|
Hydroperoxyl
The hydroperoxyl radical Radical may refer to: Politics and ideology Politics *Radical politics, the political intent of fundamental societal change *Radicalism (historical), the Radical Movement that began in late 18th century Britain and spread to continental Europe and ..., also known as the hydrogen superoxide, is the protonated form of superoxide with the chemical formula HO2. This species plays an important role in the atmosphere and as a reactive oxygen species in cell biology. Structure and reactions The molecule has a bent structure. The superoxide anion, , and the hydroperoxyl radical exist in chemical equilibrium, equilibrium in aqueous solution: : + H2O HO2 + OH− The Acid dissociation constant, p''K''a of HO2 is 4.88. Therefore, about 0.3% of any superoxide present in the cytosol of a typical cell is in the protonated form. It oxidizes nitric oxide to nitrogen dioxide: :NO + HO2 → NO2 + HO Reactive oxygen species in biology Together with its conjugat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Superoxide Anion
In chemistry, a superoxide is a compound that contains the superoxide ion, which has the chemical formula . The systematic name of the anion is dioxide(1−). The reactive oxygen ion superoxide is particularly important as the product of the one-electron reduction of dioxygen , which occurs widely in nature. Molecular oxygen (dioxygen) is a diradical containing two unpaired electrons, and superoxide results from the addition of an electron which fills one of the two degenerate molecular orbitals, leaving a charged ionic species with a single unpaired electron and a net negative charge of −1. Both dioxygen and the superoxide anion are free radicals that exhibit paramagnetism. Superoxide was historically also known as "hyperoxide". Salts Superoxide forms salts with alkali metals and alkaline earth metals. The salts caesium superoxide (), rubidium superoxide (), potassium superoxide (), and sodium superoxide () are prepared by the reaction of with the respective alkali me ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Superoxide
In chemistry, a superoxide is a compound that contains the superoxide ion, which has the chemical formula . The systematic name of the anion is dioxide(1−). The reactive oxygen ion superoxide is particularly important as the product of the one-electron reduction of dioxygen , which occurs widely in nature. Molecular oxygen (dioxygen) is a diradical containing two unpaired electrons, and superoxide results from the addition of an electron which fills one of the two degenerate molecular orbitals, leaving a charged ionic species with a single unpaired electron and a net negative charge of −1. Both dioxygen and the superoxide anion are free radicals that exhibit paramagnetism. Superoxide was historically also known as "hyperoxide". Salts Superoxide forms salts with alkali metals and alkaline earth metals. The salts caesium superoxide (), rubidium superoxide (), potassium superoxide (), and sodium superoxide () are prepared by the reaction of with the respective ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Free Radicals
In chemistry, a radical, also known as a free radical, is an atom, molecule, or ion that has at least one unpaired valence electron. With some exceptions, these unpaired electrons make radicals highly chemically reactive. Many radicals spontaneously dimerize. Most organic radicals have short lifetimes. A notable example of a radical is the hydroxyl radical (HO·), a molecule that has one unpaired electron on the oxygen atom. Two other examples are triplet oxygen and triplet carbene (꞉) which have two unpaired electrons. Radicals may be generated in a number of ways, but typical methods involve redox reactions. Ionizing radiation, heat, electrical discharges, and electrolysis are known to produce radicals. Radicals are intermediates in many chemical reactions, more so than is apparent from the balanced equations. Radicals are important in combustion, atmospheric chemistry, polymerization, plasma chemistry, biochemistry, and many other chemical processes. A majorit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nitric Oxide
Nitric oxide (nitrogen oxide or nitrogen monoxide) is a colorless gas with the formula . It is one of the principal oxides of nitrogen. Nitric oxide is a free radical: it has an unpaired electron, which is sometimes denoted by a dot in its chemical formula (•N=O or •NO). Nitric oxide is also a heteronuclear diatomic molecule, a class of molecules whose study spawned early modern theories of chemical bonding. An important intermediate in industrial chemistry, nitric oxide forms in combustion systems and can be generated by lightning in thunderstorms. In mammals, including humans, nitric oxide is a signaling molecule in many physiological and pathological processes. It was proclaimed the "Molecule of the Year" in 1992. The 1998 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine was awarded for discovering nitric oxide's role as a cardiovascular signalling molecule. Nitric oxide should not be confused with nitrogen dioxide (NO2), a brown gas and major air pollutant, or with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radical (chemistry)
In chemistry, a radical, also known as a free radical, is an atom, molecule, or ion that has at least one unpaired electron, unpaired valence electron. With some exceptions, these unpaired electrons make radicals highly chemical reaction, chemically reactive. Many radicals spontaneously dimer (chemistry), dimerize. Most organic radicals have short lifetimes. A notable example of a radical is the hydroxyl radical (HO·), a molecule that has one unpaired electron on the oxygen atom. Two other examples are triplet oxygen and methylene radical, triplet carbene (꞉) which have two unpaired electrons. Radicals may be generated in a number of ways, but typical methods involve redox reactions. Ionizing radiation, heat, electrical discharges, and electrolysis are known to produce radicals. Radicals are intermediates in many chemical reactions, more so than is apparent from the balanced equations. Radicals are important in combustion, atmospheric chemistry, polymerization, Plasma (ph ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lipid Peroxidation
Lipid peroxidation is the chain of reactions of oxidative degradation of lipids. It is the process in which free radicals "steal" electrons from the lipids in cell membranes, resulting in cell damage. This process proceeds by a free radical chain reaction mechanism. It most often affects polyunsaturated fatty acids, because they contain multiple double bonds in between which lie methylene bridges (-CH2-) that possess especially reactive hydrogen atoms. As with any radical reaction, the reaction consists of three major steps: initiation, propagation, and termination. The chemical products of this oxidation are known as lipid peroxides or lipid oxidation products (LOPs). Initiation Initiation is the step in which a fatty acid radical is produced. The most notable initiators in living cells are reactive oxygen species (ROS), such as OH· and HOO·, which combines with a hydrogen atom to make water and a fatty acid radical. Propagation The fatty acid radical is not a very sta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lipid Bilayer
The lipid bilayer (or phospholipid bilayer) is a thin polar membrane made of two layers of lipid molecules. These membranes are flat sheets that form a continuous barrier around all cells. The cell membranes of almost all organisms and many viruses are made of a lipid bilayer, as are the nuclear membrane surrounding the cell nucleus, and membranes of the membrane-bound organelles in the cell. The lipid bilayer is the barrier that keeps ions, proteins and other molecules where they are needed and prevents them from diffusing into areas where they should not be. Lipid bilayers are ideally suited to this role, even though they are only a few nanometers in width, because they are impermeable to most water-soluble ( hydrophilic) molecules. Bilayers are particularly impermeable to ions, which allows cells to regulate salt concentrations and pH by transporting ions across their membranes using proteins called ion pumps. Biological bilayers are usually composed of amphiphilic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydrogen Compounds
Hydrogen compounds are compounds containg the element hydrogen. In these compounds, hydrogen can form in the +1 and -1 oxidation states. Hydrogen can form compounds both ionically and in covalent substances. It is a part of many organic compounds such as hydrocarbons as well as water and other organic substances. The ion is often called a proton because it has one proton and no electrons, although the proton does not move freely. Brønsted–Lowry acids are capable of donating ions to bases. Covalent and organic compounds While is not very reactive under standard conditions, it does form compounds with most elements. Hydrogen can form compounds with elements that are more electronegative, such as halogens (F, Cl, Br, I), or oxygen; in these compounds hydrogen takes on a partial positive charge. When bonded to a more electronegative element, particularly fluorine, oxygen, or nitrogen, hydrogen can participate in a form of medium-strength noncovalent bonding with another el ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
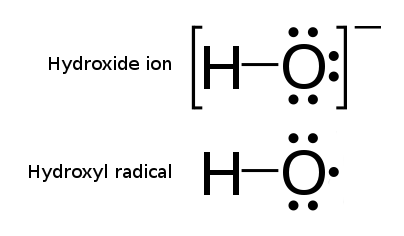
Hydroxyl Radical
The hydroxyl radical is the diatomic molecule . The hydroxyl radical is very stable as a dilute gas, but it decays very rapidly in the condensed phase. It is pervasive in some situations. Most notably the hydroxyl radicals are produced from the decomposition of hydroperoxides (ROOH) or, in atmospheric chemistry, by the reaction of excited atomic oxygen with water. It is also important in the field of radiation chemistry, since it leads to the formation of hydrogen peroxide and oxygen, which can enhance corrosion and SCC in coolant systems subjected to radioactive environments. In organic synthesis, hydroxyl radicals are most commonly generated by photolysis of 1-hydroxy-2(1''H'')-pyridinethione. Notation The unpaired electron of the hydroxyl radical is officially represented by a middle dot, •, beside the O. Biology Hydroxyl radicals can occasionally be produced as a byproduct of immune action. Macrophages and microglia most frequently generate this compound wh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydrocarbon
In organic chemistry, a hydrocarbon is an organic compound consisting entirely of hydrogen and carbon. Hydrocarbons are examples of group 14 hydrides. Hydrocarbons are generally colourless and hydrophobic, and their odors are usually weak or exemplified by the odors of gasoline and lighter fluid. They occur in a diverse range of molecular structures and phases: they can be gases (such as methane and propane), liquids (such as hexane and benzene), low melting solids (such as paraffin wax and naphthalene) or polymers (such as polyethylene and polystyrene). In the fossil fuel industries, ''hydrocarbon'' refers to the naturally occurring petroleum, natural gas and coal, and to their hydrocarbon derivatives and purified forms. Combustion of hydrocarbons is the main source of the world's energy. Petroleum is the dominant raw-material source for organic commodity chemicals such as solvents and polymers. Most anthropogenic (human-generated) emissions of greenhouse gases are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ozone
Ozone (), or trioxygen, is an inorganic molecule with the chemical formula . It is a pale blue gas with a distinctively pungent smell. It is an allotrope of oxygen that is much less stable than the diatomic allotrope , breaking down in the lower atmosphere to ( dioxygen). Ozone is formed from dioxygen by the action of ultraviolet (UV) light and electrical discharges within the Earth's atmosphere. It is present in very low concentrations throughout the latter, with its highest concentration high in the ozone layer of the stratosphere, which absorbs most of the Sun's ultraviolet (UV) radiation. Ozone's odour is reminiscent of chlorine, and detectable by many people at concentrations of as little as in air. Ozone's O3 structure was determined in 1865. The molecule was later proven to have a bent structure and to be weakly diamagnetic. In standard conditions, ozone is a pale blue gas that condenses at cryogenic temperatures to a dark blue liquid and finally a violet-black ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reactive Oxygen Species
In chemistry, reactive oxygen species (ROS) are highly reactive chemicals formed from diatomic oxygen (). Examples of ROS include peroxides, superoxide, hydroxyl radical, singlet oxygen, and alpha-oxygen. The reduction of molecular oxygen () produces superoxide (), which is the precursor to most other reactive oxygen species: :O2 + e^- -> \ ^\bullet O2- Dismutation of superoxide produces hydrogen peroxide (): :2 H+ + \ ^\bullet O2^- + \ ^\bullet O2^- -> H2O2 + O2 Hydrogen peroxide in turn may be partially reduced, thus forming hydroxide ions and hydroxyl radicals (), or fully reduced to water: :H2O2 + e^- -> HO^- + \ ^\bullet OH :2 H+ + 2 e- + H2O2 -> 2 H2O In a biological context, ROS are byproducts of the normal metabolism of oxygen. ROS have roles in cell signaling and homeostasis. ROS are intrinsic to cellular functioning, and are present at low and stationary levels in normal cells. In plants, ROS are involved in metabolic processes related to photoprotection a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |