|
Hundred-year Wave
A hundred-year wave is a statistically projected water wave, the height of which, on average, is met or exceeded once in a hundred years for a given location. The likelihood of this wave height being attained at least once in the hundred-year period is 63%. As a projection of the most extreme wave which can be expected to occur in a given body of water, the hundred-year wave is a factor commonly taken into consideration by designers of oil platforms and other offshore structures. Ch. 4. Periods of time other than a hundred years may also be taken into account, resulting in, for instance, a fifty-year wave. Various methods are employed to predict the possible steepness and period of these waves, in addition to their height. See also *Index of wave articles *Significant wave height *Shallow water equations *Rogue wave Rogue waves (also known as freak waves, monster waves, episodic waves, killer waves, extreme waves, and abnormal waves) are unusually large, unpredictable, and su ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Statistics
Statistics (from German language, German: ''wikt:Statistik#German, Statistik'', "description of a State (polity), state, a country") is the discipline that concerns the collection, organization, analysis, interpretation, and presentation of data. In applying statistics to a scientific, industrial, or social problem, it is conventional to begin with a statistical population or a statistical model to be studied. Populations can be diverse groups of people or objects such as "all people living in a country" or "every atom composing a crystal". Statistics deals with every aspect of data, including the planning of data collection in terms of the design of statistical survey, surveys and experimental design, experiments.Dodge, Y. (2006) ''The Oxford Dictionary of Statistical Terms'', Oxford University Press. When census data cannot be collected, statisticians collect data by developing specific experiment designs and survey sample (statistics), samples. Representative sampling as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ocean Surface Wave
In fluid dynamics, a wind wave, water wave, or wind-generated water wave, is a surface wave that occurs on the free surface of bodies of water as a result from the wind blowing over the water surface. The contact distance in the direction of the wind is known as the ''fetch''. Waves in the oceans can travel thousands of kilometers before reaching land. Wind waves on Earth range in size from small ripples, to waves over high, being limited by wind speed, duration, fetch, and water depth. When directly generated and affected by local wind, a wind wave system is called a wind sea. Wind waves will travel in a great circle route after being generated – curving slightly left in the southern hemisphere and slightly right in the northern hemisphere. After moving out of the area of fetch, wind waves are called '' swells'' and can travel thousands of kilometers. A noteworthy example of this is waves generated south of Tasmania during heavy winds that will travel across the Pacif ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
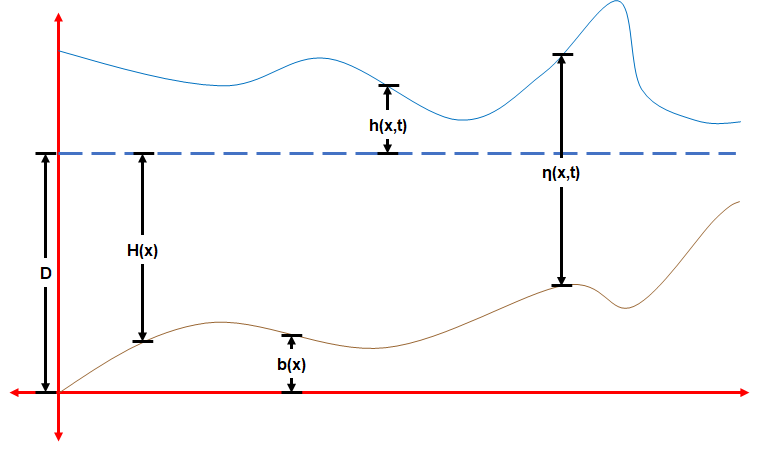
Wave Height
In fluid dynamics, the wave height of a surface wave is the difference between the elevations of a crest and a neighboring trough. ''Wave height'' is a term used by mariners, as well as in coastal, ocean and naval engineering. At sea, the term ''significant wave height'' is used as a means to introduce a well-defined and standardized statistic to denote the characteristic height of the random waves in a ''sea state'', including wind sea and swell. It is defined in such a way that it more or less corresponds to what a mariner observes when estimating visually the average wave height. Definitions Depending on context, wave height may be defined in different ways: *For a sine wave, the wave height ''H'' is twice the amplitude (i.e., the '' peak-to-peak amplitude''): H = 2a. *For a periodic wave, it is simply the difference between the maximum and minimum of the surface elevation : H = \max\left\ - \min\left\, with ''c''p the phase speed (or propagation speed) of the wave. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oil Platform
An oil platform (or oil rig, offshore platform, oil production platform, and similar terms) is a large structure with facilities to extract and process petroleum and natural gas that lie in rock formations beneath the seabed. Many oil platforms will also have facilities to accommodate the workers, although it is also common to have a separate accommodation platform bridge linked to the production platform. Most commonly, oil platforms engage in activities on the continental shelf, though they can also be used in lakes, inshore waters, and inland seas. Depending on the circumstances, the platform may be fixed Platform, fixed to the ocean floor, consist of an artificial island, or floating oil production system, float. In some arrangements the main facility may have storage facilities for the processed oil. Remote subsea wells may also be connected to a platform by flow lines and by umbilical cable, umbilical connections. These sub-sea facilities may include of one or more subsea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Index Of Wave Articles
This is a list of Wave topics. 0–9 *21 cm line A *Abbe prism *Absorption spectroscopy *Absorption spectrum *Absorption wavemeter *Acoustic wave *Acoustic wave equation *Acoustics *Acousto-optic effect *Acousto-optic modulator *Acousto-optics *Airy disc *Airy wave theory *Alfvén wave *Alpha waves *Amphidromic point *Amplitude *Amplitude modulation *Animal echolocation *Antarctic Circumpolar Wave * Antiphase *Aquamarine Power *Arrayed waveguide grating *Artificial wave *Atmospheric diffraction *Atmospheric wave *Atmospheric waveguide *Atom laser *Atomic clock *Atomic mirror *Audience wave *Autowave *Averaged Lagrangian B *Babinet's principle *Backward wave oscillator *Bandwidth-limited pulse *beat *Berry phase *Bessel beam *Beta wave *Black hole *Blazar *Bloch's theorem *Blueshift *Boussinesq approximation (water waves) *Bow wave *Bragg diffraction *Bragg's law *Breaking wave *Bremsstrahlung, Electromagnetic radiation *Brillouin scattering *Bullet bow shockwave *Burgers' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Significant Wave Height
In physical oceanography, the significant wave height (SWH, HTSGW or ''H''s) is defined traditionally as the mean ''wave height'' (trough to crest) of the highest third of the waves (''H''1/3). Nowadays it is usually defined as four times the standard deviation of the surface elevation – or equivalently as four times the square root of the zeroth-order moment (area) of the ''wave spectrum''. The symbol ''H''m0 is usually used for that latter definition. The significant wave height (Hs) may thus refer to ''H''m0 or ''H''1/3; the difference in magnitude between the two definitions is only a few percent. SWH is used to characterize ''sea state'', including winds and swell. Origin and definition The original definition resulted from work by the oceanographer Walter Munk during World War II. The significant wave height was intended to mathematically express the height estimated by a "trained observer". It is commonly used as a measure of the height of ocean waves. Time domain def ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shallow Water Equations
The shallow-water equations (SWE) are a set of hyperbolic partial differential equations (or parabolic if viscous shear is considered) that describe the flow below a pressure surface in a fluid (sometimes, but not necessarily, a free surface). The shallow-water equations in unidirectional form are also called Saint-Venant equations, after Adhémar Jean Claude Barré de Saint-Venant (see the related section below). The equations are derived from depth-integrating the Navier–Stokes equations, in the case where the horizontal length scale is much greater than the vertical length scale. Under this condition, conservation of mass implies that the vertical velocity scale of the fluid is small compared to the horizontal velocity scale. It can be shown from the momentum equation that vertical pressure gradients are nearly hydrostatic, and that horizontal pressure gradients are due to the displacement of the pressure surface, implying that the horizontal velocity field is consta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rogue Wave
Rogue waves (also known as freak waves, monster waves, episodic waves, killer waves, extreme waves, and abnormal waves) are unusually large, unpredictable, and suddenly appearing surface waves that can be extremely dangerous to ships, even to large ones. They are distinct from tsunamis, which are often almost unnoticeable in deep waters and are caused by the displacement of water due to other phenomena (such as earthquakes). A rogue wave appearing at the shore is sometimes referred to as a sneaker wave. In oceanography, rogue waves are more precisely defined as waves whose height is more than twice the significant wave height (''H'' or SWH), which is itself defined as the mean of the largest third of waves in a wave record. Therefore, rogue waves are not necessarily the biggest waves found on the water; they are, rather, unusually large waves for a given sea state. Rogue waves seem not to have a single distinct cause, but occur where physical factors such as high winds and strong ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Physical Oceanography
Physical oceanography is the study of physical conditions and physical processes within the ocean, especially the motions and physical properties of ocean waters. Physical oceanography is one of several sub-domains into which oceanography is divided. Others include biological, chemical and geological oceanography. Physical oceanography may be subdivided into ''descriptive'' and ''dynamical'' physical oceanography. Descriptive physical oceanography seeks to research the ocean through observations and complex numerical models, which describe the fluid motions as precisely as possible. Dynamical physical oceanography focuses primarily upon the processes that govern the motion of fluids with emphasis upon theoretical research and numerical models. These are part of the large field of Geophysical Fluid Dynamics (GFD) that is shared together with meteorology. GFD is a sub field of Fluid dynamics describing flows occurring on spatial and temporal scales that are greatly influenced ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)