|
Hellburner
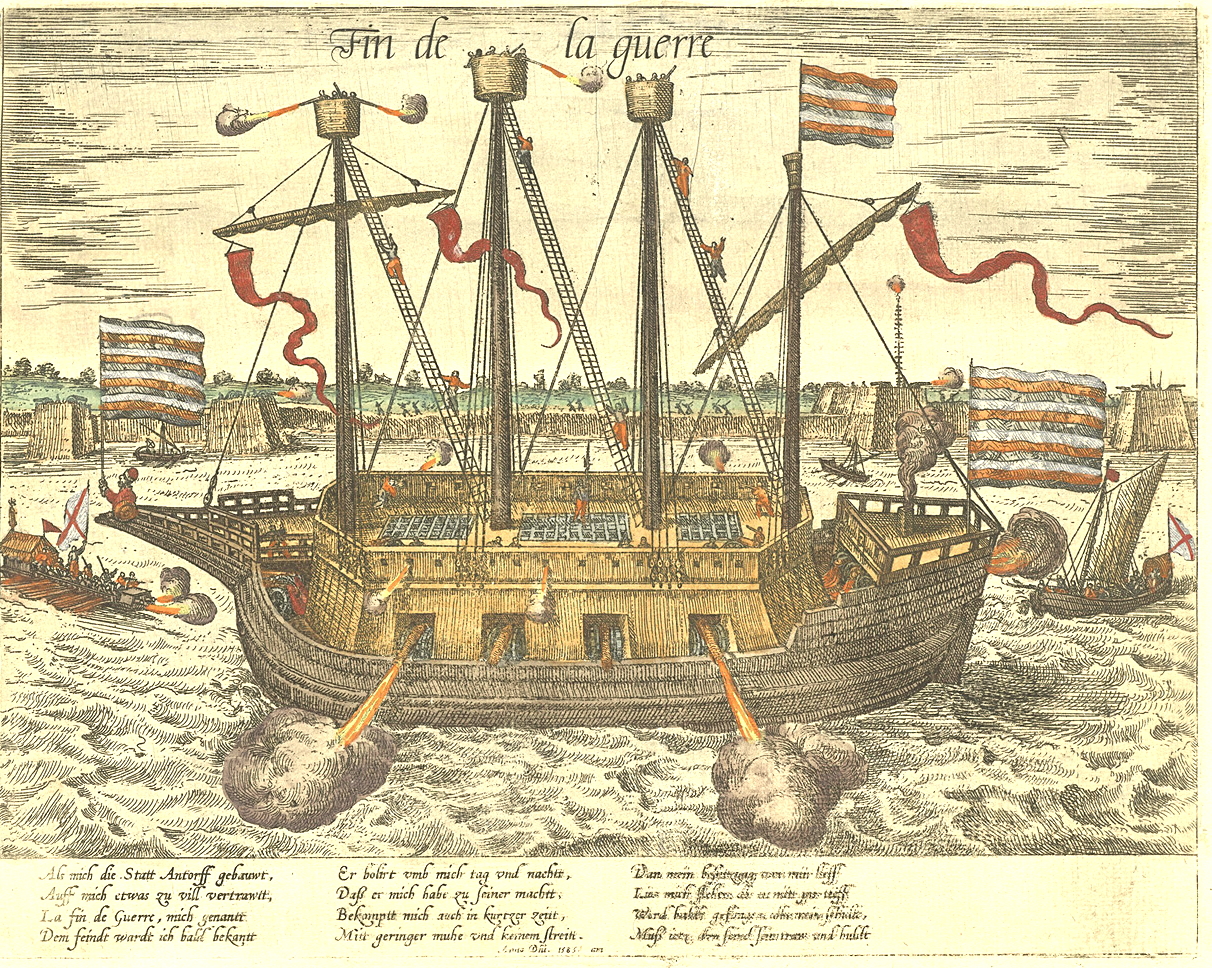
Hellburners (Dutch: ''hellebranders'') were specialised fireships used in the Siege of Antwerp (1584–1585) during the Eighty Years' War between the Dutch rebels and the Habsburgs. They were floating bombs, also called "Antwerp fire", and did immense damage to the Spanish besiegers. Hellburners have been described as an early form of weapons of mass destruction. First use against Antwerp ship bridge The hellburners were constructed by the Italian engineer Federigo Giambelli, who had been hired and subsidised by Elizabeth I of England, unofficially supporting the rebels, to assist the city. In the winter of 1585, Antwerp was besieged by the army of Alexander Farnese, the commander of the Habsburg forces in the Spanish Netherlands, who had constructed a ship bridge over the River Scheldt near Kalloo between Antwerp and the sea, to starve the population by blockade; it had been completed on 25 February. To supply the city it was imperative to destroy the ship bridge. Giambell ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hellburners
Hellburners (Dutch: ''hellebranders'') were specialised fireships used in the Siege of Antwerp (1584–1585) during the Eighty Years' War between the Dutch rebels and the Habsburgs. They were floating bombs, also called "Antwerp fire", and did immense damage to the Spanish besiegers. Hellburners have been described as an early form of weapons of mass destruction. First use against Antwerp ship bridge The hellburners were constructed by the Italian engineer Federigo Giambelli, who had been hired and subsidised by Elizabeth I of England, unofficially supporting the rebels, to assist the city. In the winter of 1585, Antwerp was besieged by the army of Alexander Farnese, the commander of the Habsburg forces in the Spanish Netherlands, who had constructed a ship bridge over the River Scheldt near Kalloo between Antwerp and the sea, to starve the population by blockade; it had been completed on 25 February. To supply the city it was imperative to destroy the ship bridge. Giambell ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Federigo Giambelli
Federigo Giambelli (or Gianibelli; also given as Genebelli or Genibelli in contemporary English texts), was an Italian military and civil engineer who worked in Spain, the Spanish Netherlands and England in the late 16th and early 17th centuries. Early life and Spanish service Giambelli was born at Mantua about the middle of the 16th century. Having had some experience as a military engineer in Italy, he went to Spain to offer his services to Philip II. However, his proposals were given a lukewarm reception, and as he could obtain no immediate employment from the king, he moved to Antwerp, where he soon gained considerable reputation for his knowledge in various departments of science. He is said to have married while living there. The Siege of Antwerp Giambelli is said to have vowed to be revenged for his rebuff at the Spanish court; and when Antwerp was besieged by Alexander Farnese, Duke of Parma in 1584, he offered his services to Elizabeth I of England, who, having satisfied ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fire Ship
A fire ship or fireship, used in the days of wooden rowed or sailing ships, was a ship filled with combustibles, or gunpowder deliberately set on fire and steered (or, when possible, allowed to drift) into an enemy fleet, in order to destroy ships, or to create panic and make the enemy break formation. Ships used as fire ships were either warships whose munitions were fully spent in battle, surplus ones which were old and worn out, or inexpensive purpose-built vessels rigged to be set afire, steered toward targets, and abandoned quickly by the crew. Explosion ships or "hellburners" were a variation on the fire ship, intended to cause damage by blowing up in proximity to enemy ships. Fireships were used to great effect by the outgunned English fleet against the Spanish Armada during the Battle of Gravelines, [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Siege Of Antwerp (1584–1585)
The Fall of Antwerp on 17 August 1585 took place during the Eighty Years' War, after a siege lasting over a year from July 1584 until August 1585. The city of Antwerp was the focal point of the Protestant-dominated Dutch Revolt, but was forced to surrender to the Spanish forces. Under the terms agreed, all Protestants were given four years to settle their affairs and leave the city. Many migrated north, especially to Amsterdam, which became the capital of the Dutch Republic. Apart from losing a high proportion of its mercantile population, Antwerp's trade suffered for two centuries as Dutch forts blockaded the River Scheldt up to 1795. Background At the time Antwerp, in modern Belgium, was not only the largest Dutch city, but was also the cultural, economic, and financial centre of the Seventeen Provinces and of north-western Europe. On 4 November 1576, unpaid Spanish soldiery mutinied: they plundered and burnt the city during what was called the Spanish Fury. Thousands of ci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spanish Armada
The Spanish Armada (a.k.a. the Enterprise of England, es, Grande y Felicísima Armada, links=no, lit=Great and Most Fortunate Navy) was a Spanish fleet that sailed from Lisbon in late May 1588, commanded by the Duke of Medina Sidonia, an aristocrat without previous naval experience appointed by Philip II of Spain. His orders were to sail up the English Channel, link up with the Duke of Parma in Flanders, and escort an invasion force that would land in England and overthrow Elizabeth I. Its purpose was to reinstate Catholicism in England, end support for the Dutch Republic, and prevent attacks by English and Dutch privateers against Spanish interests in the Americas. The Spanish were opposed by an English fleet based in Plymouth. Faster and more manoeuvrable than the larger Spanish galleons, they were able to attack the Armada as it sailed up the Channel. Several subordinates advised Medina Sidonia to anchor in The Solent and occupy the Isle of Wight, but he refused to devia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |