|
Hydroxychavicol
Hydroxychavicol is a phenylpropanoid compound present in leaves of ''Piper betle''. It is a more potent inhibitor of xanthine oxidase (IC50=16.7 µM) than allopurinol. Research It might be a useful new compound in treating cutaneous fungal infections. It is a promising agent in prevention and treatment of dental disorders as it had bactericidal and fungicidal effect on ''Streptococcus intermedius'', ''Streptococcus mutans'', and ''Candida albicans'' and inhibited biofilm formation. See also * Chavicol Chavicol (''p''-allylphenol) is a natural phenylpropene, a type of organic compound. Its chemical structure consists of a benzene ring substituted with a hydroxy group and a propenyl group. It is a colorless liquid found together with terpenes i ... References Catechols Phenylpropenes {{Aromatic-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Piper Betle
The betel (''Piper betle'') is a vine of the family Piperaceae, which includes pepper and kava. The betel plant is native to Southeast Asia. It is an evergreen, dioecious perennial, with glossy heart-shaped leaves and white catkins. Betel plants are cultivated for their leaves which is most commonly used as flavoring in chewing areca nut (betel nut chewing). Etymology The term betel was derived from the Malayalam word ''vettila'' via Portuguese. Distribution ''Piper betle'' is originally native to South Asia and in Southeast Asia, from Island Southeast Asia (Philippines, Timor-Leste and the Lesser Sunda Islands, and Peninsular Malaysia) to Indochina (Vietnam, Cambodia, Laos, Thailand, and Myanmar). Its cultivation has spread along with the Austronesian migrations and trade to other parts of Island Southeast Asia, Papua New Guinea and Melanesia, Micronesia, South Asia, the Maldives, Mauritius, Réunion Island, and Madagascar. It has also been introduced during the Colonial Era ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Natural Product Research
''Natural Product Research'' is a peer-reviewed scientific journal covering research on natural products chemistry. It was established in 1992 by Atta ur Rahman (scientist), Atta-ur-Rahman. Abstracting and indexing The journal is abstracted and indexed in *CAB Abstracts *Cambridge Crystallographic Data Centre *Chemical Abstracts Service *National Library of Medicine *PubMed *Science Citation Index Expanded *Scopus. Taylor & Francis academic journals English-language journals Chemistry journals {{chemistry-journal-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
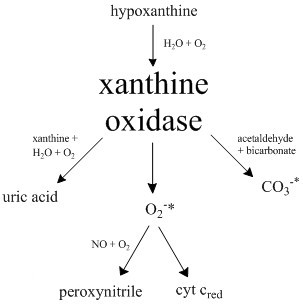
Xanthine Oxidase
Xanthine oxidase (XO, sometimes XAO) is a form of xanthine oxidoreductase, a type of enzyme that generates reactive oxygen species. These enzymes catalyze the oxidation of hypoxanthine to xanthine and can further catalyze the oxidation of xanthine to uric acid. These enzymes play an important role in the catabolism of purines in some species, including humans. Xanthine oxidase is defined as an ''enzyme activity'' (EC 1.17.3.2). The same protein, which in humans has the HGNC approved gene symbol ''XDH'', can also have xanthine dehydrogenase activity (EC 1.17.1.4). Most of the protein in the liver exists in a form with xanthine dehydrogenase activity, but it can be converted to xanthine oxidase by reversible sulfhydryl oxidation or by irreversible proteolytic modification. Reaction The following chemical reactions are catalyzed by xanthine oxidase: * hypoxanthine + H2O + O2 \rightleftharpoons xanthine + H2O2 * xanthine + H2O + O2 \rightleftharpoons uric acid + H2O2 * Xanthine o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Allopurinol
Allopurinol is a medication used to decrease high blood uric acid levels. It is specifically used to prevent gout, prevent specific types of kidney stones and for the high uric acid levels that can occur with chemotherapy. It is taken by mouth or injected into a vein. Common side effects when used by mouth include itchiness and rash. Common side effects when used by injection include vomiting and kidney problems. While not recommended historically, starting allopurinol during an attack of gout appears to be safe. In those already on the medication, it should be continued even during an acute gout attack. While use during pregnancy does not appear to result in harm, this use has not been well studied. Allopurinol is in the xanthine oxidase inhibitor family of medications. Allopurinol was approved for medical use in the United States in 1966. It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines. Allopurinol is available as a generic medication. In 2020, it was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Journal Of Natural Medicines
A journal, from the Old French ''journal'' (meaning "daily"), may refer to: *Bullet journal, a method of personal organization *Diary, a record of what happened over the course of a day or other period *Daybook, also known as a general journal, a daily record of financial transactions * Logbook, a record of events important to the operation of a vehicle, facility, or otherwise *Record (other) *Transaction log, a chronological record of data processing *Travel journal In publishing, ''journal'' can refer to various periodicals or serials: *Academic journal, an academic or scholarly periodical ** Scientific journal, an academic journal focusing on science ** Medical journal, an academic journal focusing on medicine **Law review, a professional journal focusing on legal interpretation * Magazine, non-academic or scholarly periodicals in general **Trade magazine, a magazine of interest to those of a particular profession or trade ** Literary magazine, a magazine devoted to li ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chemical & Pharmaceutical Bulletin
''Chemical and Pharmaceutical Bulletin'' is a monthly peer reviewed medical journal published by the Pharmaceutical Society of Japan. The journal was established in 1953 as the ''Pharmaceutical Bulletin''. From 1958 to 2011 it was known as the ''Chemical & Pharmaceutical Bulletin'', and as ''Chemical and Pharmaceutical Bulletin'' from 2012 onward. In 2012, the society re-organized its journals, and most material published in the '' Journal of Health Science'' now started to be published in the sister publication '' Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin'' and with some being published in ''Chemical and Pharmaceutical Bulletin''. The editor in chief is Yoshiji Takemoto (Kyoto University , mottoeng = Freedom of academic culture , established = , type = National university, Public (National) , endowment = ¥ 316 billion (2.4 1000000000 (number), billion USD) , faculty = 3,480 (Teaching Staff) , administrative_staff ...). Abstracting and indexing ''Chemical and Ph ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scientific Reports
''Scientific Reports'' is a peer-reviewed open-access scientific mega journal published by Nature Portfolio, covering all areas of the natural sciences. The journal was established in 2011. The journal states that their aim is to assess solely the scientific validity of a submitted paper, rather than its perceived importance, significance, or impact. In September 2016, the journal became the largest in the world by number of articles, overtaking '' PLOS ONE''. Abstracting and indexing The journal is abstracted and indexed in the Chemical Abstracts Service, the Science Citation Index Expanded, and selectively in Index Medicus/MEDLINE/PubMed. According to the ''Journal Citation Reports'', the journal has a 2021 impact factor 4.996. Reviewing policy The ''Guide to Referees'' states that to be published, "a paper must be scientifically valid and technically sound in methodology and analysis", and reviewers have to ensure manuscripts "are not assessed based on their perceived impor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Streptococcus Intermedius
''Streptococcus intermedius'' is an aerotolerant anaerobic commensal bacterium and a member of the ''Streptococcus anginosus'' group. The ''S. anginosus'' group, occasionally termed “''Streptococcus milleri'' group” (SMG) display hemolytic and serologic diversity, yet share core physiological traits. Despite being commensal organisms, members of the ''S. anginosus'' group display wide pathogenic potential. ''S. intermedius'' has been isolated from patients with periodontitis and fatal purulent infections, especially brain and liver abscesses.Claridge, J. E., III, S. Attorri, D. M. Musher, J. Hebert, and S. Dunbar. 2001. ''Streptococcus intermedius'', ''Streptococcus constellatus'', and Streptococcus ''anginosus'' (“''Streptococcus milleri'' group”) are of different clinical importance and are not equally associated with abscess. Clin. Infect. Dis. 32:1511–1515.Whiley, R. A., D. Beighton, T. G. Winstanley, H. Y. Fraser, and J. M. Hardie. 1992. ''Streptococcus intermedius ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Streptococcus Mutans
''Streptococcus mutans'' is a facultatively anaerobic, gram-positive coccus (round bacterium) commonly found in the human oral cavity and is a significant contributor to tooth decay. It is part of the " streptococci" (plural, non-italic lowercase), an informal general name for all species in the genus ''Streptococcus''. The microbe was first described by James Kilian Clarke in 1924. This bacterium, along with the closely related species ''Streptococcus sobrinus'', can cohabit the mouth: Both contribute to oral disease, and the expense of differentiating them in laboratory testing is often not clinically necessary. Therefore, for clinical purposes they are often considered together as a group, called the mutans streptococci (plural, non-italic due to its being an informal group name). This grouping of similar bacteria with similar tropism can also be seen in the viridans streptococci, another group of ''Streptococcus'' species. Ecology ''S. mutans'' is naturally present in the hu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Candida Albicans
''Candida albicans'' is an opportunistic pathogenic yeast that is a common member of the human gut flora. It can also survive outside the human body. It is detected in the gastrointestinal tract and mouth in 40–60% of healthy adults. It is usually a commensal organism, but it can become pathogenic in immunocompromised individuals under a variety of conditions. It is one of the few species of the genus '' Candida'' that causes the human infection candidiasis, which results from an overgrowth of the fungus. Candidiasis is, for example, often observed in HIV-infected patients. ''C. albicans'' is the most common fungal species isolated from biofilms either formed on (permanent) implanted medical devices or on human tissue. ''C. albicans'', ''C. tropicalis'', ''C. parapsilosis'', and ''C. glabrata'' are together responsible for 50–90% of all cases of candidiasis in humans. A mortality rate of 40% has been reported for patients with systemic candidiasis due to ''C. albicans''. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archives Of Oral Biology
''Archives of Oral Biology'' is a monthly peer-reviewed scientific journal covering oral and craniofacial research in all vertebrates, including work in palaeontology and comparative anatomy. It was established in 1959 and is published by Elsevier. The editors-in-chief are currently S. W. Cadden (University of Dundee) and F. T. Lundy (Queen's University Belfast). Abstracting and indexing The journal is abstracted and indexed in: According to the ''Journal Citation Reports'', the journal has a 2012 impact factor The impact factor (IF) or journal impact factor (JIF) of an academic journal is a scientometric index calculated by Clarivate that reflects the yearly mean number of citations of articles published in the last two years in a given journal, as i ... of 1.549. References {{Reflist External links Archives of Oral Biology Zoology journals Elsevier academic journals Monthly journals Publications established in 1959 English-language journals ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chavicol
Chavicol (''p''-allylphenol) is a natural phenylpropene, a type of organic compound. Its chemical structure consists of a benzene ring substituted with a hydroxy group and a propenyl group. It is a colorless liquid found together with terpenes in betel oil. Properties and reactions Chavicol is miscible with alcohol, ether, and chloroform. Dimerization of chavicol gives the neo-lignan magnolol. Uses Chavicol is used as an odorant in perfumery and as a flavor. It is found in many essential oils, including anise and Gardenia. Biosynthesis Chavicol is formed in sweet basil (''Ocimum Basilicum'') by the phenylpropanoid pathway via p-coumaryl alcohol. The allylic alcohol in p-coumaryl alcohol is converted into a leaving group. This then leaves thus forming a cation, this cation can be reagrded as a quinone methide which then is reduced by NADPH to form either anol or chavicol.Daniel G. Vassao, David R. Gang, Takao Koeduka, Brenda Jackson, Eran Pichersky, Laurence B. Davina and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |