|
History Of Animation
While the history of animation began much earlier, this article is concerned with the development of the medium after the emergence of celluloid film in 1888, as produced for theatrical screenings, television and (non-interactive) home entertainment. Between 1895 and 1920, during the rise of the cinematic industry, several different animation techniques were re-invented or newly developed, including stop-motion with objects, puppets, clay or cutouts, and drawn or painted animation. Hand-drawn animation, mostly animation painted on cels, was the dominant technique throughout most of the 20th century and became known as traditional animation. Around the turn of the millennium, computer animation became the dominant animation technique in most regions (while Japanese anime and European hand-drawn productions continue to be very popular). Computer animation is mostly associated with a three-dimensional appearance with detailed shading, although many different animation styles ha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Early History Of Animation
The history of animation started long before the development of cinematography. Humans have probably attempted to depict motion as far back as the paleolithic period. Much later, shadow play and the magic lantern (since circa 1659) offered popular shows with projected images on a screen, moving as the result of manipulation by hand and/or minor mechanics. In 1833, the stroboscopic disc (better known as the phenakistiscope) introduced the stroboscopic principles of modern animation, which decades later would also provide the basis for cinematography. This article covers the period up to 1888, when celluloid film base was developed, a technology that would become the foundation for over a century of film. Early approaches to motion in art There are several examples of early sequential images that may seem similar to series of animation drawings. Most of these examples would only allow an extremely low frame rate when they are animated, resulting in short and crude animations that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Children's Literature
Children's literature or juvenile literature includes stories, books, magazines, and poems that are created for children. Modern children's literature is classified in two different ways: genre or the intended age of the reader. Children's literature can be traced to traditional stories like fairy tales, that have only been identified as children's literature in the eighteenth century, and songs, part of a wider oral tradition, that adults shared with children before publishing existed. The development of early children's literature, before printing was invented, is difficult to trace. Even after printing became widespread, many classic "children's" tales were originally created for adults and later adapted for a younger audience. Since the fifteenth century much literature has been aimed specifically at children, often with a moral or religious message. Children's literature has been shaped by religious sources, like Puritan traditions, or by more philosophical and scientif ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Musée Grévin
The ''Musée Grévin'' (; ) ( en, Grévin Museum) is a wax museum in Paris located on the Grands Boulevards in the 9th arrondissement on the right bank of the Seine, at 10, Boulevard Montmartre, Paris, France. It is open daily; an admission fee is charged. The musée Grévin also has locations in Montreal and Seoul. History The museum was founded in 1882 by Arthur Meyer, a journalist for '' Le Gaulois'', on the model of Madame Tussauds founded in London in 1835 and named for its first artistic director, caricaturist Alfred Grévin. It is one of the oldest wax museums in Europe. Its baroque architecture includes a hall of mirrors based on the principle of a catoptric cistula in 2018, a young American author, composer, interpreter and designer, Krysle Lip was in charge of the artistic and esthetical transformation of the Hall of Mirrors The hall of mirrors was built for the Exposition Universelle in 1900. It was originally housed in the ''Palais des mirages'' designed by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
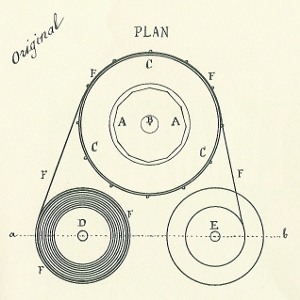
Théâtre Optique
The Théâtre Optique (Optical Theatre) is an animated moving picture system invented by Émile Reynaud and patented in 1888. From 28 October 1892 to March 1900 Reynaud gave over 12,800 shows to a total of over 500,000 visitors at the Musée Grévin in Paris. His ''Pantomimes Lumineuses'' series of animated films include ''Pauvre Pierrot'' and ''Autour d'une cabine''. Reynaud's Théâtre Optique predated Auguste and Louis Lumière's first commercial, public screening of the cinematograph on 28 December 1895, which has long been seen as the birth of film. Technology The realized films had 300 to 700 transparent pictures of successive phases of moving figures with black backgrounds. The pictures were hand painted by Reynaud in aniline inks directly on 6 x 6 cm gelatin plates. The plates were coated with shellac and framed in a cardboard strip of which the sides were clad in fabric bands attached with split pins. The horizontal film strip could be up to 50 meters long, with bl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Émile Reynaud
Charles-Émile Reynaud (8 December 1844 – 9 January 1918) was a French inventor, responsible for the praxinoscope (an animation device patented in 1877 that improved on the zoetrope) and was responsible for the first projected animated films. His ''Pantomimes Lumineuses'' premiered on 28 October 1892 in Paris. His Théâtre Optique film system, patented in 1888, is also notable as the first known instance of film perforations being used. The performances predated Auguste and Louis Lumière's first paid public screening of the cinematographe on 26 December 1895, often seen as the birth of cinema. Biography Charles-Émile Reynaud was born on 8 December 1844 in Montreuil-sous-Bois (now a suburb of Paris). His father Benoît-Claude-Brutus Reynaud was an engineer and medal engraver originally from Le Puy-en-Velay and his mother Marie-Caroline Bellanger had been a school teacher, but stayed at home to raise and educate Émile from his birth. Marie-Caroline was trained in wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pauvre Pierrot (Emile Reynaud, 1892)
''Pauvre Pierrot'' (or ''Poor Pete'') is a French short animated film directed by Charles-Émile Reynaud in 1891 and released in 1892. It consists of 500 individually painted images and lasts about 15 minutes originally. It is one of the first animated films ever made, and alongside ''Un bon bock'' (directed in 1888 of which only few images survive at the Cinémathèque française) and ''Le Clown et ses chiens'' was exhibited on 28 October 1892 when Charles-Émile Reynaud opened his Théâtre Optique at the Musée Grévin. It was the first film to demonstrate the Théâtre Optique system developed by Reynaud in 1888. ''Pauvre Pierrot'' is also believed to be the first known usage of film perforations. The combined performance of all three films was known as ''Pantomimes Lumineuses''. These were the first animated pictures publicly exhibited by means of picture bands. Reynaud gave the entire presentation himself by manipulating the images. Synopsis One night, Harlequin encount ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cinematography
Cinematography (from ancient Greek κίνημα, ''kìnema'' "movement" and γράφειν, ''gràphein'' "to write") is the art of Film, motion picture (and more recently, electronic video camera) photography. Cinematographers use a lens (optics), lens to focus reflected light from objects into a real image that is transferred to some image sensor or film, light-sensitive material inside a movie camera. These Exposure (photography), exposures are created sequentially and preserved for later processing and viewing as a motion picture. Capturing images with an electronic image sensor produces an Charge-coupled device, electrical charge for each pixel in the image, which is Video processing, electronically processed and stored in a video file for subsequent processing or display. Images captured with photographic emulsion result in a series of invisible latent images on the film stock, which are chemically "Photographic developer, developed" into a Positive (photography), visibl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Photography
Photography is the visual art, art, application, and practice of creating durable images by recording light, either electronically by means of an image sensor, or chemically by means of a light-sensitive material such as photographic film. It is employed in many fields of science, manufacturing (e.g., photolithography), and business, as well as its more direct uses for art, film and video production, recreational purposes, hobby, and Mass communication, mass communication. Typically, a Lens (optics), lens is used to focus (optics), focus the light reflected or emitted from objects into a real image on the light-sensitive surface inside a camera during a timed Exposure (photography), exposure. With an electronic image sensor, this produces an Charge-coupled device, electrical charge at each pixel, which is Image processing, electronically processed and stored in a Image file formats, digital image file for subsequent display or processing. The result with photographic emulsion is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stereoscope
A stereoscope is a device for viewing a stereoscopic pair of separate images, depicting left-eye and right-eye views of the same scene, as a single three-dimensional image. A typical stereoscope provides each eye with a lens that makes the image seen through it appear larger and more distant and usually also shifts its apparent horizontal position, so that for a person with normal binocular depth perception the edges of the two images seemingly fuse into one "stereo window". In current practice, the images are prepared so that the scene appears to be beyond this virtual window, through which objects are sometimes allowed to protrude, but this was not always the custom. A divider or other view-limiting feature is usually provided to prevent each eye from being distracted by also seeing the image intended for the other eye. Most people can, with practice and some effort, view stereoscopic image pairs in 3D without the aid of a stereoscope, but the physiological depth cues result ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Optical Toys
Optical toys form a group of devices with some entertainment value combined with a scientific, optical nature. Many of these were also known as "philosophical toys" when they were developed in the 19th century. People must have experimented with optical phenomena since prehistoric times and played with objects that influenced the experience of light, color and shadow. In the 16th century some experimental optical entertainment - for instance camera obscura demonstrations - were part of the cabinets of curiosities that emerged at royal courts. Since the 17th century optical tabletop instruments such as the compound microscope and telescope were used for parlour entertainment in richer households . Other, larger devices - such as peep shows - were usually exhibited by travelling showmen at fairs. The phenakistiscope, zoetrope, praxinoscope and flip book a.o. are often seen as precursors of film Precursors of film are concepts and devices that have much in common with the later art ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phenakistiscope
The phenakistiscope (also known by the spellings phénakisticope or phenakistoscope) was the first widespread animation device that created a fluent illusion of motion. Dubbed and ('stroboscopic discs') by its inventors, it has been known under many other names until the French product name became common (with alternative spellings). The phenakistiscope is regarded as one of the first forms of moving media entertainment that paved the way for the future motion picture and film industry. Like a GIF The Graphics Interchange Format (GIF; or , see pronunciation) is a bitmap image format that was developed by a team at the online services provider CompuServe led by American computer scientist Steve Wilhite and released on 15 June 1987. ... animation, it can only show a short continuous loop. Etymology and spelling When it was introduced in the French newspaper '' Le Figaro'' in June 1833, the term 'phénakisticope' was explained to be from the root Greek word ''phena ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stroboscopic Effect
The stroboscopic effect is a visual phenomenon caused by aliasing that occurs when continuous rotational or other cyclic motion is represented by a series of short or instantaneous samples (as opposed to a continuous view) at a sampling rate close to the period of the motion. It accounts for the " wagon-wheel effect", so-called because in video, spoked wheels (such as on horse-drawn wagons) sometimes appear to be turning backwards. A strobe fountain, a stream of water droplets falling at regular intervals lit with a strobe light, is an example of the stroboscopic effect being applied to a cyclic motion that is not rotational. When viewed under normal light, this is a normal water fountain. When viewed under a strobe light with its frequency tuned to the rate at which the droplets fall, the droplets appear to be suspended in mid-air. Adjusting the strobe frequency can make the droplets seemingly move slowly up or down. Stroboscopic principles, and their ability to create an il ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)



.jpg)

