games official website. Retrieved 2014-06-21. 2006 Special Olympics USA Games The first, quadrennial, USA National Games were held July 1–8, 2006, in |
Special Olympics
Special Olympics is the world's largest sports organization for children and adults with intellectual disabilities and physical disabilities, providing year-round training and activities to 5 million participants and Unified Sports partners in 172 countries. Special Olympics competitions are held every day, all around the world—including local, national and regional competitions, adding up to more than 100,000 events a year. Like the International Paralympic Committee, the Special Olympics organization is recognized by the International Olympic Committee; however, unlike the Paralympic Games, Special Olympics World Games are not held in the same year nor in conjunction with the Olympic Games. The Special Olympics World Games is a major event put on by the Special Olympics committee. The World Games alternate between summer and winter games, in two-year cycles, recurring every fourth year. The first games were held on July 20, 1968, in Chicago, Illinois, with about 1000 athlete ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |