|
Information Systems Audit
An information technology audit, or information systems audit, is an examination of the management controls within an Information technology (IT) infrastructure and business applications. The evaluation of evidence obtained determines if the information systems are safeguarding assets, maintaining data integrity, and operating effectively to achieve the organization's goals or objectives. These reviews may be performed in conjunction with a financial statement audit, internal audit, or other form of attestation engagement. IT audits are also known as automated data processing audits (ADP audits) and computer audits. They were formerly called electronic data processing audits (EDP audits). Purpose An IT audit is different from a financial statement audit. While a financial audit's purpose is to evaluate whether the financial statements present fairly, in all material respects, an entity's financial position, results of operations, and cash flows in conformity to standard accou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Information Technology
Information technology (IT) is the use of computers to create, process, store, retrieve, and exchange all kinds of data . and information. IT forms part of information and communications technology (ICT). An information technology system (IT system) is generally an information system, a communications system, or, more specifically speaking, a computer system — including all hardware, software, and peripheral equipment — operated by a limited group of IT users. Although humans have been storing, retrieving, manipulating, and communicating information since the earliest writing systems were developed, the term ''information technology'' in its modern sense first appeared in a 1958 article published in the '' Harvard Business Review''; authors Harold J. Leavitt and Thomas L. Whisler commented that "the new technology does not yet have a single established name. We shall call it information technology (IT)." Their definition consists of three categories: techniques ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2013
File:2013 Events Collage V2.png, From left, clockwise: Edward Snowden becomes internationally famous for leaking classified NSA wiretapping information; Typhoon Haiyan kills over 6,000 in the Philippines and Southeast Asia; The Dhaka garment factory collapse in Bangladesh kills over 1,000 people; The streak from the Chelyabinsk meteor that rocketed across the Russian morning sky; Protests occur amid the coup d'état that overthrew President Mohamed Morsi of Egypt; Smoke rises as a result of the Westgate shopping mall attack in Nairobi, Kenya, carried out by Al-Shabaab militants; The Boston Marathon bombing marks the first terrorist attack in the United States since 9/11; Pope Francis is elected to the Papacy in the 2013 papal conclave., 300x300px, thumb rect 0 0 200 200 Edward Snowden rect 200 0 400 200 Typhoon Haiyan rect 400 0 600 200 Dhaka garment factory collapse rect 0 200 300 400 2013 papal conclave rect 300 200 600 400 Chelyabinsk meteor rect 0 400 200 60 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SAS 99
{{Short description, Statutory Auditor Coderal Statement on Auditing Standards No. 99: Consideration of Fraud in a Financial Statement Audit, commonly abbreviated as SAS 99, is an auditing statement issued by the Auditing Standards Board of the American Institute of Certified Public Accountants (AICPA) in October 2002. The original exposure draft was distributed in February 2002. Please see PCAOB AS 2401. SAS 99, which supersedes SAS 82, was issued partly in response to contemporary accounting scandals at Enron, WorldCom, Adelphia, and Tyco. The standard incorporates recommendations from various contributors including thInternational Auditing & Assurance Standards Board SAS 99 became effective for audits of financial statements for periods beginning on or after December 15, 2002. Key Components of SAS 99 Describes Fraud and its characteristics. SAS 99 defines fraud as an intentional act that results in a material misstatement in financial statements. There are two types of f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
XBRL Assurance
XBRL assurance is the auditor's opinion on whether a financial statement or other business report published in XBRL, is relevant, accurate, complete, and fairly presented. An XBRL report is an electronic file and called instance in XBRL terminology. IFAC and other accounting organizations are discussing the topic to decide on a common approach and XBRL auditing standards. The auditor may give assurance to an XBRL financial statement, an XBRL business report and XBRL real-time reporting (often referred to as continuous reporting). The short term focus is on XBRL financial statements and regulatory reports, while the future focus is expected to be more on real-time reporting. Digital reporting process An XBRL report is part of a digital reporting supply chain. The auditor should not focus only on the reliability of the report itself. It is better to focus on the whole supply chain including the communication over a network of the report. The auditor needs to check if the report t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
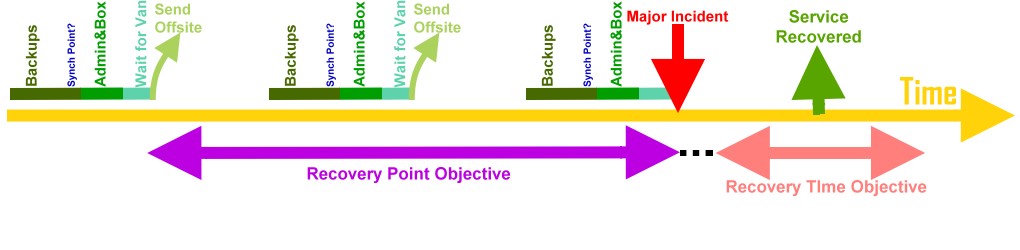
Disaster Recovery And Business Continuity Auditing
Given organizations' increasing dependency on information technology to run their operations, Business continuity planning covers the entire organization, and Disaster recovery focuses on ''IT''. Auditing of documents covering an organization's ''business continuity'' and ''disaster recovery'' plans provides a third-party validation to stakeholders that the documentation is complete and does not contain material misrepresentations. Lack of completeness can result in overlooking secondary effects, such as when vastly increased work-at-home overloads incoming recovery site telecommunications capacity, and the bi-weekly payroll that was not critical within the first 48 hours is now causing perceived problems in ever recovering, complicated by governmental and possibly union reaction. Overview Often used together, the terms Business Continuity and Disaster Recovery are very different. Business Continuity refers to the ability of a business to continue critical functions and busines ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Change Management Auditing
Change management auditing is the process by which companies can effectively manage change within their information technology systems. Changes to computer software must be monitored in order to reduce the risk of data loss, corruption, malware, errors, and security breaches. Change risks Proper change control auditing can lower the following risks: * Security features of the network turn off. * Harmful code is distributed to users. * Sensitive data is lost or becomes insecure. * Financial report errors occur. Control procedure The following features are commonly part of a change management auditing procedure: ;Change management procedures are formally documented and controlled. ;Changes are requested in a formal process. : Requests are recorded and stored for reference. ;The effect of the requested change is assessed.:Each change is assessed based on its projected effect to the computer system and business operations. The assessment is documented with the request. : Priority is bas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Helpdesk And Incident Reporting Auditing
Help desk and incident reporting auditing is an examination of the controls within the help desk operations. The audit process collects and evaluates evidence of an organization's help desk and incident reporting practices, and operations. The audit ensures that all problems reported by users have been adequately documented and that controls exist so that only authorized staff can archive the users’ entries. It also determine if there are sufficient controls to escalate issues according to priority. Types of help desks The management and support of IT assets is essential for all businesses. Help desks are now fundamental and key aspects of good business service and operation. Through the help desk, problems are reported, managed and then appropriately resolved in a timely manner. Help desks can provide both internal and external users the ability to ask questions and receive effective answers. Moreover, help desks can help the organization run smoothly and improve the quality ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Data Analysis (information Technology)
Computer-assisted audit tool (CAATs) or computer-assisted audit tools and techniques (CAATTs) is a growing field within the IT audit profession. CAATs is the practice of using computers to automate the IT audit processes. CAATs normally include using basic office productivity software such as spreadsheets, word processors and text editing programs and more advanced software packages involving use statistical analysis and business intelligence tools. But also more dedicated specialized software are available (see below). CAATs have become synonymous with data analytics in the audit process. Traditional auditing vs CAATs Traditional audit example The traditional method of auditing allows auditors to build conclusions based upon a limited sample of a population, rather than an examination of all available or a large sample of data. CAATTs alternative CAATTs, not CAATs, addresses these problems. CAATTs, as it is commonly used, is the practice of analyzing large volumes of data l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Computer Forensics
Computer forensics (also known as computer forensic science) is a branch of digital forensic science pertaining to evidence found in computers and digital storage media. The goal of computer forensics is to examine digital media in a forensically sound manner with the aim of identifying, preserving, recovering, analyzing and presenting facts and opinions about the digital information. Although it is most often associated with the investigation of a wide variety of computer crime, computer forensics may also be used in civil proceedings. The discipline involves similar techniques and principles to data recovery, but with additional guidelines and practices designed to create a legal audit trail. Evidence from computer forensics investigations is usually subjected to the same guidelines and practices of other digital evidence. It has been used in a number of high-profile cases and is accepted as reliable within U.S. and European court systems. Overview In the early 1980s per ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Payment Card Industry Security Standards Council
The Payment Card Industry Security Standards Council (PCI SSC) was formed by American Express, Discover Financial Services, JCB International, MasterCard and Visa Inc. on September 7, 2006, with the goal of managing the ongoing evolution of the Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard. The Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS) consists of twelve significant requirements including multiple sub-requirements, which contain numerous directives against which businesses may measure their own payment card security policies, procedures and guidelines. To address rising cybersecurity risks to the payment ecosystem, the PCI SSC currently manages 15 standards for payment security, which are variously applicable to payment card issuers, merchants and service providers, vendors and solution providers, and acquirers and processors. More recently, the PCI SSC has collaborated witEMVCo to provide the security requirements, testing procedures and assessor training to suppo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Institute Of Standards And Technology
The National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) is an agency of the United States Department of Commerce whose mission is to promote American innovation and industrial competitiveness. NIST's activities are organized into Outline of physical science, physical science laboratory programs that include Nanotechnology, nanoscale science and technology, engineering, information technology, neutron research, material measurement, and physical measurement. From 1901 to 1988, the agency was named the National Bureau of Standards. History Background The Articles of Confederation, ratified by the colonies in 1781, provided: The United States in Congress assembled shall also have the sole and exclusive right and power of regulating the alloy and value of coin struck by their own authority, or by that of the respective states—fixing the standards of weights and measures throughout the United States. Article 1, section 8, of the Constitution of the United States, ratified in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |