|
Inotuzumab
Inotuzumab ozogamicin, sold under the brand name Besponsa, is an antibody-drug conjugate medication used to treat relapsed or refractory B-cell precursor acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL). The medication consists of a humanized monoclonal antibody against CD22 (inotuzumab), linked to a cytotoxic agent from the class of calicheamicins called ozogamicin. This drug was discovered by scientists collaborating at Celltech and Wyeth, and it was drug development, developed by Pfizer which had acquired Wyeth. The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) considers it to be a first-in-class medication. Medical use Inotuzumab ozogamicin is used to treat relapsed or refractory B-cell precursor acute lymphoblastic leukemia. It is administered by intravenous infusion in a doctor's office or clinic. In studies in pregnant animals, the drug caused harm to the fetus at doses less than those used clinically, and so the drug has not been tested in pregnant women. Pregnant women should not take i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inotuzumab
Inotuzumab ozogamicin, sold under the brand name Besponsa, is an antibody-drug conjugate medication used to treat relapsed or refractory B-cell precursor acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL). The medication consists of a humanized monoclonal antibody against CD22 (inotuzumab), linked to a cytotoxic agent from the class of calicheamicins called ozogamicin. This drug was discovered by scientists collaborating at Celltech and Wyeth, and it was drug development, developed by Pfizer which had acquired Wyeth. The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) considers it to be a first-in-class medication. Medical use Inotuzumab ozogamicin is used to treat relapsed or refractory B-cell precursor acute lymphoblastic leukemia. It is administered by intravenous infusion in a doctor's office or clinic. In studies in pregnant animals, the drug caused harm to the fetus at doses less than those used clinically, and so the drug has not been tested in pregnant women. Pregnant women should not take i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
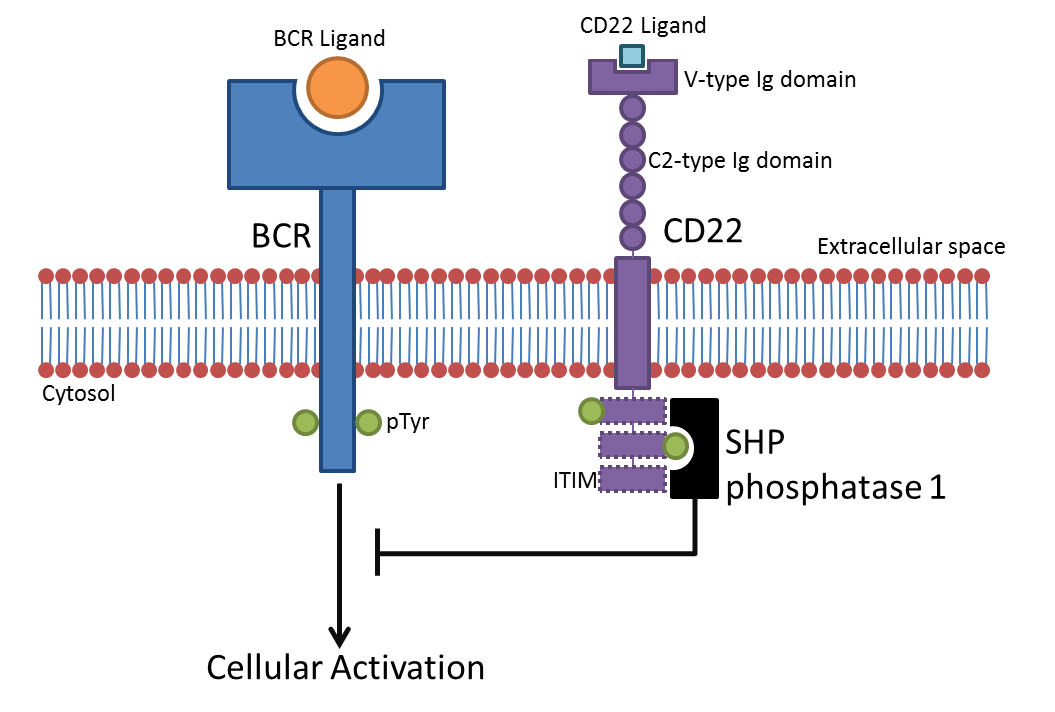
CD22
CD22, or cluster of differentiation-22, is a molecule belonging to the SIGLEC family of lectins. It is found on the surface of mature B cells and to a lesser extent on some immature B cells. Generally speaking, CD22 is a regulatory molecule that prevents the overactivation of the immune system and the development of autoimmune diseases. CD22 is a sugar binding transmembrane protein, which specifically binds sialic acid with an immunoglobulin (Ig) domain located at its N-terminus. The presence of Ig domains makes CD22 a member of the immunoglobulin superfamily. CD22 functions as an inhibitory receptor for B cell receptor (BCR) signaling. It is also involved in the B cell trafficking to Peyer's patches in mice. In mice, it has been shown that CD22 blockade restores homeostatic microglial phagocytosis in aging brains. Structure CD22 is a transmembrane protein with a molecular weight of 140 kDa. The extracellular part of CD22 consists of seven immunoglobulin domains and the intr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antibody-drug Conjugate
Antibody-drug conjugates or ADCs are a class of biopharmaceutical drugs designed as a targeted therapy for treating cancer. Unlike chemotherapy, ADCs are intended to target and kill tumor cells while sparing healthy cells. As of 2019, some 56 pharmaceutical companies were developing ADCs. ADCs are complex molecules composed of an antibody linked to a biologically active cytotoxic (anticancer) payload or drug. Antibody-drug conjugates are an example of bioconjugates and immunoconjugates. ADCs combine the targeting properties of Monoclonal antibody, monoclonal antibodies with the cancer-killing capabilities of cytotoxic drugs, designed to discriminate between healthy and diseased tissue. Mechanism of action An anticancer drug is coupled to an antibody that targets a specific tumor antigen (or protein) that, ideally, is only found in or on tumor cells. Antibodies attach themselves to the antigens on the surface of cancerous cells. The biochemical reaction that occurs upon attaching ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
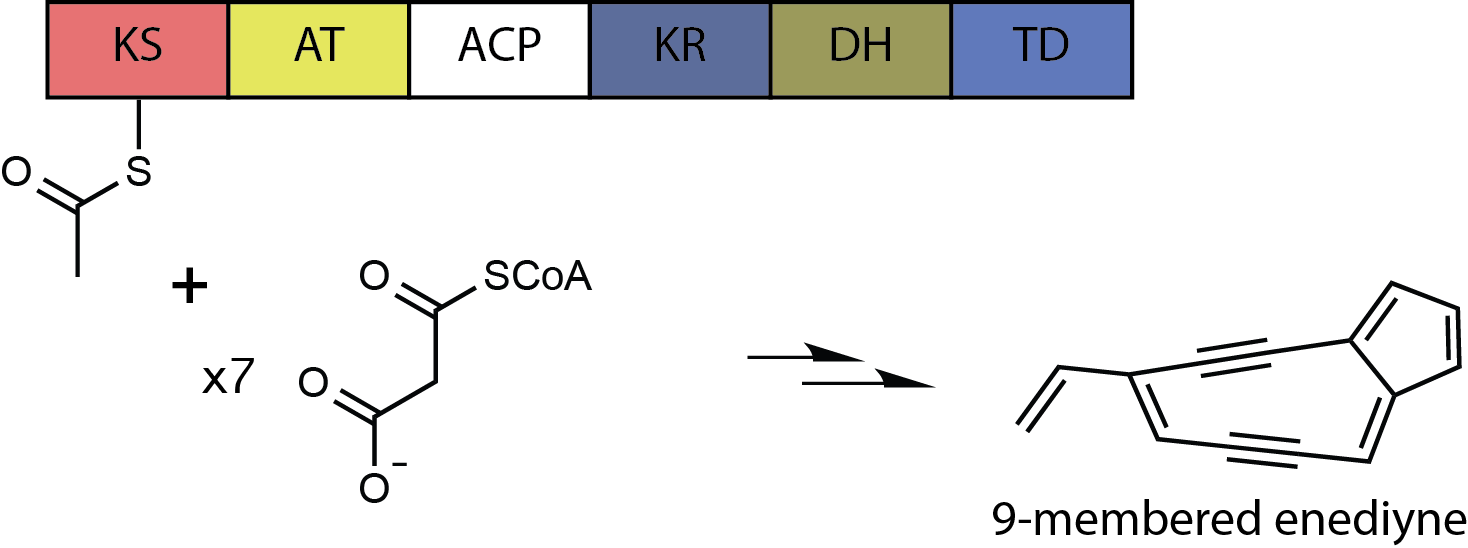
Calicheamicin
The calicheamicins are a class of enediyne antitumor antibiotics derived from the bacterium ''Micromonospora echinospora'', with calicheamicin γ1 being the most notable. It was isolated originally in the mid-1980s from the chalky soil, or "caliche pits", located in Kerrville, Texas. The sample was collected by a scientist working for Lederle Labs. It is extremely toxic to all cells and, in 2000, a CD33 antigen-targeted immunoconjugate N-acetyl dimethyl hydrazide calicheamicin was developed and marketed as targeted therapy against the non-solid tumor cancer acute myeloid leukemia (AML). A second calicheamicin-linked monoclonal antibody, inotuzumab ozogamicin (marketed as Besponsa) an anti-CD22-directed antibody-drug conjugate, was approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration on August 17, 2017, for use in the treatment of adults with relapsed or refractory B-cell precursor acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Calicheamicin γ1 and the related enediyne esperamicin are the two of the m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
First-in-class Medication
A first-in-class medication is a pharmaceutical that uses a "new and unique mechanism of action" to treat a particular medical condition. While the Food and Drug Administration's Center for Drug Evaluation and Research tracks first-in-class medications and reports on them annually, first-in-class is not considered a regulatory category. Although many first-in-class medications qualify as breakthrough therapies, Regenerative Medicine Advanced Therapies and/or orphan drugs, first-in-class status itself has no regulatory effect. Examples Controversy Safety By definition, a first-in-class drug does not have the safety evidence from analogous products that not-first-in-class drugs would have. However, a study investigating recalls and warnings in relation to first-in-class drugs approved between 1997 and 2012 by Health Canada has found that first-in-class drugs actually have a more favourable benefit-to-harm ratio. Economics First-in-class drugs are often seen as commerci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ozogamicin
The term ozogamicin in the names of monoclonal antibodies or antibody-drug conjugates indicates that they are linked to a cytotoxic agent from the class of calicheamicins. See also *Gemtuzumab ozogamicin Gemtuzumab ozogamicin, sold under the brand name Mylotarg, is an antibody-drug conjugate (a drug-linked monoclonal antibody) that is used to treat acute myeloid leukemia. The most common grade 3 and higher adverse reactions that occurred during ... * Inotuzumab ozogamicin References {{Reflist Antibodies Antibody-drug conjugates ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Celltech
Celltech Group plc was a leading British-based biotechnology business based in Slough. It was listed on the London Stock Exchange and was a constituent of the FTSE 100 Index. History Celltech was founded by Gerard Fairtlough in 1980 with finance from the National Enterprise Board. Amongst the work conducted at Celltech was the cloning of the glutamine synthetase (GS) gene in CHO cells leading to the creation of a biotechnology tool still widely used to express recombinant eukaryotic proteins. In 1999 Celltech led consolidation in the UK biosciences market merging with ''Chiroscience plc'', after which it was briefly referred to as ''Celltech Chiroscience,'' and then buying ''Medeva plc''. Then in 2000 it bought ''Cistron'', a US biosciences business. It expanded into Germany in 2001 buying Thiemann, a German biosciences business, and went on to buy Oxford Glycosciences in July 2003 for £102m. Celltech was acquired by UCB, a Belgian drugmaker, in 2004. Since then it has bee ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gemtuzumab Ozogamicin
Gemtuzumab ozogamicin, sold under the brand name Mylotarg, is an antibody-drug conjugate (a drug-linked monoclonal antibody) that is used to treat acute myeloid leukemia. The most common grade 3 and higher adverse reactions that occurred during Induction 1 and Intensification 2 in ≥ 5% of people who received gemtuzumab ozogamicin were infection, febrile neutropenia, decreased appetite, hyperglycemia, mucositis, hypoxia, hemorrhage, increased transaminase, diarrhea, nausea, and hypotension. Medical uses In the United States, gemtuzumab ozogamicin is indicated for newly diagnosed CD33-positive acute myeloid leukemia (AML) for adults and children one month and older and for the treatment of relapsed or refractory CD33-positive AML in adults and children two years and older. Mechanism and side effects Gemtuzumab is a monoclonal antibody to CD33 linked to a cytotoxic agent from the class of calicheamicins ( ozogamicin). CD33 is expressed in most leukemic blast cells but also i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lysosome
A lysosome () is a membrane-bound organelle found in many animal cells. They are spherical vesicles that contain hydrolytic enzymes that can break down many kinds of biomolecules. A lysosome has a specific composition, of both its membrane proteins, and its lumenal proteins. The lumen's pH (~4.5–5.0) is optimal for the enzymes involved in hydrolysis, analogous to the activity of the stomach. Besides degradation of polymers, the lysosome is involved in various cell processes, including secretion, plasma membrane repair, apoptosis, cell signaling, and energy metabolism. Lysosomes act as the waste disposal system of the cell by digesting used materials in the cytoplasm, from both inside and outside the cell. Material from outside the cell is taken up through endocytosis, while material from the inside of the cell is digested through autophagy. The sizes of the organelles vary greatly—the larger ones can be more than 10 times the size of the smaller ones. They were discov ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cell Nucleus
The cell nucleus (pl. nuclei; from Latin or , meaning ''kernel'' or ''seed'') is a membrane-bound organelle found in eukaryotic cells. Eukaryotic cells usually have a single nucleus, but a few cell types, such as mammalian red blood cells, have no nuclei, and a few others including osteoclasts have many. The main structures making up the nucleus are the nuclear envelope, a double membrane that encloses the entire organelle and isolates its contents from the cellular cytoplasm; and the nuclear matrix, a network within the nucleus that adds mechanical support. The cell nucleus contains nearly all of the cell's genome. Nuclear DNA is often organized into multiple chromosomes – long stands of DNA dotted with various proteins, such as histones, that protect and organize the DNA. The genes within these chromosomes are structured in such a way to promote cell function. The nucleus maintains the integrity of genes and controls the activities of the cell by regulating gene expres ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neutropenia
Neutropenia is an abnormally low concentration of neutrophils (a type of white blood cell) in the blood. Neutrophils make up the majority of circulating white blood cells and serve as the primary defense against infections by destroying bacteria, bacterial fragments and immunoglobulin-bound viruses in the blood. People with neutropenia are more susceptible to bacterial infections and, without prompt medical attention, the condition may become life-threatening (neutropenic sepsis). Neutropenia can be divided into congenital and acquired, with severe congenital neutropenia (SCN) and cyclic neutropenia (CyN) being autosomal dominant and mostly caused by heterozygous mutations in the ELANE gene (neutrophil elastase). Neutropenia can be acute (temporary) or chronic (long lasting). The term is sometimes used interchangeably with "leukopenia" ("deficit in the number of white blood cells"). Decreased production of neutrophils is associated with deficiencies of vitamin B12 and folic aci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Endocytosis
Endocytosis is a cellular process in which substances are brought into the cell. The material to be internalized is surrounded by an area of cell membrane, which then buds off inside the cell to form a vesicle containing the ingested material. Endocytosis includes pinocytosis (cell drinking) and phagocytosis (cell eating). It is a form of active transport. History The term was proposed by De Duve in 1963. Phagocytosis was discovered by Élie Metchnikoff in 1882. Pathways Endocytosis pathways can be subdivided into four categories: namely, receptor-mediated endocytosis (also known as clathrin-mediated endocytosis), caveolae, pinocytosis, and phagocytosis Phagocytosis () is the process by which a cell uses its plasma membrane to engulf a large particle (≥ 0.5 μm), giving rise to an internal compartment called the phagosome. It is one type of endocytosis. A cell that performs phagocytosis is .... *Clathrin-mediated endocytosis is mediated by the production of smal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |