|
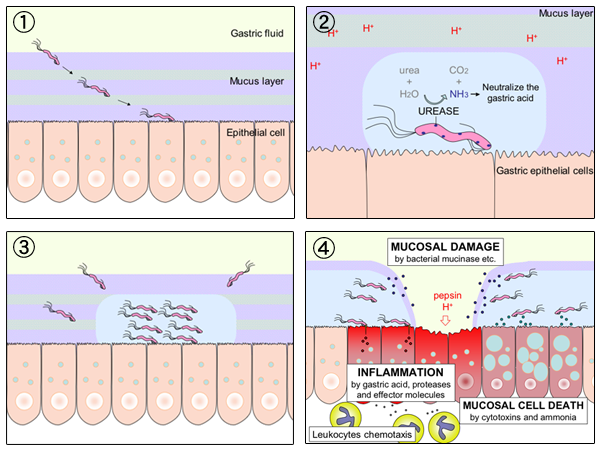
Helicobacter
''Helicobacter'' is a genus of gram-negative bacteria possessing a characteristic helical shape. They were initially considered to be members of the genus '' Campylobacter'', but in 1989, Goodwin ''et al.'' published sufficient reasons to justify the new genus name ''Helicobacter''. The genus ''Helicobacter'' contains about 35 species. Some species have been found living in the lining of the upper gastrointestinal tract, as well as the liver of mammals and some birds. The most widely known species of the genus is '' H. pylori'', which infects up to 50% of the human population. It also serves as the type species of the genus. Some strains of this bacterium are pathogenic to humans, as they are strongly associated with peptic ulcers, chronic gastritis, duodenitis, and stomach cancer. ''Helicobacter'' species are able to thrive in the very acidic mammalian stomach by producing large quantities of the enzyme urease, which locally raises the pH from about 2 to a more biocompatible ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Helicobacter Pylori
''Helicobacter pylori'', previously known as ''Campylobacter pylori'', is a gram-negative, Flagellum#bacterial, flagellated, Bacterial cellular morphologies#Helical, helical bacterium. Mutants can have a rod or curved rod shape that exhibits less virulence. Its Helix, helical body (from which the genus name ''Helicobacter'' derives) is thought to have evolved to penetrate the gastric mucosa, mucous lining of the stomach, helped by its flagella, and thereby establish infection. While many earlier reports of an association between bacteria and the ulcers had existed, such as the works of John Lykoudis, it was only in 1983 when the bacterium was formally described for the first time in the English-language Western literature as the causal agent of peptic ulcer, gastric ulcers by Australian physician-scientists Barry Marshall and Robin Warren. In 2005, the pair was awarded the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine for their discovery. Infection of the stomach with ''H. pylori'' doe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Peptic Ulcer
Peptic ulcer disease is when the inner part of the stomach's gastric mucosa (lining of the stomach), the first part of the small intestine, or sometimes the lower esophagus, gets damaged. An ulcer in the stomach is called a gastric ulcer, while one in the first part of the intestines is a duodenal ulcer. The most common symptoms of a duodenal ulcer are waking at night with epigastrium, upper abdominal pain, and upper abdominal pain that improves with eating. With a gastric ulcer, the pain may worsen with eating. The pain is often described as a dyspepsia, burning or dull ache. Other symptoms include belching, vomiting, weight loss, or Anorexia (symptom), poor appetite. About a third of older people with peptic ulcers have no symptoms. Complications may include gastrointestinal bleeding, bleeding, gastrointestinal perforation, perforation, and gastric outlet obstruction, blockage of the stomach. Bleeding occurs in as many as 15% of cases. Common causes include infection with ''Hel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Gastritis
Gastritis is the inflammation of the lining of the stomach. It may occur as a short episode or may be of a long duration. There may be no symptoms but, when symptoms are present, the most common is upper abdominal pain (see dyspepsia). Other possible symptoms include nausea and vomiting, bloating, loss of appetite and heartburn. Complications may include stomach bleeding, stomach ulcers, and stomach tumors. When due to autoimmune problems, low red blood cells due to not enough vitamin B12 may occur, a condition known as pernicious anemia. Common causes include infection with '' Helicobacter pylori'' and use of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs ( NSAIDs). When caused by ''H. pylori'' this is now termed ''Helicobacter pylori'' induced gastritis, and included as a listed disease in ICD11. Less common causes include alcohol, smoking, cocaine, severe illness, autoimmune problems, radiation therapy and Crohn's disease. Endoscopy, a type of X-ray known as an upper gast ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
World Journal Of Gastroenterology
''World Journal of Gastroenterology'' is a weekly peer-reviewed open access medical journal that covers research in gastroenterology. It was established in 1995 and is published by Baishideng Publishing Group. The editor-in-chief is Andrzej S. Tarnawski (California State University, Long Beach). Abstracting and indexing The journal is abstracted and indexed in: In 2004, the journal was delisted from the ''Journal Citation Reports'' for excessive self-citation, but it was restored to this index in 2008, at which time its impact factor The impact factor (IF) or journal impact factor (JIF) of an academic journal is a type of journal ranking. Journals with higher impact factor values are considered more prestigious or important within their field. The Impact Factor of a journa ... was determined to be 2.081. According to the ''Journal Citation Reports'', the journal has a 2020 impact factor of 5.742, ranking it 28th out of 92 journals in the category "Gastroenterology and Hepat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Flagella
A flagellum (; : flagella) (Latin for 'whip' or 'scourge') is a hair-like appendage that protrudes from certain plant and animal sperm cells, from fungal spores ( zoospores), and from a wide range of microorganisms to provide motility. Many protists with flagella are known as flagellates. A microorganism may have from one to many flagella. A gram-negative bacterium '' Helicobacter pylori'', for example, uses its flagella to propel itself through the stomach to reach the mucous lining where it may colonise the epithelium and potentially cause gastritis, and ulcers – a risk factor for stomach cancer. In some swarming bacteria, the flagellum can also function as a sensory organelle, being sensitive to wetness outside the cell. Across the three domains of Bacteria, Archaea, and Eukaryota, the flagellum has a different structure, protein composition, and mechanism of propulsion but shares the same function of providing motility. The Latin word means " whip" to describe its ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Capnophiles
Capnophiles are microorganisms that thrive in the presence of high concentrations of carbon dioxide (). Some capnophiles may have a metabolic requirement for carbon dioxide, while others merely compete more successfully for resources under these conditions. The term is a generally descriptive one and has less relevance as a means of establishing a taxonomic or evolutionary relationship among organisms with this characteristic. For example, the ability of capnophiles to tolerate (or utilize) the amount of oxygen that is also in their environment may vary widely and may be far more critical to their survival. Species of ''Campylobacter'' are bacterial capnophiles that are more easily identified because they are also microaerophiles, organisms that can grow in high carbon dioxide as long as a small amount of free oxygen is present, but at a dramatically reduced concentration. (In the Earth's atmosphere carbon dioxide levels are approximately five hundred times lower than that of oxy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Oxygen
Oxygen is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol O and atomic number 8. It is a member of the chalcogen group (periodic table), group in the periodic table, a highly reactivity (chemistry), reactive nonmetal (chemistry), nonmetal, and a potent oxidizing agent that readily forms oxides with most elements as well as with other chemical compound, compounds. Oxygen is abundance of elements in Earth's crust, the most abundant element in Earth's crust, making up almost half of the Earth's crust in the form of various oxides such as water, carbon dioxide, iron oxides and silicates.Atkins, P.; Jones, L.; Laverman, L. (2016).''Chemical Principles'', 7th edition. Freeman. It is abundance of chemical elements, the third-most abundant element in the universe after hydrogen and helium. At standard temperature and pressure, two oxygen atoms will chemical bond, bind covalent bond, covalently to form dioxygen, a colorless and odorless diatomic gas with the chemical formula ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Microaerophilic
A microaerophile is a microorganism that requires environments containing lower levels of dioxygen than that are present in the atmosphere (i.e. < 21% O2; typically 2–10% O2) for optimal growth. A more restrictive interpretation requires the microorganism to be obligate in this requirement. Many microaerophiles are also capnophiles, requiring an elevated concentration of (e.g. 10% CO2 in the case of '' Campylobacter'' ). The original ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Penicillin
Penicillins (P, PCN or PEN) are a group of beta-lactam antibiotic, β-lactam antibiotics originally obtained from ''Penicillium'' Mold (fungus), moulds, principally ''Penicillium chrysogenum, P. chrysogenum'' and ''Penicillium rubens, P. rubens''. Most penicillins in clinical use are synthesised by ''Penicillium chrysogenum, P. chrysogenum'' using industrial fermentation, deep tank fermentation and then purified. A number of natural penicillins have been discovered, but only two purified compounds are in clinical use: benzylpenicillin, penicillin G (intramuscular injection, intramuscular or Intravenous therapy, intravenous use) and phenoxymethylpenicillin, penicillin V (given by mouth). Penicillins were among the first medications to be effective against many bacterial infections caused by staphylococcus, staphylococci and streptococcus, streptococci. They are still widely used today for various bacterial infections, though many types of bacteria have developed antibiotic res ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Antibiotics
An antibiotic is a type of antimicrobial substance active against bacteria. It is the most important type of antibacterial agent for fighting pathogenic bacteria, bacterial infections, and antibiotic medications are widely used in the therapy, treatment and antibiotic prophylaxis, prevention of such infections. They may either bactericide, kill or bacteriostatic agent, inhibit the growth of bacteria. A limited number of antibiotics also possess antiprotozoal activity. Antibiotics are not effective against viruses such as the ones which cause the common cold or influenza. Drugs which inhibit growth of viruses are termed antiviral drugs or antivirals. Antibiotics are also not effective against fungi. Drugs which inhibit growth of fungi are called antifungal drugs. Sometimes, the term ''antibiotic''—literally "opposing life", from the Greek language, Greek roots ἀντι ''anti'', "against" and βίος ''bios'', "life"—is broadly used to refer to any substance used against ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Urease
Ureases (), functionally, belong to the superfamily of amidohydrolases and phosphotriesterases. Ureases are found in numerous Bacteria, Archaea, fungi, algae, plants, and some invertebrates. Ureases are nickel-containing metalloenzymes of high molecular weight. Ureases are distinct from Urecases are important in degrading avian faecal matter, which is rich in uric acid, the breakdown product of which is urea, which is then degraded by urease as described here. These enzymes catalyze the hydrolysis of urea into carbon dioxide and ammonia: : (NH2)2CO + H2O CO2 + 2NH3 The hydrolysis of urea occurs in two stages. In the first stage, ammonia and carbamic acid are produced. The carbamate spontaneously and rapidly hydrolyzes to ammonia and carbonic acid. Urease activity increases the pH of its environment as ammonia is produced, which is basic. History Urease activity was first identified in 1876 by Frédéric Alphonse Musculus as a soluble ferment. In 1926, James B. Sumner ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Enzyme
An enzyme () is a protein that acts as a biological catalyst by accelerating chemical reactions. The molecules upon which enzymes may act are called substrate (chemistry), substrates, and the enzyme converts the substrates into different molecules known as product (chemistry), products. Almost all metabolism, metabolic processes in the cell (biology), cell need enzyme catalysis in order to occur at rates fast enough to sustain life. Metabolic pathways depend upon enzymes to catalyze individual steps. The study of enzymes is called ''enzymology'' and the field of pseudoenzyme, pseudoenzyme analysis recognizes that during evolution, some enzymes have lost the ability to carry out biological catalysis, which is often reflected in their amino acid sequences and unusual 'pseudocatalytic' properties. Enzymes are known to catalyze more than 5,000 biochemical reaction types. Other biocatalysts include Ribozyme, catalytic RNA molecules, also called ribozymes. They are sometimes descr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |