|
Hexagonal Truncated Trapezohedron
In geometry, the truncated hexagonal trapezohedron is the fourth in an infinite series of truncated trapezohedra. It has 12 pentagon and 2 hexagon faces. It can be constructed by taking a hexagonal trapezohedron and Truncation (geometry), truncating the polar axis vertices. Weaire–Phelan structure The Weaire–Phelan structure contains another form of this polyhedron that has ''D''''2d'' symmetry and is a part of a honeycomb (geometry), space-filling honeycomb along with an irregular dodecahedron. See also * Goldberg polyhedron External links Wearie-Phelan Bubbles Try: "t6dA6". Polyhedra {{Polyhedron-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Truncated Trapezohedron
In geometry, an truncated trapezohedron is a polyhedron formed by a trapezohedron with Pyramid (geometry), pyramids Truncation (geometry), truncated from its two polar axis Vertex (geometry), vertices. The vertices exist as 4 in four parallel planes, with alternating orientation in the middle creating the pentagons. The regular dodecahedron is the most common polyhedron in this class, being a Platonic solid, with 12 Congruence (geometry), congruent pentagonal faces. A truncated trapezohedron has all vertices with 3 faces. This means that the dual polyhedra, the set of gyroelongated dipyramids, have all triangular faces. For example, the icosahedron is the dual of the dodecahedron. Forms *Triangular truncated trapezohedron (Dürer's solid) – 6 pentagons, 2 triangles, dual gyroelongated triangular dipyramid *Truncated square trapezohedron – 8 pentagons, 2 squares, dual gyroelongated square dipyramid *''Truncated pentagonal trapezohedron'' or regular dodecahedron – 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Truncation (geometry)
In geometry, a truncation is an operation in any dimension that cuts polytope vertices, creating a new Facet (geometry), facet in place of each vertex. The term originates from Kepler's names for the Archimedean solids. Uniform truncation In general any polyhedron (or polytope) can also be truncated with a degree of freedom as to how deep the cut is, as shown in Conway polyhedron notation truncation operation. A special kind of truncation, usually implied, is a uniform truncation, a truncation operator applied to a regular polyhedron (or regular polytope) which creates a resulting uniform polyhedron (uniform polytope) with equal edge lengths. There are no degrees of freedom, and it represents a fixed geometric, just like the regular polyhedra. In general all single ringed uniform polytopes have a uniform truncation. For example, the icosidodecahedron, represented as Schläfli symbols r or \begin 5 \\ 3 \end, and Coxeter-Dynkin diagram or has a uniform truncation, the truncate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
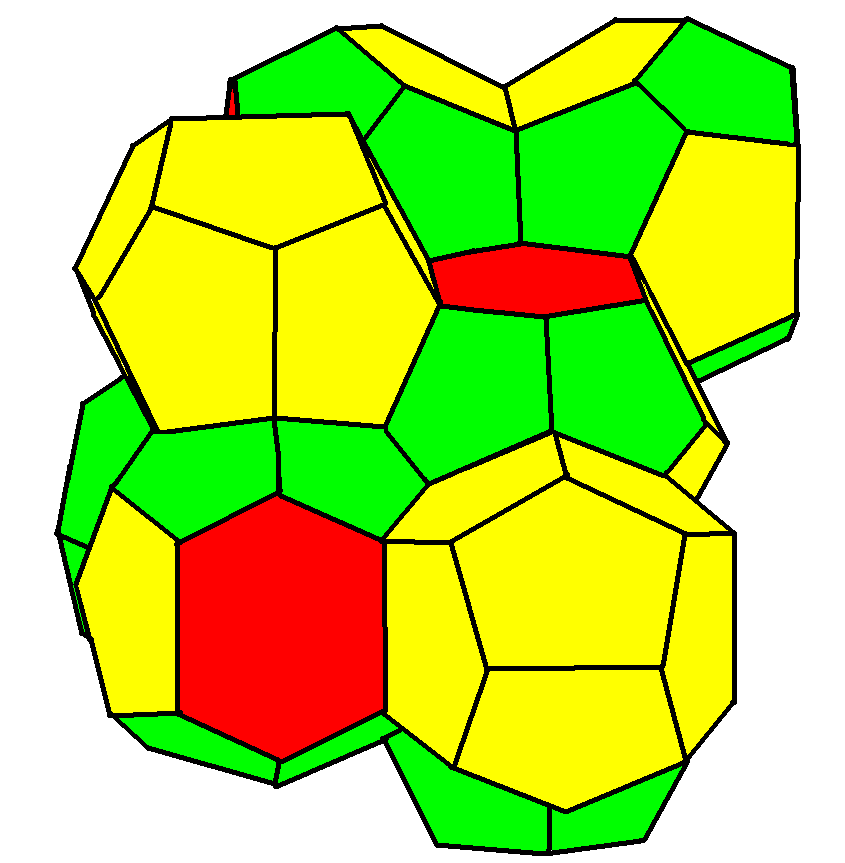
12-14-hedral Honeycomb
1 (one, unit, unity) is a number, numeral, and glyph. It is the first and smallest positive integer of the infinite sequence of natural numbers. This fundamental property has led to its unique uses in other fields, ranging from science to sports, where it commonly denotes the first, leading, or top thing in a group. 1 is the unit of counting or measurement, a determiner for singular nouns, and a gender-neutral pronoun. Historically, the representation of 1 evolved from ancient Sumerian and Babylonian symbols to the modern Arabic numeral. In mathematics, 1 is the multiplicative identity, meaning that any number multiplied by 1 equals the same number. 1 is by convention not considered a prime number. In digital technology, 1 represents the "on" state in binary code, the foundation of computing. Philosophically, 1 symbolizes the ultimate reality or source of existence in various traditions. In mathematics The number 1 is the first natural number after 0. Each natural number, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Tetradecahedron
240px, A tetradecahedron with D2d-symmetry, existing in the Weaire–Phelan structure A tetradecahedron is a polyhedron with 14 faces. There are numerous topologically distinct forms of a tetradecahedron, with many constructible entirely with regular polygon faces. A tetradecahedron is sometimes called a tetrakaidecahedron. No difference in meaning is ascribed. The Greek word '' kai'' means 'and'. There is evidence that mammalian epidermal cells are shaped like flattened tetrakaidecahedra, an idea first suggested by Lord Kelvin. The polyhedron can also be found in soap bubbles and in sintered ceramics, due to its ability to tesselate in 3D space. Convex There are 1,496,225,352 topologically distinct ''convex'' tetradecahedra, excluding mirror images, having at least 9 vertices. (Two polyhedra are "topologically distinct" if they have intrinsically different arrangements of faces and vertices, such that it is impossible to distort one into the other simply by changing the l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Space-filling Tetrakaidecahedron
{{disambiguation ...
Space filling or spacefilling may refer to: *Space-filling curve *Space-filling model, in chemistry *Space-filling polyhedron *Space-filling tree *Space-filling bubble in a foam Foams are two-phase materials science, material systems where a gas is dispersed in a second, non-gaseous material, specifically, in which gas cells are enclosed by a distinct liquid or solid material. Note, this source focuses only on liquid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Dodecahedron
In geometry, a dodecahedron (; ) or duodecahedron is any polyhedron with twelve flat faces. The most familiar dodecahedron is the regular dodecahedron with regular pentagons as faces, which is a Platonic solid. There are also three Kepler–Poinsot polyhedron, regular star dodecahedra, which are constructed as stellations of the convex form. All of these have icosahedral symmetry, order 120. Some dodecahedra have the same combinatorial structure as the regular dodecahedron (in terms of the graph formed by its vertices and edges), but their pentagonal faces are not regular: The #Pyritohedron, pyritohedron, a common crystal form in pyrite, has pyritohedral symmetry, while the #Tetartoid, tetartoid has tetrahedral symmetry. The rhombic dodecahedron can be seen as a limiting case of the pyritohedron, and it has octahedral symmetry. The elongated dodecahedron and trapezo-rhombic dodecahedron variations, along with the rhombic dodecahedra, are space-filling polyhedra, space-filling. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Honeycomb (geometry)
In geometry, a honeycomb is a ''space filling'' or ''close packing'' of polyhedron, polyhedral or higher-dimensional ''cells'', so that there are no gaps. It is an example of the more general mathematical ''tiling'' or ''tessellation'' in any number of dimensions. Its dimension can be clarified as ''n''-honeycomb for a honeycomb of ''n''-dimensional space. Honeycombs are usually constructed in ordinary Euclidean geometry, Euclidean ("flat") space. They may also be constructed in non-Euclidean geometry, non-Euclidean spaces, such as #Hyperbolic honeycombs, hyperbolic honeycombs. Any finite uniform polytope can be projected to its circumsphere to form a uniform honeycomb in spherical space. Classification There are infinitely many honeycombs, which have only been partially classified. The more regular ones have attracted the most interest, while a rich and varied assortment of others continue to be discovered. The simplest honeycombs to build are formed from stacked layers or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Weaire–Phelan Structure
In geometry, the Weaire–Phelan structure is a three-dimensional structure representing an idealised foam of equal-sized bubbles, with two different shapes. In 1993, Denis Weaire and Robert Phelan found that this structure was a better solution of the Kelvin problem of tiling space by equal volume cells of minimum surface area than the previous best-known solution, the Kelvin structure. History and the Kelvin problem In two dimensions, the subdivision of the plane into cells of equal area with minimum average perimeter is given by the hexagonal tiling, but although the first record of this honeycomb conjecture goes back to the ancient Roman scholar Marcus Terentius Varro (116-27 BCE), it was not proven until the work of Thomas C. Hales in 1999. In 1887, Lord Kelvin asked the corresponding question for three-dimensional space: how can space be partitioned into cells of equal volume with the least area of surface between them? Or, in short, what was the most efficient soap bubbl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Hexagonal Trapezohedron
In geometry, a hexagonal trapezohedron or deltohedron is the fourth in an infinite series of trapezohedra which are dual polyhedra to the antiprisms. It has twelve faces which are congruence (geometry), congruent kite (geometry), kites. It can be described by the Conway polyhedron notation, Conway notation] It is an isohedral (face-transitive) figure, meaning that all its face (geometry), faces are the same. More specifically, all faces are not merely congruent but also ''transitive'', i.e. lie within the same ''symmetry orbit''. Convex polytope, Convex isohedral polyhedra are the shapes that will make fair dice. Symmetry The symmetry group, symmetry a hexagonal trapezohedron is D6d of order 24. The Point groups in three dimensions#Rotation groups, rotation group is D6 of order 12. Variations One degree of freedom within D6 symmetry changes the kites into congruent quadrilaterals with 3 edges lengths. In the limit, one edge of each quadrilateral goes to zero length, and these ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Pentagon
In geometry, a pentagon () is any five-sided polygon or 5-gon. The sum of the internal angles in a simple polygon, simple pentagon is 540°. A pentagon may be simple or list of self-intersecting polygons, self-intersecting. A self-intersecting ''regular pentagon'' (or ''star polygon, star pentagon'') is called a pentagram. Regular pentagons A ''regular polygon, regular pentagon'' has Schläfli symbol and interior angles of 108°. A ''regular polygon, regular pentagon'' has five lines of reflectional symmetry, and rotational symmetry of order 5 (through 72°, 144°, 216° and 288°). The diagonals of a convex polygon, convex regular pentagon are in the golden ratio to its sides. Given its side length t, its height H (distance from one side to the opposite vertex), width W (distance between two farthest separated points, which equals the diagonal length D) and circumradius R are given by: :\begin H &= \frac~t \approx 1.539~t, \\ W= D &= \frac~t\approx 1.618~t, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Truncated Trapezohedra
In geometry, an truncated trapezohedron is a polyhedron formed by a trapezohedron with Pyramid (geometry), pyramids Truncation (geometry), truncated from its two polar axis Vertex (geometry), vertices. The vertices exist as 4 in four parallel planes, with alternating orientation in the middle creating the pentagons. The regular dodecahedron is the most common polyhedron in this class, being a Platonic solid, with 12 Congruence (geometry), congruent pentagonal faces. A truncated trapezohedron has all vertices with 3 faces. This means that the dual polyhedra, the set of gyroelongated dipyramids, have all triangular faces. For example, the icosahedron is the dual of the dodecahedron. Forms *Triangular truncated trapezohedron (Dürer's solid) – 6 pentagons, 2 triangles, dual gyroelongated triangular dipyramid *Truncated square trapezohedron – 8 pentagons, 2 squares, dual gyroelongated square dipyramid *''Truncated pentagonal trapezohedron'' or regular dodecahedron – 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Geometry
Geometry (; ) is a branch of mathematics concerned with properties of space such as the distance, shape, size, and relative position of figures. Geometry is, along with arithmetic, one of the oldest branches of mathematics. A mathematician who works in the field of geometry is called a ''List of geometers, geometer''. Until the 19th century, geometry was almost exclusively devoted to Euclidean geometry, which includes the notions of point (geometry), point, line (geometry), line, plane (geometry), plane, distance, angle, surface (mathematics), surface, and curve, as fundamental concepts. Originally developed to model the physical world, geometry has applications in almost all sciences, and also in art, architecture, and other activities that are related to graphics. Geometry also has applications in areas of mathematics that are apparently unrelated. For example, methods of algebraic geometry are fundamental in Wiles's proof of Fermat's Last Theorem, Wiles's proof of Fermat's ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |