|
Homozygotes
Zygosity (the noun, zygote, is from the Greek "yoked," from "yoke") () is the degree to which both copies of a chromosome or gene have the same genetic sequence. In other words, it is the degree of similarity of the alleles in an organism. Most eukaryotes have two matching sets of chromosomes; that is, they are diploid. Diploid organisms have the same loci on each of their two sets of homologous chromosomes except that the sequences at these loci may differ between the two chromosomes in a matching pair and that a few chromosomes may be mismatched as part of a chromosomal sex-determination system. If both alleles of a diploid organism are the same, the organism is homozygous at that locus. If they are different, the organism is heterozygous at that locus. If one allele is missing, it is hemizygous, and, if both alleles are missing, it is nullizygous. The DNA sequence of a gene often varies from one individual to another. These gene variants are called alleles. While some gen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dominance (genetics)
In genetics, dominance is the phenomenon of one variant (allele) of a gene on a chromosome masking or overriding the effect of a different variant of the same gene on the other copy of the chromosome. The first variant is termed dominant and the second recessive. This state of having two different variants of the same gene on each chromosome is originally caused by a mutation in one of the genes, either new (''de novo'') or inherited. The terms autosomal dominant or autosomal recessive are used to describe gene variants on non-sex chromosomes ( autosomes) and their associated traits, while those on sex chromosomes (allosomes) are termed X-linked dominant, X-linked recessive or Y-linked; these have an inheritance and presentation pattern that depends on the sex of both the parent and the child (see Sex linkage). Since there is only one copy of the Y chromosome, Y-linked traits cannot be dominant or recessive. Additionally, there are other forms of dominance such as incomplete d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dominant Allele
In genetics, dominance is the phenomenon of one variant (allele) of a gene on a chromosome masking or overriding the effect of a different variant of the same gene on the other copy of the chromosome. The first variant is termed dominant and the second recessive. This state of having two different variants of the same gene on each chromosome is originally caused by a mutation in one of the genes, either new (''de novo'') or inherited. The terms autosomal dominant or autosomal recessive are used to describe gene variants on non-sex chromosomes ( autosomes) and their associated traits, while those on sex chromosomes (allosomes) are termed X-linked dominant, X-linked recessive or Y-linked; these have an inheritance and presentation pattern that depends on the sex of both the parent and the child (see Sex linkage). Since there is only one copy of the Y chromosome, Y-linked traits cannot be dominant or recessive. Additionally, there are other forms of dominance such as incomplete d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heterozygote Advantage
A heterozygote advantage describes the case in which the heterozygous genotype has a higher relative fitness (biology), fitness than either the homozygous Dominance (genetics), dominant or homozygous recessive gene, recessive genotype. Loci exhibiting heterozygote advantage are a small minority of loci. The specific case of heterozygote advantage due to a single locus (genetics), locus is known as overdominance. Overdominance is a rare condition in genetics where the phenotype of the heterozygote lies outside of the phenotypical range of both homozygote parents, and heterozygous individuals have a higher fitness (biology), fitness than homozygous individuals. Polymorphism (biology), Polymorphism can be maintained by Natural selection, selection favoring the heterozygote, and this mechanism is used to explain the occurrence of some kinds of genetic variation, genetic variability. A common example is the case where the heterozygote conveys both advantages and disadvantages, while bo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Loss-of-function Mutation
In biology, a mutation is an alteration in the nucleic acid sequence of the genome of an organism, virus, or extrachromosomal DNA. Viral genomes contain either DNA or RNA. Mutations result from errors during DNA or viral replication, mitosis, or meiosis or other types of damage to DNA (such as pyrimidine dimers caused by exposure to ultraviolet radiation), which then may undergo error-prone repair (especially microhomology-mediated end joining), cause an error during other forms of repair, or cause an error during replication (translesion synthesis). Mutations may also result from insertion or deletion of segments of DNA due to mobile genetic elements. Mutations may or may not produce detectable changes in the observable characteristics (phenotype) of an organism. Mutations play a part in both normal and abnormal biological processes including: evolution, cancer, and the development of the immune system, including junctional diversity. Mutation is the ultimate source of a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alleles
An allele (, ; ; modern formation from Greek ἄλλος ''állos'', "other") is a variation of the same sequence of nucleotides at the same place on a long DNA molecule, as described in leading textbooks on genetics and evolution. ::"The chromosomal or genomic location of a gene or any other genetic element is called a locus (plural: loci) and alternative DNA sequences at a locus are called alleles." The simplest alleles are single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNP). but they can also be insertions and deletions of up to several thousand base pairs. Popular definitions of 'allele' typically refer only to different alleles within genes. For example, the ABO blood grouping is controlled by the ABO gene, which has six common alleles (variants). In population genetics, nearly every living human's phenotype for the ABO gene is some combination of just these six alleles. Most alleles observed result in little or no change in the function of the gene product it codes for. However, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Allele
An allele (, ; ; modern formation from Greek ἄλλος ''állos'', "other") is a variation of the same sequence of nucleotides at the same place on a long DNA molecule, as described in leading textbooks on genetics and evolution. ::"The chromosomal or genomic location of a gene or any other genetic element is called a locus (plural: loci) and alternative DNA sequences at a locus are called alleles." The simplest alleles are single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNP). but they can also be insertions and deletions of up to several thousand base pairs. Popular definitions of 'allele' typically refer only to different alleles within genes. For example, the ABO blood grouping is controlled by the ABO gene, which has six common alleles (variants). In population genetics, nearly every living human's phenotype for the ABO gene is some combination of just these six alleles. Most alleles observed result in little or no change in the function of the gene product it codes for. However, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genotype
The genotype of an organism is its complete set of genetic material. Genotype can also be used to refer to the alleles or variants an individual carries in a particular gene or genetic location. The number of alleles an individual can have in a specific gene depends on the number of copies of each chromosome found in that species, also referred to as ploidy. In diploid species like humans, two full sets of chromosomes are present, meaning each individual has two alleles for any given gene. If both alleles are the same, the genotype is referred to as homozygous. If the alleles are different, the genotype is referred to as heterozygous. Genotype contributes to phenotype, the observable traits and characteristics in an individual or organism. The degree to which genotype affects phenotype depends on the trait. For example, the petal color in a pea plant is exclusively determined by genotype. The petals can be purple or white depending on the alleles present in the pea plant. Howev ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transgenic Maize
Genetically modified maize (corn) is a genetically modified crop. Specific maize strains have been genetically engineered to express agriculturally-desirable traits, including resistance to pests and to herbicides. Maize strains with both traits are now in use in multiple countries. GM maize has also caused controversy with respect to possible health effects, impact on other insects and impact on other plants via gene flow. One strain, called Starlink, was approved only for animal feed in the US but was found in food, leading to a series of recalls starting in 2000. Marketed products Herbicide-resistant maize Corn varieties resistant to glyphosate herbicides were first commercialized in 1996 by Monsanto, and are known as "Roundup Ready Corn". They tolerate the use of Roundup. Bayer CropScience developed "Liberty Link Corn" that is resistant to glufosinate. Pioneer Hi-Bred has developed and markets corn hybrids with tolerance to imidazoline herbicides under the trademark ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ploidy
Ploidy () is the number of complete sets of chromosomes in a cell (biology), cell, and hence the number of possible alleles for Autosome, autosomal and Pseudoautosomal region, pseudoautosomal genes. Sets of chromosomes refer to the number of maternal and paternal chromosome copies, respectively, in each homologous chromosome pair, which chromosomes naturally exist as. Somatic cells, Tissue (biology), tissues, and Individual#Biology, individual organisms can be described according to the number of sets of chromosomes present (the "ploidy level"): monoploid (1 set), diploid (2 sets), triploid (3 sets), tetraploid (4 sets), pentaploid (5 sets), hexaploid (6 sets), heptaploid or septaploid (7 sets), etc. The generic term polyploidy, polyploid is often used to describe cells with three or more chromosome sets. Virtually all sexual reproduction, sexually reproducing organisms are made up of somatic cells that are diploid or greater, but ploidy level may vary widely between different or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
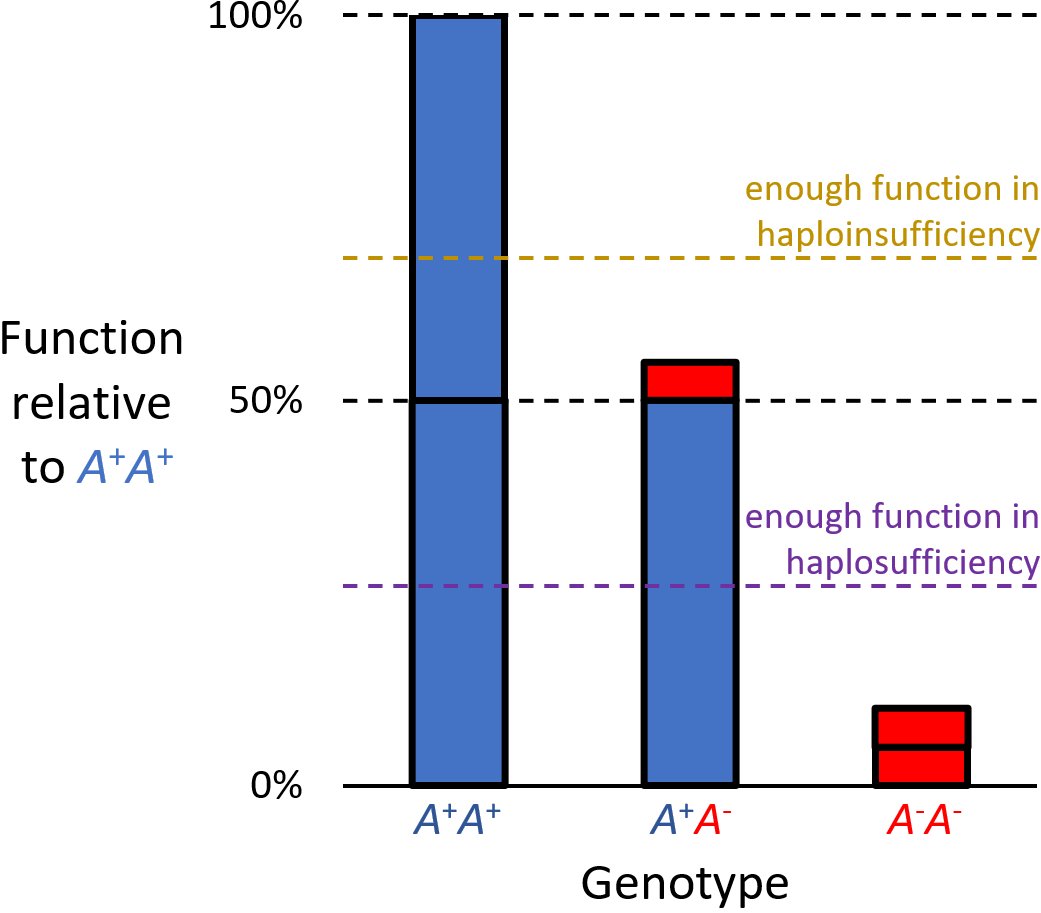
Haploinsufficiency
Haploinsufficiency in genetics describes a model of dominant gene action in diploid organisms, in which a single copy of the wild-type allele at a locus in heterozygous combination with a variant allele is insufficient to produce the wild-type phenotype. Haploinsufficiency may arise from a ''de novo'' or inherited loss-of-function mutation in the variant allele, such that it yields little or no gene product (often a protein). Although the other, standard allele still produces the standard amount of product, the total product is insufficient to produce the standard phenotype. This heterozygous genotype may result in a non- or sub-standard, deleterious, and (or) disease phenotype. Haploinsufficiency is the standard explanation for dominant deleterious alleles. In the alternative case of haplosufficiency, the loss-of-function allele behaves as above, but the single standard allele in the heterozygous genotype produces sufficient gene product to produce the same, standard phenotype ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heterogametic Sex
Heterogametic sex (digametic sex) refers to the individuals of a species in which the sex chromosomes are not the same. For example, in humans, males with an X and a Y sex chromosome would be referred to as the heterogametic sex, and females having two X sex chromosomes would be referred to as the homogametic sex. This arrangement is known as the XY sex-determination system. However, in birds and some reptiles, males have two Z sex chromosomes and so are the homogametic sex, while females, with one Z and one W chromosome, are the heterogametic sex. Platypus males are heterogametic while females are homogametic. Among the insects, Lepidopterans (butterflies and moths) have heterogametic females, but in ''Drosophila'', males are the heterogametic sex. This arrangement is known as the ZW sex-determination system. Heterogamesis can lead to reduced or absent meiotic recombination between the sex chromosomes, and in some species, this extends to the autosomes, a phenomenon called ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
X Chromosome
The X chromosome is one of the two sex-determining chromosomes (allosomes) in many organisms, including mammals (the other is the Y chromosome), and is found in both males and females. It is a part of the XY sex-determination system and XO sex-determination system. The X chromosome was named for its unique properties by early researchers, which resulted in the naming of its counterpart Y chromosome, for the next letter in the alphabet, following its subsequent discovery. Discovery It was first noted that the X chromosome was special in 1890 by Hermann Henking in Leipzig. Henking was studying the testicles of ''Pyrrhocoris'' and noticed that one chromosome did not take part in meiosis. Chromosomes are so named because of their ability to take up staining (''chroma'' in Greek means ''color''). Although the X chromosome could be stained just as well as the others, Henking was unsure whether it was a different class of object and consequently named it ''X element'', which later be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

_(14582377398).jpg)