|
Hydrogen Molecular Ion
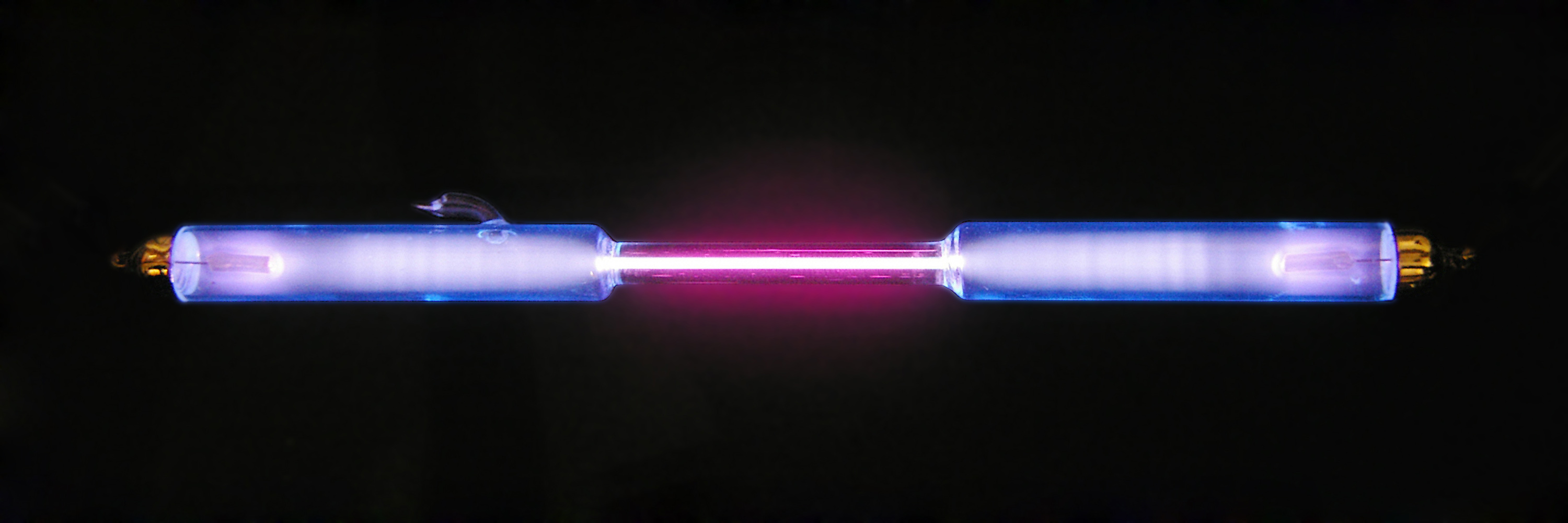
The dihydrogen cation or hydrogen molecular ion is a cation (positive ion) with formula . It consists of two hydrogen nuclei (protons) sharing a single electron. It is the simplest molecular ion. The ion can be formed from the ionization of a neutral hydrogen molecule . It is commonly formed in molecular clouds in space, by the action of cosmic rays. The dihydrogen cation is of great historical and theoretical interest because, having only one electron, the equations of quantum mechanics that describe its structure can be solved in a relatively straightforward way. The first such solution was derived by Ø. Burrau in 1927, just one year after the wave theory of quantum mechanics was published. Physical properties Bonding in can be described as a covalent one-electron bond, which has a formal bond order of one half. The ground state energy of the ion is -0.597 Hartree. Isotopologues The dihydrogen cation has six isotopologues, that result from replacement of one or more ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cation
An ion () is an atom or molecule with a net electrical charge. The charge of an electron is considered to be negative by convention and this charge is equal and opposite to the charge of a proton, which is considered to be positive by convention. The net charge of an ion is not zero because its total number of electrons is unequal to its total number of protons. A cation is a positively charged ion with fewer electrons than protons while an anion is a negatively charged ion with more electrons than protons. Opposite electric charges are pulled towards one another by electrostatic force, so cations and anions attract each other and readily form ionic compounds. Ions consisting of only a single atom are termed atomic or monatomic ions, while two or more atoms form molecular ions or polyatomic ions. In the case of physical ionization in a fluid (gas or liquid), "ion pairs" are created by spontaneous molecule collisions, where each generated pair consists of a free electron and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deuterium
Deuterium (or hydrogen-2, symbol or deuterium, also known as heavy hydrogen) is one of two Stable isotope ratio, stable isotopes of hydrogen (the other being Hydrogen atom, protium, or hydrogen-1). The atomic nucleus, nucleus of a deuterium atom, called a deuteron, contains one proton and one neutron, whereas the far more common protium has no neutrons in the nucleus. Deuterium has a natural abundance in Earth's oceans of about one atom of deuterium among all atoms of hydrogen (see heavy water). Thus deuterium accounts for approximately 0.0156% by number (0.0312% by mass) of all the naturally occurring hydrogen in the oceans, while protium accounts for more than 99.98%. The abundance of deuterium changes slightly from one kind of natural water to another (see Vienna Standard Mean Ocean Water). (Tritium is yet another hydrogen isotope, with two neutrons, that is far more rare and is radioactive.) The name ''deuterium'' is derived from the Greek , meaning "second", to denot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Harold Urey
Harold Clayton Urey ( ; April 29, 1893 – January 5, 1981) was an American physical chemist whose pioneering work on isotopes earned him the Nobel Prize in Chemistry in 1934 for the discovery of deuterium. He played a significant role in the development of the atom bomb, as well as contributing to theories on the development of organic life from non-living matter. Born in Walkerton, Indiana, Urey studied thermodynamics under Gilbert N. Lewis at the University of California, Berkeley. After he received his PhD in 1923, he was awarded a fellowship by the American-Scandinavian Foundation to study at the Niels Bohr Institute in Copenhagen. He was a research associate at Johns Hopkins University before becoming an associate professor of Chemistry at Columbia University. In 1931, he began work with the separation of isotopes that resulted in the discovery of deuterium. During World War II, Urey turned his knowledge of isotope separation to the problem of uranium enrichment. He he ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wolfgang Pauli
Wolfgang Ernst Pauli (; ; 25 April 1900 – 15 December 1958) was an Austrian theoretical physicist and one of the pioneers of quantum physics. In 1945, after having been nominated by Albert Einstein, Pauli received the Nobel Prize in Physics for his "decisive contribution through his discovery of a new law of Nature, the exclusion principle or Pauli principle". The discovery involved spin theory, which is the basis of a theory of the structure of matter. Early years Pauli was born in Vienna to a chemist, Wolfgang Joseph Pauli (''né'' Wolf Pascheles, 1869–1955), and his wife, Bertha Camilla Schütz; his sister was Hertha Pauli, a writer and actress. Pauli's middle name was given in honor of his godfather, physicist Ernst Mach. Pauli's paternal grandparents were from prominent families of Prague; his great-grandfather was the publisher Wolf Pascheles. Pauli's mother, Bertha Schütz, was raised in her mother's Roman Catholic religion; Pauli was raised as a Roman Catholic, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Karel Niessen
Karel Frederik Niessen (1895 in Velsen – 1967) was a Dutch theoretical physicist who made contributions to quantum mechanics and is known for the Pauli–Niessen model. Education Niessen began his studies in physics at the University of Utrecht in 1914. In 1922, he received his doctorate under L. S. Ornstein. He was an assistant at the University from 1921 to 1928, except for his postdoctoral study and research at the Ludwig Maximilian University of Munich under Arnold Sommerfeld, 1925 to 1926 on a Rockefeller Foundation Fellowship. He also spent 1928 to 1929 on a Rockefeller Foundation Fellowship at the University of Wisconsin–Madison.Author Catalog: Niessen – American Philosophical Society In 1922, Niessen’s doctoral thesis, as well as [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Old Quantum Theory
The old quantum theory is a collection of results from the years 1900–1925 which predate modern quantum mechanics. The theory was never complete or self-consistent, but was rather a set of heuristic corrections to classical mechanics. The theory is now understood as the semi-classical approximation to modern quantum mechanics. The main and final accomplishments of the old quantum theory were the determination of the modern form of the periodic table by Edmund Stoner and the Pauli Exclusion Principle which were both premised on the Arnold Sommerfeld enhancements to the Bohr model of the atom. The main tool of the old quantum theory was the Bohr–Sommerfeld quantization condition, a procedure for selecting out certain states of a classical system as allowed states: the system can then only exist in one of the allowed states and not in any other state. History The old quantum theory was instigated by the 1900 work of Max Planck on the emission and absorption of light in a bla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Erwin Schrödinger
Erwin Rudolf Josef Alexander Schrödinger (, ; ; 12 August 1887 – 4 January 1961), sometimes written as or , was a Nobel Prize-winning Austrian physicist with Irish citizenship who developed a number of fundamental results in quantum theory: the Schrödinger equation provides a way to calculate the wave function of a system and how it changes dynamically in time. In addition, he wrote many works on various aspects of physics: statistical mechanics and thermodynamics, physics of dielectrics, colour theory, electrodynamics, general relativity, and cosmology, and he made several attempts to construct a unified field theory. In his book ''What Is Life?'' Schrödinger addressed the problems of genetics, looking at the phenomenon of life from the point of view of physics. He also paid great attention to the philosophical aspects of science, ancient, and oriental philosophical concepts, ethics, and religion. He also wrote on philosophy and theoretical biology. In popular culture, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quantum Chemistry
Quantum chemistry, also called molecular quantum mechanics, is a branch of physical chemistry focused on the application of quantum mechanics to chemical systems, particularly towards the quantum-mechanical calculation of electronic contributions to physical and chemical properties of Molecule, molecules, Material, materials, and solutions at the atomic level. These calculations include systematically applied approximations intended to make calculations computationally feasible while still capturing as much information about important contributions to the computed Wave function, wave functions as well as to observable properties such as structures, spectra, and thermodynamic properties. Quantum chemistry is also concerned with the computation of quantum effects on molecular dynamics and chemical kinetics. Chemists rely heavily on spectroscopy through which information regarding the Quantization (physics), quantization of energy on a molecular scale can be obtained. Common metho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Experimental Mathematics
Experimental mathematics is an approach to mathematics in which computation is used to investigate mathematical objects and identify properties and patterns. It has been defined as "that branch of mathematics that concerns itself ultimately with the codification and transmission of insights within the mathematical community through the use of experimental (in either the Galilean, Baconian, Aristotelian or Kantian sense) exploration of conjectures and more informal beliefs and a careful analysis of the data acquired in this pursuit." As expressed by Paul Halmos: "Mathematics is not a deductive science—that's a cliché. When you try to prove a theorem, you don't just list the hypotheses, and then start to reason. What you do is trial and error, experimentation, guesswork. You want to find out what the facts are, and what you do is in that respect similar to what a laboratory technician does." History Mathematicians have always practiced experimental mathematics. Existing records of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Computer Algebra System
A computer algebra system (CAS) or symbolic algebra system (SAS) is any mathematical software with the ability to manipulate mathematical expressions in a way similar to the traditional manual computations of mathematicians and scientists. The development of the computer algebra systems in the second half of the 20th century is part of the discipline of "computer algebra" or "symbolic computation", which has spurred work in algorithms over mathematical objects such as polynomials. Computer algebra systems may be divided into two classes: specialized and general-purpose. The specialized ones are devoted to a specific part of mathematics, such as number theory, group theory, or teaching of elementary mathematics. General-purpose computer algebra systems aim to be useful to a user working in any scientific field that requires manipulation of mathematical expressions. To be useful, a general-purpose computer algebra system must include various features such as: *a user interface allo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lambert W Function
In mathematics, the Lambert function, also called the omega function or product logarithm, is a multivalued function, namely the Branch point, branches of the converse relation of the function , where is any complex number and is the exponential function. For each integer there is one branch, denoted by , which is a complex-valued function of one complex argument. is known as the principal branch. These functions have the following property: if and are any complex numbers, then :w e^ = z holds if and only if :w=W_k(z) \ \ \text k. When dealing with real numbers only, the two branches and suffice: for real numbers and the equation :y e^ = x can be solved for only if ; we get if and the two values and if . The Lambert relation cannot be expressed in terms of elementary functions. It is useful in combinatorics, for instance, in the enumeration of tree graph, trees. It can be used to solve various equations involving exponentials (e.g. the maxima of the Planck' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electron Correlation
Electronic correlation is the interaction between electrons in the electronic structure of a quantum system. The correlation energy is a measure of how much the movement of one electron is influenced by the presence of all other electrons. Atomic and molecular systems Within the Hartree–Fock method of quantum chemistry, the antisymmetric wave function is approximated by a single Slater determinant. Exact wave functions, however, cannot generally be expressed as single determinants. The single-determinant approximation does not take into account Coulomb correlation, leading to a total electronic energy different from the exact solution of the non-relativistic Schrödinger equation within the Born–Oppenheimer approximation. Therefore, the Hartree–Fock limit is always above this exact energy. The difference is called the ''correlation energy'', a term coined by Löwdin. The concept of the correlation energy was studied earlier by Wigner. A certain amount of electron cor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |