|
Home Directory
A home directory is a file system directory on a multi-user operating system containing files for a given user of the system. The specifics of the home directory (such as its name and location) are defined by the operating system involved; for example, Linux / BSD ( FHS) systems use /home/ and Windows systems between 2000 and Server 2003 keep home directories in a folder named Documents and Settings. Description A user's home directory is intended to contain that user's files; including text documents, music, pictures, videos, etc. It may also include their configuration files of preferred settings for any software they have used there and might have tailored to their liking: web browser bookmarks, favorite desktop wallpaper and themes, stored passwords to any external services accessed via a given software, etc. The user can install executable software in this directory, but it will only be available to users with permission to execute files in this directory. The home direc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Directory (file Systems)
Directory may refer to: * Directory (computing), or folder, a file system structure in which to store computer files * Directory (OpenVMS command) * Directory service, a software application for organizing information about a computer network's users and resources * Directory (political), a system under which a country is ruled by a college of several people who jointly exercise the powers of a head of state or head of government ** French Directory, the government in revolutionary France from 1795 to 1799 * Business directory, a listing of information about suppliers and manufacturers * Telephone directory, a book which allows telephone numbers to be found given the subscriber's name * Web directory, an organized collection of links to websites See also * Director (other) * Directorate (other) Directorate may refer to: Contemporary *Directorates of the Scottish Government * Directorate-General, a type of specialised administrative body in the European Union ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
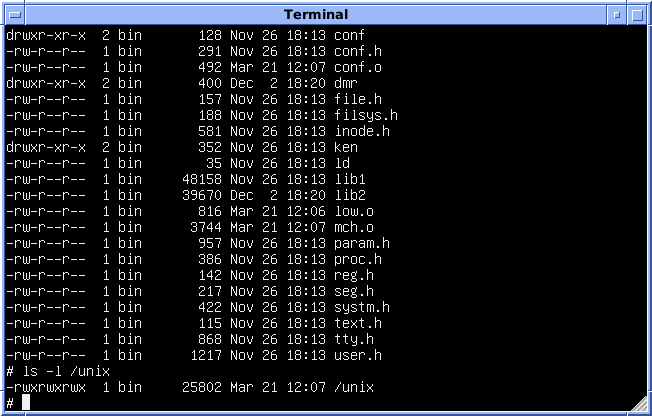
File-system Permissions
Most file systems include attributes of files and directories that control the ability of users to read, change, navigate, and execute the contents of the file system. In some cases, menu options or functions may be made visible or hidden depending on a user's permission level; this kind of user interface is referred to as permission-driven. Two types of permissions are widely available: traditional Unix file system permissions and access-control lists (ACLs) which are capable of more specific control. File system variations The original File Allocation Table file system has a per-file all-user read-only attribute. NTFS implemented in Microsoft Windows NT and its derivatives, use ACLs to provide a complex set of permissions. OpenVMS uses a permission scheme similar to that of Unix. There are four categories (system, owner, group, and world) and four types of access permissions (Read, Write, Execute and Delete). The categories are not mutually disjoint: World includes Group, w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MacOS
macOS (; previously OS X and originally Mac OS X) is a Unix operating system developed and marketed by Apple Inc. since 2001. It is the primary operating system for Apple's Mac computers. Within the market of desktop and laptop computers it is the second most widely used desktop OS, after Microsoft Windows and ahead of ChromeOS. macOS succeeded the classic Mac OS, a Mac operating system with nine releases from 1984 to 1999. During this time, Apple cofounder Steve Jobs had left Apple and started another company, NeXT, developing the NeXTSTEP platform that would later be acquired by Apple to form the basis of macOS. The first desktop version, Mac OS X 10.0, was released in March 2001, with its first update, 10.1, arriving later that year. All releases from Mac OS X 10.5 Leopard and after are UNIX 03 certified, with an exception for OS X 10.7 Lion. Apple's other operating systems (iOS, iPadOS, watchOS, tvOS, audioOS) are derivatives of macOS. A promi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Solaris (operating System)
Solaris is a proprietary Unix operating system originally developed by Sun Microsystems. After the Sun acquisition by Oracle in 2010, it was renamed Oracle Solaris. Solaris superseded the company's earlier SunOS in 1993, and became known for its scalability, especially on SPARC systems, and for originating many innovative features such as DTrace, ZFS and Time Slider. Solaris supports SPARC and x86-64 workstations and servers from Oracle and other vendors. Solaris was registered as compliant with the Single UNIX Specification until 29 April 2019. Historically, Solaris was developed as proprietary software. In June 2005, Sun Microsystems released most of the codebase under the CDDL license, and founded the OpenSolaris open-source project. With OpenSolaris, Sun wanted to build a developer and user community around the software. After the acquisition of Sun Microsystems in January 2010, Oracle decided to discontinue the OpenSolaris distribution and the development model. In Aug ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SunOS
SunOS is a Unix-branded operating system developed by Sun Microsystems for their workstation and server computer systems. The ''SunOS'' name is usually only used to refer to versions 1.0 to 4.1.4, which were based on BSD, while versions 5.0 and later are based on UNIX System V Release 4, and are marketed under the brand name ''Solaris''. History SunOS 1 only supported the Sun-2 series systems, including Sun-1 systems upgraded with Sun-2 (68010) CPU boards. SunOS 2 supported Sun-2 and Sun-3 (68020) series systems. SunOS 4 supported Sun-2 (until release 4.0.3), Sun-3 (until 4.1.1), Sun386i (4.0, 4.0.1 and 4.0.2 only) and Sun-4 (SPARC) architectures. Although SunOS 4 was intended to be the first release to fully support Sun's new SPARC processor, there was also a SunOS 3.2 release with preliminary support for Sun-4 systems. SunOS 4.1.2 introduced support for Sun's first sun4m-architecture multiprocessor machines (the SPARCserver 600MP series); since it ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
$HOME
An environment variable is a dynamic-named value that can affect the way running processes will behave on a computer. They are part of the environment in which a process runs. For example, a running process can query the value of the TEMP environment variable to discover a suitable location to store temporary files, or the HOME or USERPROFILE variable to find the directory structure owned by the user running the process. They were introduced in their modern form in 1979 with Version 7 Unix, so are included in all Unix operating system flavors and variants from that point onward including Linux and macOS. From PC DOS 2.0 in 1982, all succeeding Microsoft operating systems, including Microsoft Windows, and OS/2 also have included them as a feature, although with somewhat different syntax, usage and standard variable names. Design In all Unix and Unix-like systems, as well as on Windows, each process has its own separate set of environment variables. By default, when a p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ancient UNIX
Ancient UNIX is any early release of the Unix code base prior to Unix System III, particularly the Research Unix releases prior to and including Version 7 (the base for UNIX/32V as well as later developments of AT&T Unix). After the publication of the Lions' book, work was undertaken to release earlier versions of the codebase. SCO first released the code under a limited educational license. Later, in January 2002, Caldera International (now SCO Group) relicensed (but has not made available) several versions under the four-clause BSD license, namely: *Research Unix: (early versions only) ** Version 1 Unix ** Version 2 Unix ** Version 3 Unix ** Version 4 Unix ** Version 5 Unix ** Version 6 Unix ** Version 7 Unix *** UNIX/32V , there has been no widespread use of the code, but it can be used on emulator systems, and ''Version 5 Unix'' runs on the Nintendo Game Boy Advance using the SIMH PDP-11 emulator. ''Version 6 Unix'' provides the basis for the MIT xv6 teaching system, whi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Environment Variable
An environment variable is a dynamic-named value that can affect the way running processes will behave on a computer. They are part of the environment in which a process runs. For example, a running process can query the value of the TEMP environment variable to discover a suitable location to store temporary files, or the HOME or USERPROFILE variable to find the directory structure owned by the user running the process. They were introduced in their modern form in 1979 with Version 7 Unix, so are included in all Unix operating system flavors and variants from that point onward including Linux and macOS. From PC DOS 2.0 in 1982, all succeeding Microsoft operating systems, including Microsoft Windows, and OS/2 also have included them as a feature, although with somewhat different syntax, usage and standard variable names. Design In all Unix and Unix-like systems, as well as on Windows, each process has its own separate set of environment variables. By default, when a p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Path (computing)
A path is a string of characters used to uniquely identify a location in a directory structure. It is composed by following the directory tree hierarchy in which components, separated by a delimiting character, represent each directory. The delimiting character is most commonly the slash ("/"), the backslash character ("\"), or colon (":"), though some operating systems may use a different delimiter. Paths are used extensively in computer science to represent the directory/file relationships common in modern operating systems and are essential in the construction of Uniform Resource Locators (URLs). Resources can be represented by either ''absolute'' or ''relative'' paths. History Multics first introduced a hierarchical file system with directories (separated by ">") in the mid-1960s. Around 1970, Unix introduced the slash character ("/") as its directory separator. In 1981, the first version of Microsoft DOS was released. MS-DOS 1.0 did not support file directories. Also, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Operating System
An operating system (OS) is system software that manages computer hardware, software resources, and provides common services for computer programs. Time-sharing operating systems schedule tasks for efficient use of the system and may also include accounting software for cost allocation of processor time, mass storage, printing, and other resources. For hardware functions such as input and output and memory allocation, the operating system acts as an intermediary between programs and the computer hardware, although the application code is usually executed directly by the hardware and frequently makes system calls to an OS function or is interrupted by it. Operating systems are found on many devices that contain a computer from cellular phones and video game consoles to web servers and supercomputers. The dominant general-purpose personal computer operating system is Microsoft Windows with a market share of around 74.99%. macOS by Apple Inc. is in second place (14.84%), and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
System File
A system file in computers is a critical computer file without which a computer system may not operate correctly. These files may come as part of the operating system, a third-party device driver or other sources. Microsoft Windows and MS-DOS mark their more valuable system files with a "system" attribute to protect them against accidental deletion. (Although the system attribute can be manually put on any arbitrary file; these files do not become system files.) Specific example of system files include the files with .sys filename extension in MS-DOS. In Windows NT family, the system files are mainly under the folder C:\Windows\System32. In Mac OS they are in the '' System suitcase''. And in Linux system the system files are located under folders /boot (the kernel Kernel may refer to: Computing * Kernel (operating system), the central component of most operating systems * Kernel (image processing), a matrix used for image convolution * Compute kernel, in GPGPU programming * Ke ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
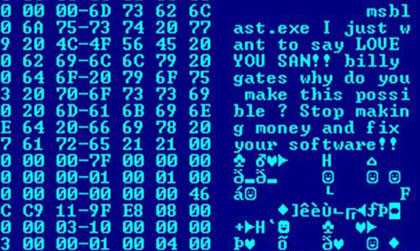
Computer Worm
A computer worm is a standalone malware computer program that replicates itself in order to spread to other computers. It often uses a computer network to spread itself, relying on security failures on the target computer to access it. It will use this machine as a host to scan and infect other computers. When these new worm-invaded computers are controlled, the worm will continue to scan and infect other computers using these computers as hosts, and this behaviour will continue. Computer worms use recursive methods to copy themselves without host programs and distribute themselves based on the law of exponential growth, thus controlling and infecting more and more computers in a short time. Worms almost always cause at least some harm to the network, even if only by consuming bandwidth, whereas viruses almost always corrupt or modify files on a targeted computer. Many worms are designed only to spread, and do not attempt to change the systems they pass through. However, as th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |