|
Heliosheath
The heliosphere is the magnetosphere, astrosphere and outermost atmospheric layer of the Sun. It takes the shape of a vast, bubble-like region of space. In plasma physics terms, it is the cavity formed by the Sun in the surrounding interstellar medium. The "bubble" of the heliosphere is continuously "inflated" by plasma originating from the Sun, known as the solar wind. Outside the heliosphere, this solar plasma gives way to the interstellar plasma permeating the Milky Way. As part of the interplanetary magnetic field, the heliosphere shields the Solar System from significant amounts of cosmic ionizing radiation; uncharged gamma rays are, however, not affected. Its name was likely coined by Alexander J. Dessler, who is credited with first use of the word in scientific literature in 1967. The scientific study of the heliosphere is heliophysics, which includes space weather and space climate. Flowing unimpeded through the Solar System for billions of kilometres, the solar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bow Shock
In astrophysics, a bow shock occurs when the magnetosphere of an astrophysical object interacts with the nearby flowing ambient plasma such as the solar wind. For Earth and other magnetized planets, it is the boundary at which the speed of the stellar wind abruptly drops as a result of its approach to the magnetopause. For stars, this boundary is typically the edge of the astrosphere, where the stellar wind meets the interstellar medium. Description The defining criterion of a shock wave is that the bulk velocity of the plasma drops from " supersonic" to "subsonic", where the speed of sound cs is defined by c_s^2 = \gamma p/ \rho where \gamma is the ratio of specific heats, p is the pressure, and \rho is the density of the plasma. A common complication in astrophysics is the presence of a magnetic field. For instance, the charged particles making up the solar wind follow spiral paths along magnetic field lines. The velocity of each particle as it gyrates around ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Interstellar Medium
In astronomy, the interstellar medium is the matter and radiation that exist in the space between the star systems in a galaxy. This matter includes gas in ionic, atomic, and molecular form, as well as dust and cosmic rays. It fills interstellar space and blends smoothly into the surrounding intergalactic space. The energy that occupies the same volume, in the form of electromagnetic radiation, is the interstellar radiation field. The interstellar medium is composed of multiple phases distinguished by whether matter is ionic, atomic, or molecular, and the temperature and density of the matter. The interstellar medium is composed, primarily, of hydrogen, followed by helium with trace amounts of carbon, oxygen, and nitrogen. The thermal pressures of these phases are in rough equilibrium with one another. Magnetic fields and turbulent motions also provide pressure in the ISM, and are typically more important, dynamically, than the thermal pressure is. In the interstellar medium, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
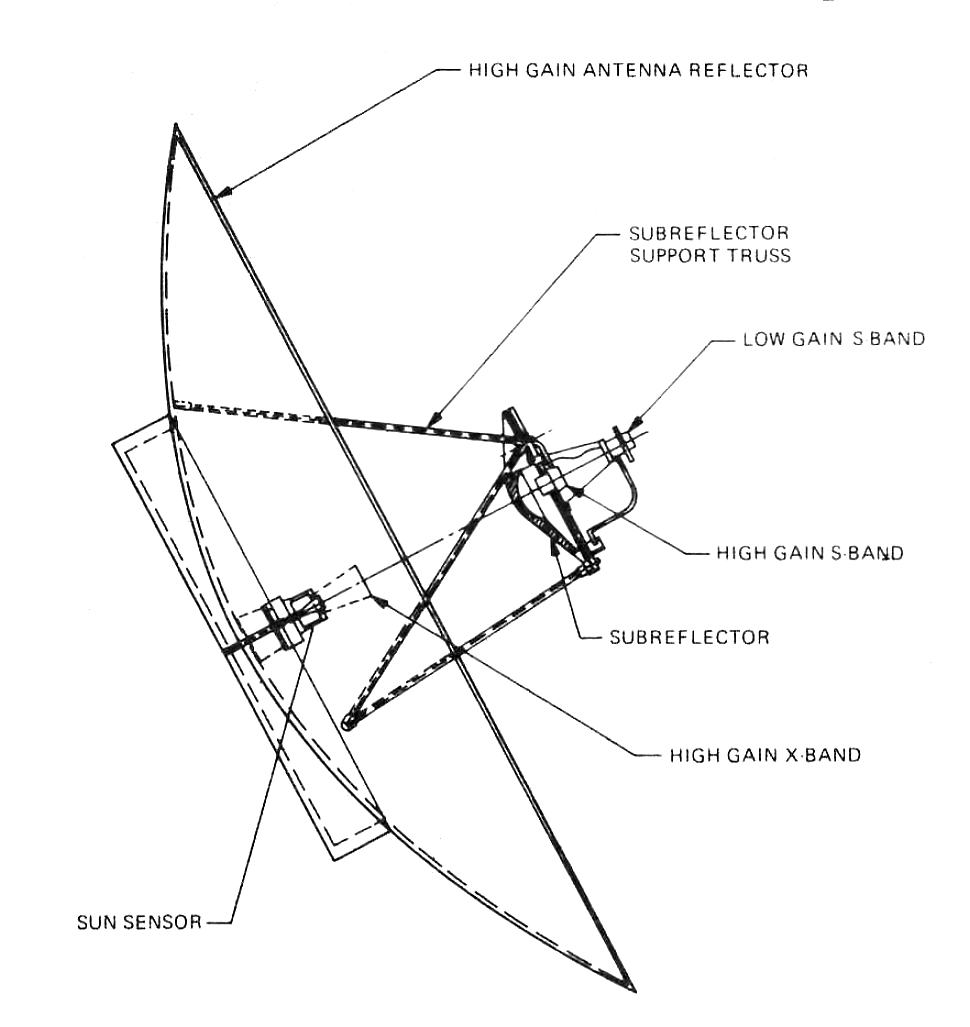
Voyager 1
''Voyager 1'' is a space probe launched by NASA on September 5, 1977, as part of the Voyager program to study the outer Solar System and interstellar space beyond the Sun's heliosphere. Launched 16 days after its twin ''Voyager 2'', ''Voyager 1'' has been operating for as of . It communicates through NASA's Deep Space Network to receive routine commands and to transmit data to Earth. Real-time distance and velocity data is provided by NASA and JPL. At a distance of from Earth , it is the most distant human-made object from Earth. The probe made flybys of Jupiter, Saturn, and Saturn's largest moon, Titan. NASA had a choice of either doing a Pluto or Titan flyby; exploration of the moon took priority because it was known to have a substantial atmosphere. ''Voyager 1'' studied the weather, magnetic fields, and rings of the two gas giants and was the first probe to provide detailed images of their moons. As part of the Voyager program and like its sister craft ''Voyager ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Solar System
The Solar SystemCapitalization of the name varies. The International Astronomical Union, the authoritative body regarding astronomical nomenclature, specifies capitalizing the names of all individual astronomical objects but uses mixed "Solar System" and "solar system" structures in theinaming guidelines document. The name is commonly rendered in lower case ('solar system'), as, for example, in the ''Oxford English Dictionary'' an''Merriam-Webster's 11th Collegiate Dictionary''. is the gravity, gravitationally bound system of the Sun and the objects that orbit it. It Formation and evolution of the Solar System, formed 4.6 billion years ago from the gravitational collapse of a giant interstellar molecular cloud. The solar mass, vast majority (99.86%) of the system's mass is in the Sun, with most of the Jupiter mass, remaining mass contained in the planet Jupiter. The four inner Solar System, inner system planets—Mercury (planet), Mercury, Venus, Earth and Mars—are terrest ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
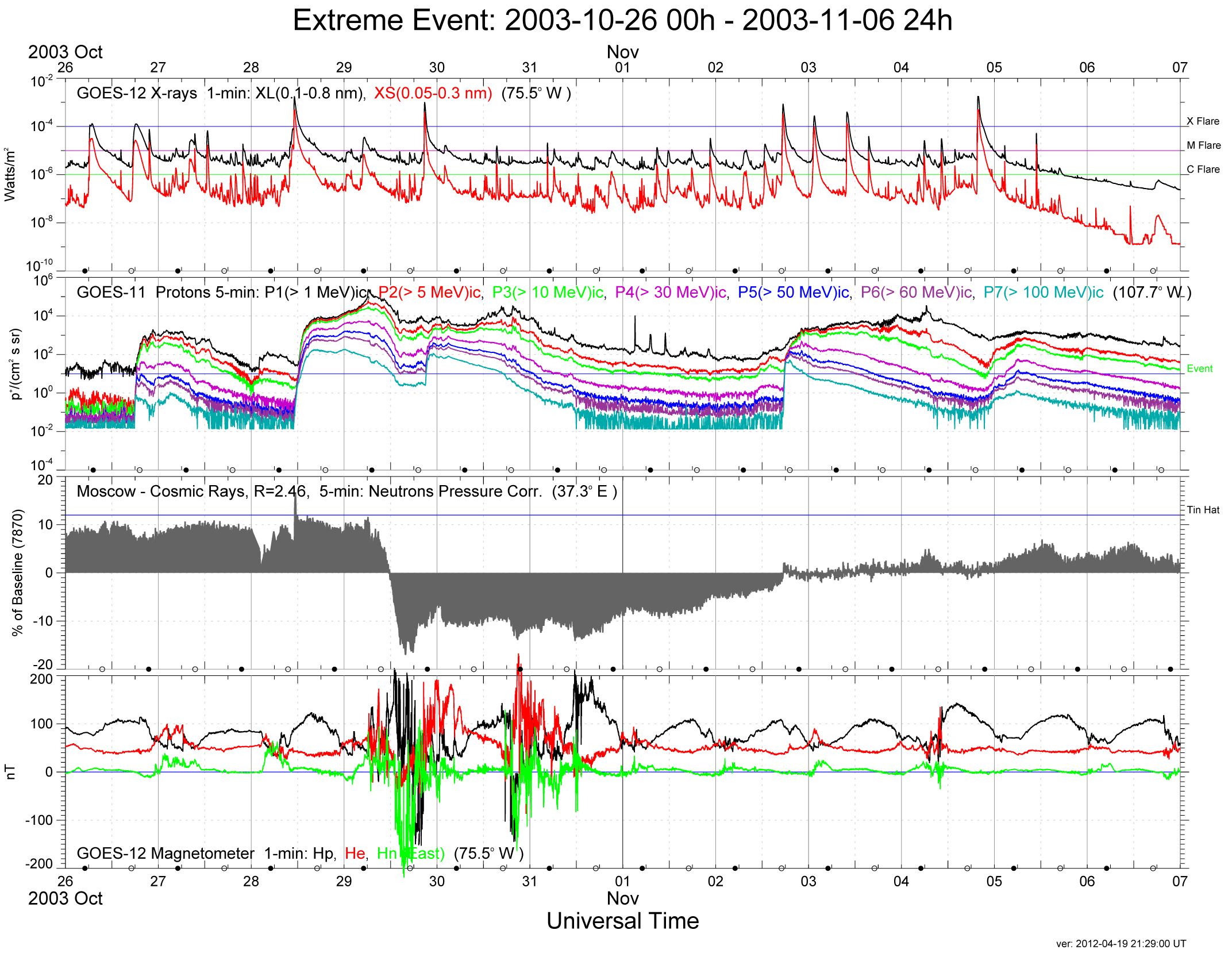
Space Weather
Space weather is a branch of space physics and aeronomy, or heliophysics, concerned with the time varying conditions within the Solar System, including the solar wind, emphasizing the space surrounding the Earth, including conditions in the magnetosphere, ionosphere, thermosphere, and exosphere. Space weather is distinct from, but conceptually related to, the terrestrial weather of the atmosphere of Earth (troposphere and stratosphere). The term "space weather" was first used in the 1950s and came into common usage in the 1990s. Later, it was generalized to a " space climate" research discipline, which focuses on general behaviors of longer and larger-scale variabilities and effects. History For many centuries, the effects of space weather were noticed, but not understood. Displays of auroral light have long been observed at high latitudes. Genesis In 1724, George Graham reported that the needle of a magnetic compass was regularly deflected from magnetic north over the c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Interplanetary Magnetic Field
The interplanetary magnetic field (IMF), now more commonly referred to as the heliospheric magnetic field (HMF), is the component of the solar magnetic field that is dragged out from the solar corona by the solar wind flow to fill the Solar System. Coronal and solar wind plasma The coronal and solar wind plasmas are highly electrically conductive, meaning the magnetic field lines and the plasma flows are effectively "frozen" together and the magnetic field cannot diffuse through the plasma on time scales of interest. In the solar corona, the magnetic pressure greatly exceeds the plasma pressure and thus the plasma is primarily structured and confined by the magnetic field. However, with increasing altitude through the corona, the solar wind accelerates as it extracts energy from the magnetic field through the Lorentz force interaction, resulting in the flow momentum exceeding the restraining magnetic tension force and the coronal magnetic field is dragged out by the solar wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Voyager Speed And Distance From Sun
Voyager may refer to: Computing and communications * LG Voyager, a mobile phone model manufactured by LG Electronics * NCR Voyager, a computer platform produced by NCR Corporation * Voyager (computer worm), a computer worm affecting Oracle databases * Voyager (library program), the integrated library system from Ex Libris Group * Voyager (web browser), a web browser for Amiga computers * HP Voyager series, code name for a Hewlett-Packard series of handheld programmable calculators Transport Air * Airbus Voyager, Royal Air Force version of the Airbus A330 MRTT * Frequent flyer program of South African Airways * Egvoyager Voyager 203, an Italian ultralight aircraft * Raj Hamsa Voyager, an Indian ultralight trike design * Rutan Voyager, the first airplane to fly around the world nonstop without refuelling Land * Bombardier Voyager, a high-speed train operated in the United Kingdom ** Bombardier ''Voyager'' (British Rail Class 220), a non-tilting train built 2000–2001 ** Bo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
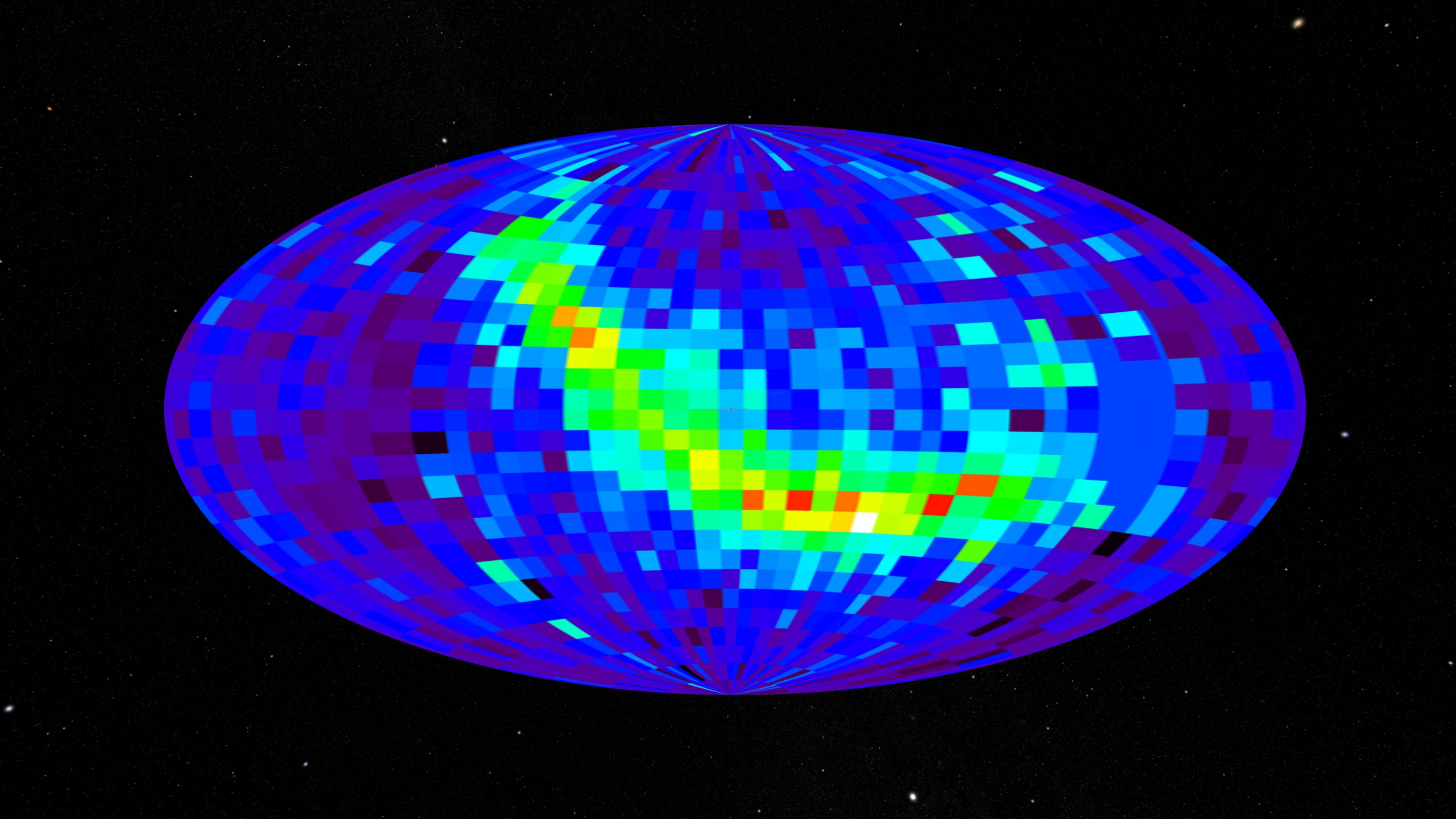
IBEX All Sky Map
An ibex (plural ibex, ibexes or ibices) is any of several species of wild goat (genus ''Capra''), distinguished by the male's large recurved horns, which are transversely ridged in front. Ibex are found in Eurasia, North Africa and East Africa. The name ''ibex'' comes from Latin, borrowed from Iberian or Aquitanian, akin to Old Spanish ''bezerro'' "bull", modern Spanish ''becerro'' "yearling". Ranging in height from and weighing , ibex can live 20 years. Two closely related varieties of goats found in the wild are not usually called ibex: the markhor and the feral goat. A male ibex is referred to as a buck, a female is a doe, and young juveniles are called kids. An ibex buck is commonly larger and heavier than a doe. The most noticeable difference between the sexes is the larger size of a buck's horns. The doe grows a pair of smaller, thinner horns which develop considerably more slowly than those of a buck. The ibex's horns appear at birth and continue to grow through the r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Outer Space
Outer space, commonly shortened to space, is the expanse that exists beyond Earth and its atmosphere and between celestial bodies. Outer space is not completely empty—it is a near-perfect vacuum containing a low density of particles, predominantly a plasma of hydrogen and helium, as well as electromagnetic radiation, magnetic fields, neutrinos, dust, and cosmic rays. The baseline temperature of outer space, as set by the background radiation from the Big Bang, is . The plasma between galaxies is thought to account for about half of the baryonic (ordinary) matter in the universe, having a number density of less than one hydrogen atom per cubic metre and a kinetic temperature of millions of kelvins. Local concentrations of matter have condensed into stars and galaxies. Studies indicate that 90% of the mass in most galaxies is in an unknown form, called dark matter, which interacts with other matter through gravitational but not electromagnetic forces. Observations s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Voyager 2
''Voyager 2'' is a space probe launched by NASA on August 20, 1977, to study the outer planets and interstellar space beyond the Sun's heliosphere. As a part of the Voyager program, it was launched 16 days before its twin, ''Voyager 1'', on a trajectory that took longer to reach gas giants Jupiter and Saturn but enabled further encounters with ice giants Uranus and Neptune. ''Voyager 2'' remains the only spacecraft to have visited either of the ice giant planets. ''Voyager 2'' was the fourth of five spacecraft to achieve Solar escape velocity, which allowed it to leave the Solar System. ''Voyager 2'' successfully fulfilled its primary mission of visiting the Jovian system in 1979, the Saturnian system in 1981, Uranian system in 1986, and the Neptunian system in 1989. The spacecraft is now in its extended mission of studying interstellar space. It has been operating for as of ; , it has reached a distance of from Earth. The probe entered interstellar space on November 5, 2 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Density
Density (volumetric mass density or specific mass) is the substance's mass per unit of volume. The symbol most often used for density is ''ρ'' (the lower case Greek letter rho), although the Latin letter ''D'' can also be used. Mathematically, density is defined as mass divided by volume: : \rho = \frac where ''ρ'' is the density, ''m'' is the mass, and ''V'' is the volume. In some cases (for instance, in the United States oil and gas industry), density is loosely defined as its weight per unit volume, although this is scientifically inaccurate – this quantity is more specifically called specific weight. For a pure substance the density has the same numerical value as its mass concentration. Different materials usually have different densities, and density may be relevant to buoyancy, purity and packaging. Osmium and iridium are the densest known elements at standard conditions for temperature and pressure. To simplify comparisons of density across different s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |