|
Hydrogen Cycle
The hydrogen cycle consists of hydrogen exchanges between biotic (living) and abiotic (non-living) sources and sinks of hydrogen-containing compounds. Hydrogen (H) is the most abundant element in the universe. On Earth, common H-containing inorganic molecules include water (H2O), hydrogen gas (H2), hydrogen sulfide (H2S), and ammonia (NH3). Many organic compounds also contain H atoms, such as hydrocarbons and organic matter. Given the ubiquity of hydrogen atoms in inorganic and organic chemical compounds, the hydrogen cycle is focused on molecular hydrogen, H2. Hydrogen gas can be produced naturally through rock-water interactions or as a byproduct of microbial metabolisms. Free H2 can then be consumed by other microbes, oxidized photochemically in the atmosphere, or lost to space. Hydrogen is also thought to be an important reactant in pre-biotic chemistry and the early evolution of life on Earth, and potentially elsewhere in the Solar System. Abiotic cycles Sources Abiot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydrogen
Hydrogen is the chemical element with the symbol H and atomic number 1. Hydrogen is the lightest element. At standard conditions hydrogen is a gas of diatomic molecules having the formula . It is colorless, odorless, tasteless, non-toxic, and highly combustible. Hydrogen is the most abundant chemical substance in the universe, constituting roughly 75% of all normal matter.However, most of the universe's mass is not in the form of baryons or chemical elements. See dark matter and dark energy. Stars such as the Sun are mainly composed of hydrogen in the plasma state. Most of the hydrogen on Earth exists in molecular forms such as water and organic compounds. For the most common isotope of hydrogen (symbol 1H) each atom has one proton, one electron, and no neutrons. In the early universe, the formation of protons, the nuclei of hydrogen, occurred during the first second after the Big Bang. The emergence of neutral hydrogen atoms throughout the universe occurred about 370,000 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fischer–Tropsch Process
The Fischer–Tropsch process is a collection of chemical reactions that converts a mixture of carbon monoxide and hydrogen, known as syngas, into liquid hydrocarbons. These reactions occur in the presence of metal catalysts, typically at temperatures of and pressures of one to several tens of atmospheres. The process was first developed by Franz Fischer and Hans Tropsch at the Kaiser Wilhelm Institute for Coal Research in Mülheim an der Ruhr, Germany, in 1925. As a premier example of C1 chemistry, the Fischer–Tropsch process is an important reaction in both coal liquefaction and gas to liquids technology for producing liquid hydrocarbons. In the usual implementation, carbon monoxide and hydrogen, the feedstocks for FT, are produced from coal, natural gas, or biomass in a process known as gasification. The process then converts these gases into synthetic oil, synthetic lubrication oil and synthetic fuel. This process has received intermittent attention as a source of low-s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
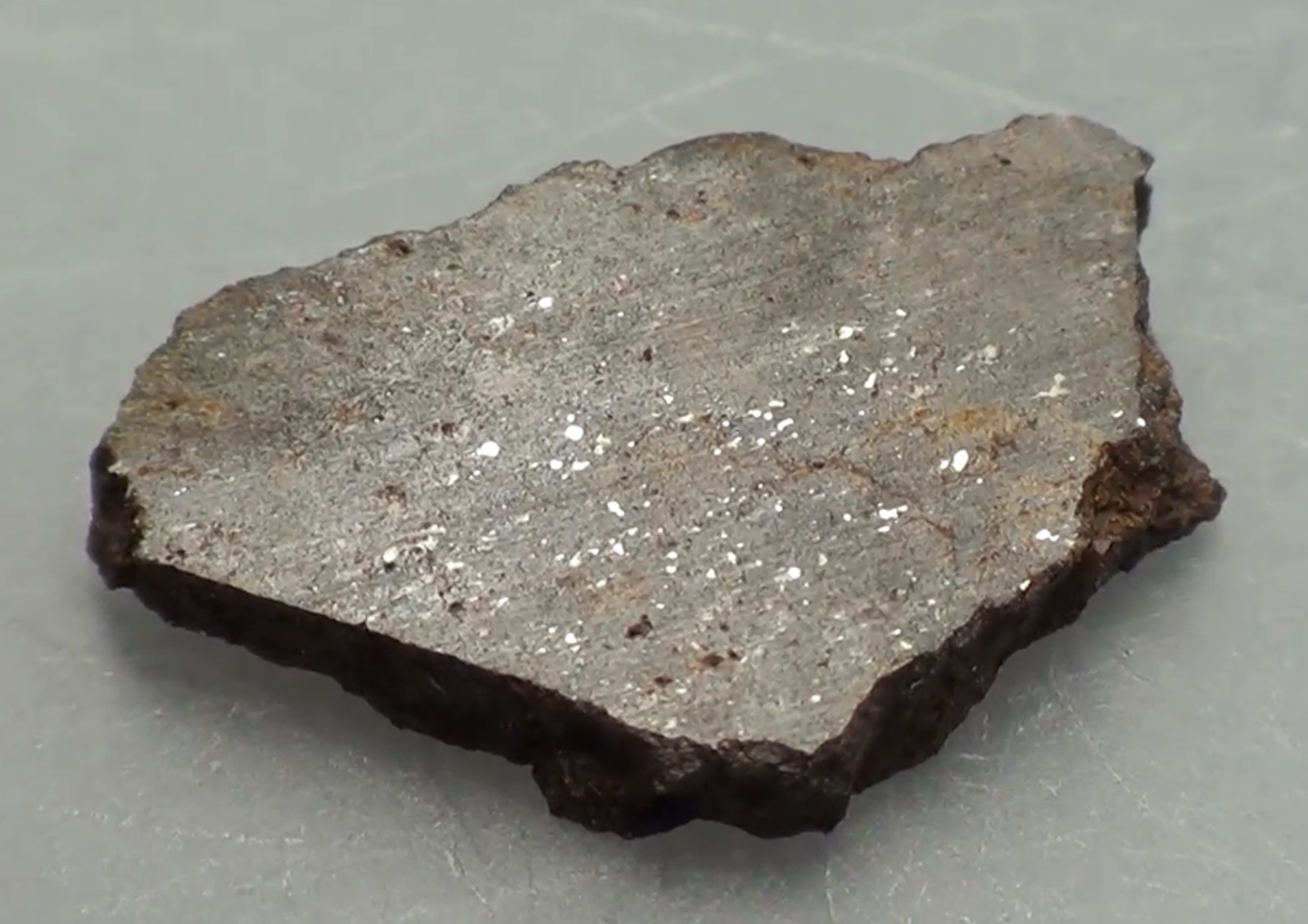
Chondrite
A chondrite is a stony (non-metallic) meteorite that has not been modified, by either melting or differentiation of the parent body. They are formed when various types of dust and small grains in the early Solar System accreted to form primitive asteroids. Some such bodies that are captured in the planet's gravity well become the most common type of meteorite by (whether quickly, or after many orbits) arriving on a trajectory toward the planet's surface. Estimates for their contribution to the total meteorite population vary between 85.7% and 86.2%. Their study provides important clues for understanding the origin and age of the Solar System, the synthesis of organic compounds, the origin of life and the presence of water on Earth. One of their characteristics is the presence of chondrules (from the Ancient Greek χόνδρος ''chondros'', grain), which are round grains formed as molten, or partially molten droplets, in the space by distinct minerals, that normally consti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Methanogenesis
Methanogenesis or biomethanation is the formation of methane coupled to energy conservation by microbes known as methanogens. Organisms capable of producing methane for energy conservation have been identified only from the domain Archaea, a group phylogenetically distinct from both eukaryotes and bacteria, although many live in close association with anaerobic bacteria. Other forms of methane production that are not coupled to ATP synthesis exist within all three domains of life. The production of methane is an important and widespread form of microbial metabolism. In anoxic environments, it is the final step in the decomposition of biomass. Methanogenesis is responsible for significant amounts of natural gas accumulations, the remainder being thermogenic. Biochemistry Methanogenesis in microbes is a form of anaerobic respiration. Methanogens do not use oxygen to respire; in fact, oxygen inhibits the growth of methanogens. The terminal electron acceptor in methanogenesis is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydrogenotroph
Hydrogenotrophs are organisms that are able to metabolize molecular hydrogen as a source of energy. An example of hydrogenotrophy is performed by carbon dioxide-reducing organismsStams, J.M., and Plugge, C.M. (2010) The microbiology of methanogenesis. ''In'' Reay, D., Smith, P., and Van Amstel, A., eds. ''Methane and Climate Change'', 14-26. which use CO2 and H2 to produce methane (CH4) by the following reaction: *CO2 + 4H2 → CH4 + 2H2O Other hydrogenotrophic metabolic pathways include acetogenesis, sulfate reduction, and other hydrogen oxidizing bacteria. Those that metabolize methane are called methanogenic. Hydrogenotrophs belong to a group of organisms known as methanogens, organisms that carry out anaerobic processes that are responsible for the production of methane through carbon dioxide reduction. Methanogens also include a group of organisms called methylotrophs, organisms that can use single-carbon molecules or molecules with no carbon-carbon bonds. Background In ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iron–sulfur World Hypothesis
The iron–sulfur world hypothesis is a set of proposals for the origin of life and the early evolution of life advanced in a series of articles between 1988 and 1992 by Günter Wächtershäuser, a Munich patent lawyer with a degree in chemistry, who had been encouraged and supported by philosopher Karl R. Popper to publish his ideas. The hypothesis proposes that early life may have formed on the surface of iron sulfide minerals, hence the name. It was developed by retrodiction (making a " prediction" about the past) from extant biochemistry (non-extinct, surviving biochemistry) in conjunction with chemical experiments. Origin of life Pioneer organism Wächtershäuser proposes that the earliest form of life, termed the "pioneer organism", originated in a volcanic hydrothermal flow at high pressure and high (100 °C) temperature. It had a composite structure of a mineral base with catalytic transition metal centers (predominantly iron and nickel, but also perhaps cobalt, manga ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Greenhouse Gas
A greenhouse gas (GHG or GhG) is a gas that Absorption (electromagnetic radiation), absorbs and Emission (electromagnetic radiation), emits radiant energy within the thermal infrared range, causing the greenhouse effect. The primary greenhouse gases in Atmosphere of Earth, Earth's atmosphere are water vapor (), carbon dioxide (), methane (), nitrous oxide (), and ozone (). Without greenhouse gases, the average temperature of Earth#Surface, Earth's surface would be about , rather than the present average of . The atmospheres of atmosphere of Venus, Venus, atmosphere of Mars, Mars and atmosphere of Titan, Titan also contain greenhouse gases. Human activities since the beginning of the Industrial Revolution (around 1750) have increased the Carbon dioxide in Earth's atmosphere, atmospheric concentration of carbon dioxide by over 50%, from 280 parts per million, ppm in 1750 to 421 ppm in 2022. The last time the atmospheric concentration of carbon dioxide was this high was over 3&nbs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Interspecies Hydrogen Transfer
Interspecies hydrogen transfer (IHT) is a form of interspecies electron transfer. It is a syntrophic process by which H2 is transferred from one organism to another, particularly in the rumen and other anaerobic environments. IHT was discovered between '' Methanobacterium bryantii'' strain M.o.H and an "S" organism in 1967 by Marvin Bryant, Eileen Wolin, Meyer Wolin, and Ralph Wolfe at the University of Illinois. The two form a culture that was mistaken as a species ''Methanobacillus omelianskii''. It was shown in 1973 that this process occurs between ''Ruminococcus albus'' and ''Wolinella succinogenes''. A more recent publication describes how the gene expression profiles of these organisms changes when they undergo interspecies hydrogen transfer; of note, a switch to an electron-confurcating hydrogenase occurs in ''R. albus'' 7. This process affects the carbon cycle: methanogen Methanogens are microorganisms that produce methane as a metabolic byproduct in hypoxic conditions. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Knallgas-bacteria
Hydrogen-oxidizing bacteria are a group of facultative Autotroph, autotrophs that can use hydrogen as an electron donor. They can be divided into Aerobic organism, aerobes and Anaerobic organism, anaerobes. The former use hydrogen as an electron donor and oxygen as an acceptor while the latter use sulphate or nitrogen dioxide as electron acceptors. Species of both types have been isolated from a variety of environments, including fresh waters, sediments, soils, activated sludge, hot springs, hydrothermal vents and percolating water. These bacteria are able to exploit the special properties of molecular hydrogen (for instance redox potential and diffusion coefficient) thanks to the presence of Hydrogenase, hydrogenases. The aerobic hydrogen-oxidizing bacteria are facultative autotrophs, but they can also have Mixotroph, mixotrophic or completely heterotrophic growth. Most of them show greater growth on organic substrates. The use of hydrogen as an electron donor coupled with the abili ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fermentative Hydrogen Production
Fermentative hydrogen production is the fermentative conversion of organic substrates to H2. Hydrogen produced in this manner is often called biohydrogen. The conversion is effected by bacteria and protozoa, which employ enzymes. Fermentative hydrogen production is one of several anaerobic conversions. Dark vs photofermentation Dark fermentation reactions do not require light energy. These are capable of constantly producing hydrogen from organic compounds throughout the day and night. Typically these reactions are coupled to the formation of carbon dioxide or formate. Important reactions that result in hydrogen production start with glucose, which is converted to acetic acid: :C6H12O6 + 2 H2O → 2 CH3CO2H + 2 CO2 + 4 H2 A related reaction gives formate instead of carbon dioxide: :C6H12O6 + 2 H2O → 2 CH3CO2H + 2 HCO2H + 2 H2 These reactions are exergonic by 216 and 209 kcal/mol, respectively. Using synthetic biology, bacteria can be genetically altered ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Domain (biology)
In biological taxonomy, a domain ( or ) (Latin: ''regio''), also dominion, superkingdom, realm, or empire, is the highest taxonomic rank of all organisms taken together. It was introduced in the three-domain system of taxonomy devised by Carl Woese, Otto Kandler and Mark Wheelis in 1990. According to the domain system, the tree of life consists of either three domains such as Archaea, Bacteria, and Eukarya, or two domains consisting of Archaea and Bacteria, with Eukarya included in Archaea. The first two are all prokaryotes, single-celled microorganisms without a membrane-bound nucleus. All organisms that have a cell nucleus and other membrane-bound organelles are included in Eukarya. Non-cellular life is not included in this system. Alternatives to the three-domain system include the earlier two-empire system (with the empires Prokaryota and Eukaryota), and the eocyte hypothesis (with two domains of Bacteria and Archaea, with Eukarya included as a branch of Archaea). Term ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nitrogenase
Nitrogenases are enzymes () that are produced by certain bacteria, such as cyanobacteria (blue-green bacteria) and rhizobacteria. These enzymes are responsible for the Organic redox reaction, reduction of nitrogen (N2) to ammonia (NH3). Nitrogenases are the only family of enzymes known to catalyze this reaction, which is a key step in the process of nitrogen fixation. Nitrogen fixation is required for all forms of life, with nitrogen being essential for the biosynthesis of molecules (nucleotides, amino acids) that create plants, animals and other organisms. They are encoded by the Nif genes or Homologous chromosome, homologs. They are related to protochlorophyllide reductase. Classification and structure Although the equilibrium formation of ammonia from molecular hydrogen and nitrogen has an overall negative enthalpy of reaction ( \Delta H^ = -45.2 \ \mathrm \, \mathrm \; \mathrm ), the activation energy is very high ( E_\mathrm = 230-420 \ \mathrm \, \mathrm ). Nitrogenase a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |