|
Hexamethyldisiloxane
Hexamethyldisiloxane (HMDSO) is an organosilicon compound with the formula O i(CH3)3sub>2. This volatile colourless liquid is used as a solvent and as a reagent in organic synthesis. It is prepared by the hydrolysis of trimethylsilyl chloride. The molecule is the protypical disiloxane and resembles a subunit of polydimethylsiloxane. Synthesis and reactions Hexamethyldisiloxane can be produced by addition of trimethylsilyl chloride to purified water: : 2 Me3SiCl + H2O → 2 HCl + O i(CH3)3sub>2 It also results from the hydrolysis of silylethers and other silyl-protected functional groups. HMDSO can be converted back to the chloride by reaction with Me2SiCl2.Röshe, L.; John, P.; Reitmeier, R. “Organic Silicon Compounds” ''Ullmann’s Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry''. John Wiley and Sons: San Francisco, 2003. . Hexamethyldisiloxane is mainly used as source of the trimethylsilyl functional group (-Si(CH3)3) in organic synthesis. For example, in the presence of acid c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Disiloxane
Disiloxane has the chemical formula . It is the simplest known siloxane with hydrogen only R groups. The molecule contains six equivalent Si-H bonds and two equivalent Si-O bonds. Disiloxane exists as a colorless, pungent gas under standard conditions. However, it is generally safe for human use as evidence in its widespread use in cosmetics. It is also commonly known as disilyl ether, disilyl oxide, and perhydrodisiloxane Structure Disiloxane has a simple structure that consists of a siloxane bond (Si–O–Si) and hydrogen R groups. The structure of disiloxane has been studied by a variety of spectroscopic methods such as electron diffraction, X-ray crystallography, dipole moment, and nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Due to their unusual nature, the Si–O–Si bond angles are commonly studied. These bonds typically exhibit angles that are larger than average, around 130 to 160 degrees, and larger bond lengths are not uncommon. For example, in the solid state at a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
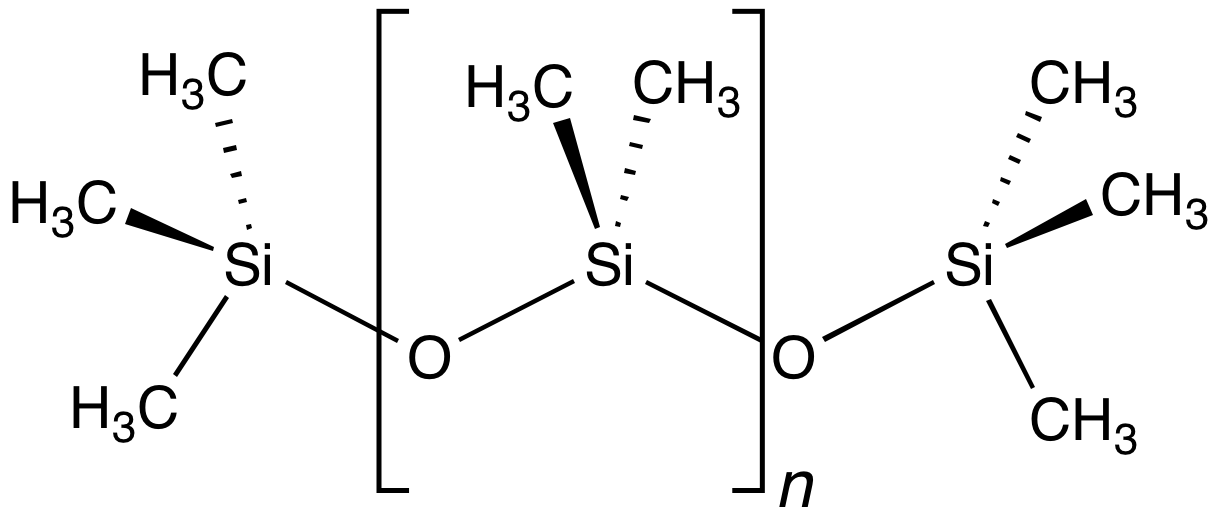
Siloxanes
A siloxane is a functional group in organosilicon chemistry with the Si−O−Si linkage. The parent siloxanes include the oligomeric and polymeric hydrides with the formulae H(OSiH2)''n''OH and (OSiH2)n. Siloxanes also include branched compounds, the defining feature of which is that each pair of silicon centres is separated by one oxygen (O2-) atom. The siloxane functional group forms the backbone of silicones, the premier example of which is polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS). The functional group R3SiO− (where the three Rs may be different) is called siloxy. Siloxanes are manmade and have many commercial and industrial applications because of the compounds’ hydrophobicity, low thermal conductivity, and high flexibility. Structure Siloxanes generally adopt structures expected for linked tetrahedral ("''sp''3-like") centers. The Si−O bond length is 1.64 Å (vs Si–C distance of 1.92 Å) and the Silicon–oxygen bond#Bond angles, Si-O-Si angle is rather open at ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |