|
Heat-assisted Magnetic Recording
Heat-assisted magnetic recording (HAMR) (pronounced "''hammer")'' is a magnetic storage technology for greatly increasing the amount of data that can be stored on a magnetic device such as a hard disk drive by temporarily heating the disk material during writing, which makes it much more receptive to magnetic effects and allows writing to much smaller regions (and much higher levels of data on a disk). The technology was initially seen as extremely difficult to achieve, with doubts expressed about its feasibility in 2013. The regions being written must be heated in a tiny area - small enough that diffraction prevents the use of normal laser focused heating - and requires a heating, writing and cooling cycle of less than 1 nanosecond, while also controlling the effects of repeated spot-heating on the drive platters, the drive-to-head contact, and the adjacent magnetic data which must not be affected. These challenges required the development of nano-scale surface plasmons (surfac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magnetic Storage
Magnetic storage or magnetic recording is the storage of data on a magnetized medium. Magnetic storage uses different patterns of magnetisation in a magnetizable material to store data and is a form of non-volatile memory. The information is accessed using one or more read/write heads. Magnetic storage media, primarily hard disks, are widely used to store computer data as well as audio and video signals. In the field of computing, the term ''magnetic storage'' is preferred and in the field of audio and video production, the term ''magnetic recording'' is more commonly used. The distinction is less technical and more a matter of preference. Other examples of magnetic storage media include floppy disks, magnetic tape, and magnetic stripes on credit cards. History Magnetic storage in the form of wire recording—audio recording on a wire—was publicized by Oberlin Smith in the Sept 8, 1888 issue of ''Electrical World''. Smith had previously filed a patent in September, 187 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magnetic Recording Trilemma
Magnetism is the class of physical attributes that are mediated by a magnetic field, which refers to the capacity to induce attractive and repulsive phenomena in other entities. Electric currents and the magnetic moments of elementary particles give rise to a magnetic field, which acts on other currents and magnetic moments. Magnetism is one aspect of the combined phenomena of electromagnetism. The most familiar effects occur in ferromagnetic materials, which are strongly attracted by magnetic fields and can be magnetized to become permanent magnets, producing magnetic fields themselves. Demagnetizing a magnet is also possible. Only a few substances are ferromagnetic; the most common ones are iron, cobalt, and nickel and their alloys. The rare-earth metals neodymium and samarium are less common examples. The prefix ' refers to iron because permanent magnetism was first observed in lodestone, a form of natural iron ore called magnetite, Fe3O4. All substances exhibit some type of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Near-field Optics
Near-field optics is that branch of optics that considers configurations that depend on the passage of light to, from, through, or near an element with subwavelength features, and the coupling of that light to a second element located a subwavelength distance from the first. The barrier of spatial resolution imposed by the very nature of light itself in conventional optical microscopy contributed significantly to the development of near-field optical devices, most notably the near-field scanning optical microscope, or NSOM. The relatively new optical science of dressed photons (DPs) can also find its origin in near-field optics. Size constraints The limit of optical resolution in a conventional microscope, the so-called diffraction limit, is in the order of half the wavelength of the light used to image. Thus, when imaging at visible wavelengths, the smallest resolvable features are several hundred nanometers in size (although point-like sources, such as quantum dots, can be reso ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Semiconductor Diode Laser
The laser diode chip removed and placed on the eye of a needle for scale A laser diode (LD, also injection laser diode or ILD, or diode laser) is a semiconductor device similar to a light-emitting diode in which a diode pumped directly with electrical current can create lasing conditions at the diode's junction. Driven by voltage, the doped p–n-transition allows for recombination of an electron with a hole. Due to the drop of the electron from a higher energy level to a lower one, radiation, in the form of an emitted photon is generated. This is spontaneous emission. Stimulated emission can be produced when the process is continued and further generates light with the same phase, coherence and wavelength. The choice of the semiconductor material determines the wavelength of the emitted beam, which in today's laser diodes range from infra-red to the UV spectrum. Laser diodes are the most common type of lasers produced, with a wide range of uses that include fiber optic co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seagate Technology
Seagate Technology Holdings plc is an American data storage company. It was incorporated in 1978 as Shugart Technology and commenced business in 1979. Since 2010, the company has been incorporated in Dublin, Ireland, with operational headquarters in Fremont, California, United States. Seagate developed the first 5.25-inch hard disk drive (HDD), the 5-megabyte ST-506, in 1980. They were a major supplier in the microcomputer market during the 1980s, especially after the introduction of the IBM XT in 1983. Much of their growth has come through their acquisition of competitors. In 1989, Seagate acquired Control Data Corporation's Imprimis division, the makers of CDC's HDD products. Seagate acquired Conner Peripherals in 1996, Maxtor in 2006, and Samsung's HDD business in 2011. Today, Seagate, along with its competitor Western Digital, dominates the HDD market. History Founding as Shugart Technology Seagate Technology (then called Shugart Technology) was incorporated on No ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thermal Conduction
Conduction is the process by which heat is transferred from the hotter end to the colder end of an object. The ability of the object to conduct heat is known as its ''thermal conductivity'', and is denoted . Heat spontaneously flows along a temperature gradient (i.e. from a hotter body to a colder body). For example, heat is conducted from the hotplate of an electric stove to the bottom of a saucepan in contact with it. In the absence of an opposing external driving energy source, within a body or between bodies, temperature differences decay over time, and thermal equilibrium is approached, temperature becoming more uniform. In conduction, the heat flow is within and through the body itself. In contrast, in heat transfer by thermal radiation, the transfer is often between bodies, which may be separated spatially. Heat can also be transferred by a combination of conduction and radiation. In solids, conduction is mediated by the combination of vibrations and collisions of molec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hard Disk Drive Platter
A hard disk drive platter (or disk) is the circular disk on which magnetic data is stored in a hard disk drive. The rigid nature of the platters in a hard drive is what gives them their name (as opposed to the flexible materials which are used to make floppy disks). Hard drives typically have several platters which are mounted on the same spindle. A platter can store information on both sides, requiring two heads per platter. Design The magnetic surface of each platter is divided into small sub-micrometer-sized magnetic regions, each of which is used to represent a single binary unit of information. A typical magnetic region on a hard-disk platter (as of 2006) is about 200–250 nanometers wide (in the radial direction of the platter) and extends about 25–30 nanometers in the down-track direction (the circumferential direction on the platter), corresponding to about 100 billion bits per square inch of disk area (15.5 Gbit/cm2). The material of the main ''magnetic mediu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
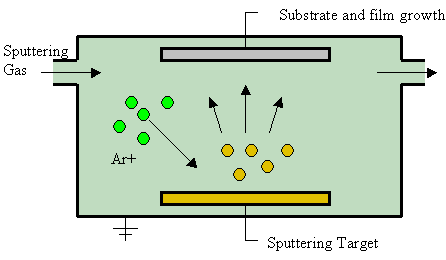
Sputter Deposition
Sputter deposition is a physical vapor deposition (PVD) method of thin film deposition by the phenomenon of sputtering. This involves ejecting material from a "target" that is a source onto a "substrate" such as a silicon wafer. Resputtering is re-emission of the deposited material during the deposition process by ion or atom bombardment. Sputtered atoms ejected from the target have a wide energy distribution, typically up to tens of eV (100,000 K). The sputtered ions (typically only a small fraction of the ejected particles are ionized — on the order of 1 percent) can ballistically fly from the target in straight lines and impact energetically on the substrates or vacuum chamber (causing resputtering). Alternatively, at higher gas pressures, the ions collide with the gas atoms that act as a moderator and move diffusively, reaching the substrates or vacuum chamber wall and condensing after undergoing a random walk. The entire range from high-energy ballistic impact to low-e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wavelength
In physics, the wavelength is the spatial period of a periodic wave—the distance over which the wave's shape repeats. It is the distance between consecutive corresponding points of the same phase on the wave, such as two adjacent crests, troughs, or zero crossings, and is a characteristic of both traveling waves and standing waves, as well as other spatial wave patterns. The inverse of the wavelength is called the spatial frequency. Wavelength is commonly designated by the Greek letter '' lambda'' (λ). The term ''wavelength'' is also sometimes applied to modulated waves, and to the sinusoidal envelopes of modulated waves or waves formed by interference of several sinusoids. Assuming a sinusoidal wave moving at a fixed wave speed, wavelength is inversely proportional to frequency of the wave: waves with higher frequencies have shorter wavelengths, and lower frequencies have longer wavelengths. Wavelength depends on the medium (for example, vacuum, air, or water) tha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flame
A flame (from Latin '' flamma'') is the visible, gaseous part of a fire. It is caused by a highly exothermic chemical reaction taking place in a thin zone. When flames are hot enough to have ionized gaseous components of sufficient density they are then considered plasma. Mechanism Color and temperature of a flame are dependent on the type of fuel involved in the combustion, as, for example, when a lighter is held to a candle. The applied heat causes the fuel molecules in the candle wax to vaporize (if this process happens in inert atmosphere without oxidizer, it is called pyrolysis). In this state they can then readily react with oxygen in the air, which gives off enough heat in the subsequent exothermic reaction to vaporize yet more fuel, thus sustaining a consistent flame. The high temperature of the flame causes the vaporized fuel molecules to decompose, forming various incomplete combustion products and free radicals, and these products then react with each other and wit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sewing Needle
A sewing needle, used for hand-sewing, is a long slender tool with a pointed tip at one end and a hole (or ''eye'') to hold the sewing thread. The earliest needles were made of bone or wood; modern needles are manufactured from high carbon steel wire and are nickel- or 18K gold-plated for corrosion resistance. High quality embroidery needles are plated with two-thirds platinum and one-third titanium alloy. Traditionally, needles have been kept in needle books or needlecases which have become objects of adornment. Sewing needles may also be kept in an étui, a small box that held needles and other items such as scissors, pencils and tweezers. Types of hand sewing needles Hand sewing needles come in a variety of types/classes designed according to their intended use and in a variety of sizes within each type. * Sharp needles: used for general hand sewing; built with a sharp point, a round eye, and are of medium length. Those with a double-eyes are able to carry two strands of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |