|
Head (geology)
Head describes deposits consisting of fragmented material which, following weathering, have moved downslope through a process of solifluction. The term has been used by British geologists since the middle of the 19th century to describe such material in a range of different settings from flat hilltops to the bottoms of valleys. Areas identified as head include deposits of aeolian origin such as blown sand and loess, slope deposits such as gelifluctates and solifluctates, and recently eroded soil material, called colluvium. With geologists becoming more interested in studying the near-surface environment and its related processes, the term head is becoming obsolete. A related term is 'combe (or coombe) rock', descriptive of a body of chalk and flint fragments contained within a mass of chalky earth typically found on the chalk downland Downland, chalkland, chalk downs or just downs are areas of open chalk hills, such as the North Downs. This term is used to describe the chara ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deposition (geology)
Deposition is the geological process in which sediments, soil and rocks are added to a landform or landmass. Wind, ice, water, and gravity transport previously weathered surface material, which, at the loss of enough kinetic energy in the fluid, is deposited, building up layers of sediment. Deposition occurs when the forces responsible for sediment transportation are no longer sufficient to overcome the forces of gravity and friction, creating a resistance to motion; this is known as the null-point hypothesis. Deposition can also refer to the buildup of sediment from organically derived matter or chemical processes. For example, chalk is made up partly of the microscopic calcium carbonate skeletons of marine plankton, the deposition of which has induced chemical processes (diagenesis) to deposit further calcium carbonate. Similarly, the formation of coal begins with the deposition of organic material, mainly from plants, in anaerobic conditions. Null-point hypothesis The null ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Weathering
Weathering is the deterioration of rocks, soils and minerals as well as wood and artificial materials through contact with water, atmospheric gases, and biological organisms. Weathering occurs ''in situ'' (on site, with little or no movement), and so is distinct from erosion, which involves the transport of rocks and minerals by agents such as water, ice, snow, wind, waves and gravity. Weathering processes are divided into ''physical'' and ''chemical weathering''. Physical weathering involves the breakdown of rocks and soils through the mechanical effects of heat, water, ice, or other agents. Chemical weathering involves the chemical reaction of water, atmospheric gases, and biologically produced chemicals with rocks and soils. Water is the principal agent behind both physical and chemical weathering, though atmospheric oxygen and carbon dioxide and the activities of biological organisms are also important. Chemical weathering by biological action is also known as biological wea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
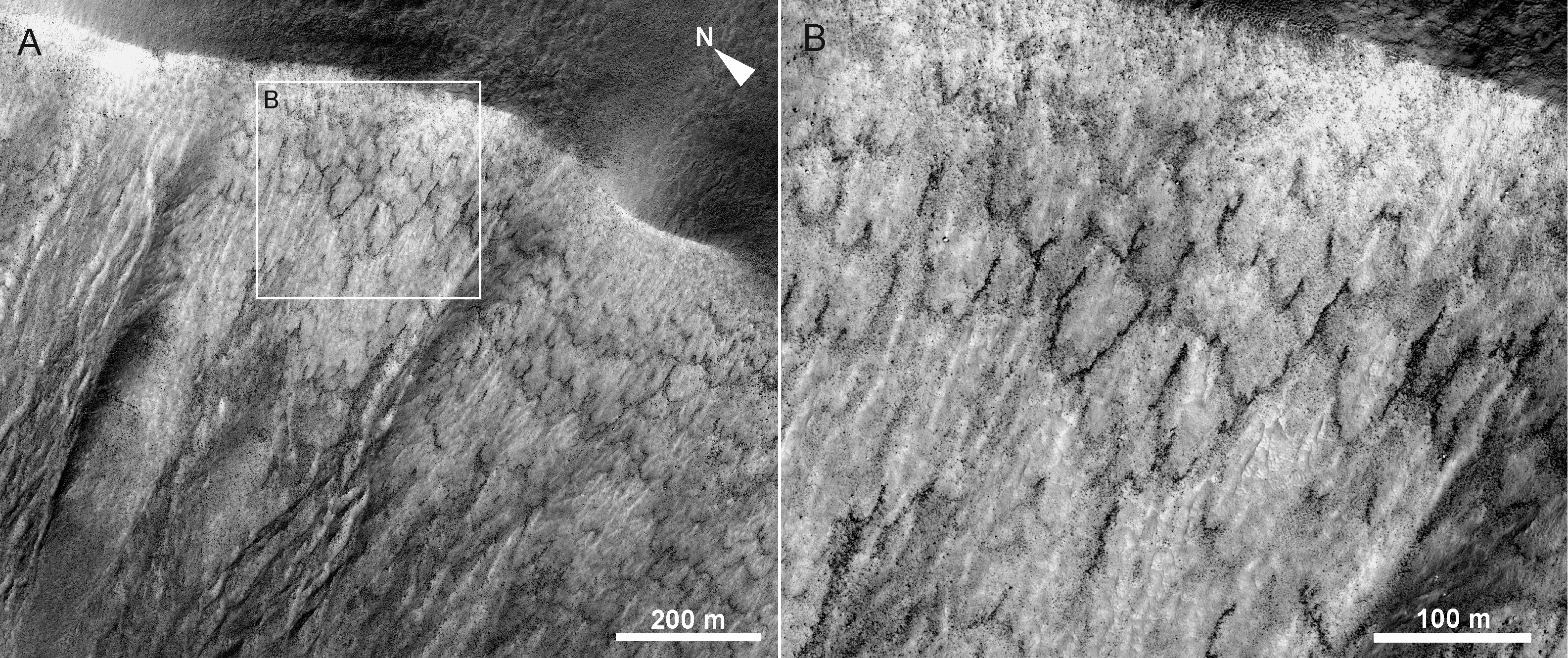
Solifluction
Solifluction is a collective name for gradual processes in which a mass moves down a slope ("mass wasting") related to freeze-thaw activity. This is the standard modern meaning of solifluction, which differs from the original meaning given to it by Johan Gunnar Andersson in 1906. Origin and evolution of the concept In the original sense it meant the movement of waste saturated in water found in periglacial regions. However it was later discovered that various slow waste movements in periglacial regions did not require saturation in water, but were rather associated to freeze-thaw processes. The term solifluction was appropriated to refer to these slow processes, and therefore excludes rapid periglacial movements. In slow periglacial solifluction there are not clear gliding planes, and therefore skinflows and active layer detachments are not included in the concept. On the other hand, movement of waste saturated in water can occur in any humid climate, and therefore this kind of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aeolian Processes
Aeolian processes, also spelled eolian, pertain to wind activity in the study of geology and weather and specifically to the wind's ability to shape the surface of the Earth (or other planets). Winds may erode, transport, and deposit materials and are effective agents in regions with sparse vegetation, a lack of soil moisture and a large supply of unconsolidated sediments. Although water is a much more powerful eroding force than wind, aeolian processes are important in arid environments such as deserts. The term is derived from the name of the Greek god Aeolus, the keeper of the winds. Definition and setting ''Aeolian processes'' are those processes of erosion, transport, and deposition of sediments that are caused by wind at or near the surface of the earth. Sediment deposits produced by the action of wind and the sedimentary structures characteristic of these deposits are also described as ''aeolian''. Aeolian processes are most important in areas where there is little or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blown Sand
Blow commonly refers to: *Cocaine *Exhalation *Strike (attack) Blow, Blew, Blowing, or Blown may also refer to: People * Blew (surname) * Blow (surname) Arts and entertainment Music *The Blow, an American electro-pop band Albums * ''Blow'' (Foetus album), 2001 * ''Blow'' (Ghinzu album) or the title song, 2004 * ''Blow'' (Heather Nova album), 1993 * ''Blow'' (Messy Marv and Berner album), 2009 **'' Blow: Blocks and Boat Docks'' or the title song, by Messy Marv and Berner, 2010 * ''Blow'' (Red Lorry Yellow Lorry album) or the title song, 1989 * ''Blow'' (Straitjacket Fits album), 1993 Songs *"Blew", by Nirvana, 1989 * "Blow" (Beyoncé song), 2013 * "Blow" (Ed Sheeran, Chris Stapleton and Bruno Mars song), 2019 * "Blow" (Kesha song), 2011 * "Blow" (Martin Solveig song), 2014 *"B.L.O.W.", by Tory Lanez, 2015 *"Blow", by Ashnikko, 2018 *"Blow", by Atreyu from ''Lead Sails Paper Anchor'', 2007 *"Blow", by the Prom Kings from ''The Prom Kings'', 2005 *"Blow", by Rick Ross from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Loess
Loess (, ; from german: Löss ) is a clastic, predominantly silt-sized sediment that is formed by the accumulation of wind-blown dust. Ten percent of Earth's land area is covered by loess or similar deposits. Loess is a periglacial or aeolian (windborne) sediment, defined as an accumulation of 20% or less of clay and a balance of roughly equal parts sand and silt (with a typical grain size from 20 to 50 micrometers), often loosely cemented by calcium carbonate. It is usually homogeneous and highly porous and is traversed by vertical capillaries that permit the sediment to fracture and form vertical bluffs. Properties Loess is homogeneous, porous, friable, pale yellow or buff, slightly coherent, typically non- stratified and often calcareous. Loess grains are angular, with little polishing or rounding, and composed of crystals of quartz, feldspar, mica and other minerals. Loess can be described as a rich, dust-like soil. Loess deposits may become very thick, more than ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gelifluction
Gelifluction, very similar to solifluction, is the seasonal freeze-thaw action upon waterlogging topsoils which induces downslope movement. Gelifluction is prominent in periglacial Periglaciation (adjective: "periglacial", also referring to places at the edges of glacial areas) describes geomorphic processes that result from seasonal thawing of snow in areas of permafrost, the runoff from which refreezes in ice wedges and o ... regions where snow falls during six to eight months of the year. In spring, the snow and ice melt, and the landscape is effectively inundated with half a year's worth of rainfall in the space of a couple of days. The top soil becomes waterlogged, and flows like a liquid. Because the wet soil behaves like a fluid, gelifluction is a form of mass movement that can occur on slopes with a slope angle of less than half a degree. Landforms The most distinctive landforms created by gelifluction include gelifluction lobes and gelifluction benches. The former refe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Solifluction
Solifluction is a collective name for gradual processes in which a mass moves down a slope ("mass wasting") related to freeze-thaw activity. This is the standard modern meaning of solifluction, which differs from the original meaning given to it by Johan Gunnar Andersson in 1906. Origin and evolution of the concept In the original sense it meant the movement of waste saturated in water found in periglacial regions. However it was later discovered that various slow waste movements in periglacial regions did not require saturation in water, but were rather associated to freeze-thaw processes. The term solifluction was appropriated to refer to these slow processes, and therefore excludes rapid periglacial movements. In slow periglacial solifluction there are not clear gliding planes, and therefore skinflows and active layer detachments are not included in the concept. On the other hand, movement of waste saturated in water can occur in any humid climate, and therefore this kind of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Soil
Soil, also commonly referred to as earth or dirt, is a mixture of organic matter, minerals, gases, liquids, and organisms that together support life. Some scientific definitions distinguish ''dirt'' from ''soil'' by restricting the former term specifically to displaced soil. Soil consists of a solid phase of minerals and organic matter (the soil matrix), as well as a porous phase that holds gases (the soil atmosphere) and water (the soil solution). Accordingly, soil is a three-state system of solids, liquids, and gases. Soil is a product of several factors: the influence of climate, relief (elevation, orientation, and slope of terrain), organisms, and the soil's parent materials (original minerals) interacting over time. It continually undergoes development by way of numerous physical, chemical and biological processes, which include weathering with associated erosion. Given its complexity and strong internal connectedness, soil ecologists regard soil as an ecosystem. Most ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Colluvium
Colluvium (also colluvial material or colluvial soil) is a general name for loose, unconsolidated sediments that have been deposited at the base of hillslopes by either rainwash, sheetwash, slow continuous downslope creep, or a variable combination of these processes. Colluvium is typically composed of a heterogeneous range of rock types and sediments ranging from silt to Rock (geology), rock fragments of various sizes. This term is also used to specifically refer to sediment deposited at the base of a hillslope by unconcentrated surface runoff or sheet erosion. Location Colluviation refers to the buildup of colluvium at the base of a hillslope.Jackson, JA, J Mehl, and K. Neuendorf (2005) ''Glossary of Geology'' American Geological Institute, Alexandria, Virginia. 800 pp. Goodie, AS (2003) ''Colluvium'' in A. S. Goodie, ed., pp. 173, Encyclopedia of Geomorphology Volume 1, A–I. Routledge, New York, New York. 1200 pp. Colluvium is typically loosely consolidated angular materi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chalk
Chalk is a soft, white, porous, sedimentary carbonate rock. It is a form of limestone composed of the mineral calcite and originally formed deep under the sea by the compression of microscopic plankton that had settled to the sea floor. Chalk is common throughout Western Europe, where deposits underlie parts of France, and steep cliffs are often seen where they meet the sea in places such as the Dover cliffs on the Kent coast of the English Channel. Chalk is mined for use in industry, such as for quicklime, bricks and builder's putty, and in agriculture, for raising pH in soils with high acidity. It is also used for " blackboard chalk" for writing and drawing on various types of surfaces, although these can also be manufactured from other carbonate-based minerals, or gypsum. Description Chalk is a fine-textured, earthy type of limestone distinguished by its light color, softness, and high porosity. It is composed mostly of tiny fragments of the calcite shells or skeletons ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flint
Flint, occasionally flintstone, is a sedimentary cryptocrystalline form of the mineral quartz, categorized as the variety of chert that occurs in chalk or marly limestone. Flint was widely used historically to make stone tools and start fires. It occurs chiefly as nodules and masses in sedimentary rocks, such as chalks and limestones.''The Flints from Portsdown Hill'' Inside the nodule, flint is usually dark grey, black, green, white or brown in colour, and often has a glassy or waxy appearance. A thin layer on the outside of the nodules is usually different in colour, typically white and rough in texture. The nodules can often be found along s and |




%2C_Western_Negev%2C_Israel.jpg)
