|
Hydrogen Hypothesis
The hydrogen hypothesis is a model proposed by William F. Martin and Miklós Müller in 1998 that describes a possible way in which the mitochondrion arose as an endosymbiont within a prokaryotic host in the archaea, giving rise to a symbiotic association of two cells from which the first eukaryotic cell could have arisen (symbiogenesis). According to the hydrogen hypothesis: * The hosts that acquired the mitochondria were hydrogen-dependent archaea, possibly similar in physiology to modern methanogenic archaea, which use hydrogen and carbon dioxide to produce methane; * The future mitochondrion was a facultatively anaerobic eubacterium which produced hydrogen and carbon dioxide as byproducts of anaerobic respiration; * A symbiotic relationship between the two started, based on the host's hydrogen dependence (anaerobic syntrophy). Mechanism The hypothesis differs from many alternative views within the endosymbiotic theory framework, which suggest that the first eukaryotic cells e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William F
William is a male given name of Germanic origin.Hanks, Hardcastle and Hodges, ''Oxford Dictionary of First Names'', Oxford University Press, 2nd edition, , p. 276. It became very popular in the English language after the Norman conquest of England in 1066,All Things William"Meaning & Origin of the Name"/ref> and remained so throughout the Middle Ages and into the modern era. It is sometimes abbreviated "Wm." Shortened familiar versions in English include Will, Wills, Willy, Willie, Bill, and Billy. A common Irish form is Liam. Scottish diminutives include Wull, Willie or Wullie (as in Oor Wullie or the play ''Douglas''). Female forms are Willa, Willemina, Wilma and Wilhelmina. Etymology William is related to the given name ''Wilhelm'' (cf. Proto-Germanic ᚹᛁᛚᛃᚨᚺᛖᛚᛗᚨᛉ, ''*Wiljahelmaz'' > German ''Wilhelm'' and Old Norse ᚢᛁᛚᛋᛅᚼᛅᛚᛘᛅᛋ, ''Vilhjálmr''). By regular sound changes, the native, inherited English form of the name shoul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Endosymbiotic Theory
Symbiogenesis (endosymbiotic theory, or serial endosymbiotic theory,) is the leading evolutionary theory of the origin of eukaryotic cells from prokaryotic organisms. The theory holds that mitochondria, plastids such as chloroplasts, and possibly other organelles of eukaryotic cells are descended from formerly free-living prokaryotes (more closely related to the Bacteria than to the Archaea) taken one inside the other in endosymbiosis. Mitochondria appear to be phylogenetically related to Rickettsiales bacteria, while chloroplasts are thought to be related to cyanobacteria. The idea that chloroplasts were originally independent organisms that merged into a symbiotic relationship with other one-celled organisms dates back to the 19th century, when it was espoused by researchers such as Andreas Schimper. The endosymbiotic theory was articulated in 1905 and 1910 by the Russian botanist Konstantin Mereschkowski, and advanced and substantiated with microbiological evidence by Lynn M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archezoa
Archezoa was a kingdom proposed in the 20th century by Thomas Cavalier-Smith (1942–2021), and was believed to encompass eukaryotes which did not have mitochondria (and are therefore ''amitochondriate'') or peroxisomes (e.g. '' Giardia''). The category was dropped after it was discovered that all the amitochondriates were descendants of eukaryotes with mitochondria that had lost them. History Origin This taxonomic category was proposed upon the discovery that some protists lacked mitochondria, which suggested to Cavalier-Smith that the initial ancestor of eukaryotes emerged prior to the endosymbiosis of mitochondria (cf. '' Giardia''). Eukaryotes that eventually acquired a bacterial endosymbiont that became the mitochondria were placed in a taxonomic group which Cavalier-Smith called the Metakaryota, whereas the Archezoa represented a paraphyletic group involving four phyla representing primitive eukaryotes which evolved prior to the acquisition of mitochondria. Organisms making up ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Actin
Actin is a family of globular multi-functional proteins that form microfilaments in the cytoskeleton, and the thin filaments in muscle fibrils. It is found in essentially all eukaryotic cells, where it may be present at a concentration of over 100 μM; its mass is roughly 42 kDa, with a diameter of 4 to 7 nm. An actin protein is the monomeric subunit of two types of filaments in cells: microfilaments, one of the three major components of the cytoskeleton, and thin filaments, part of the contractile apparatus in muscle cells. It can be present as either a free monomer called G-actin (globular) or as part of a linear polymer microfilament called F-actin (filamentous), both of which are essential for such important cellular functions as the mobility and contraction of cells during cell division. Actin participates in many important cellular processes, including muscle contraction, cell motility, cell division and cytokinesis, vesicle and organelle movement, cell sign ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lokiarchaeota
Lokiarchaeota is a proposed phylum of the Archaea. The phylum includes all members of the group previously named Deep Sea Archaeal Group (DSAG), also known as Marine Benthic Group B (MBG-B). Lokiarchaeota is part of the superphylum Asgard containing the phyla: Lokiarchaeota, Thorarchaeota, Odinarchaeota, Heimdallarchaeota, and Helarchaeota. A phylogenetic analysis disclosed a monophyletic grouping of the Lokiarchaeota with the eukaryotes. The analysis revealed several genes with cell membrane-related functions. The presence of such genes support the hypothesis of an archaeal host for the emergence of the eukaryotes; the eocyte-like scenarios. Lokiarchaeota was introduced in 2015 after the identification of a candidate genome in a metagenomic analysis of a mid-oceanic sediment sample. This analysis suggests the existence of a genus of unicellular life dubbed ''Lokiarchaeum''. The sample was taken near a hydrothermal vent at a vent field known as Loki's Castle located at the ben ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chimera (genetics)
A genetic chimerism or chimera ( ) is a single organism composed of cells with more than one distinct genotype. In animals, this means an individual derived from two or more zygotes, which can include possessing blood cells of different blood types, subtle variations in form (phenotype) and, if the zygotes were of differing sexes, then even the possession of both female and male sex organs. Animal chimeras are produced by the merger of two (or more) embryos. In plant chimeras, however, the distinct types of tissue may originate from the same zygote, and the difference is often due to mutation during ordinary cell division. Normally, genetic chimerism is not visible on casual inspection; however, it has been detected in the course of proving parentage. Another way that chimerism can occur in animals is by organ transplantation, giving one individual tissues that developed from a different genome. For example, transplantation of bone marrow often determines the recipient's en ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acetate
An acetate is a salt (chemistry), salt formed by the combination of acetic acid with a base (e.g. Alkali metal, alkaline, Alkaline earth metal, earthy, Transition metal, metallic, nonmetallic or radical Radical (chemistry), base). "Acetate" also describes the conjugate acid, conjugate base or ion (specifically, the negatively charged ion called an anion) typically found in aqueous solution and written with the chemical formula . The neutral molecules formed by the combination of the acetate ion and a ''positive'' ion (called a cation) are also commonly called "acetates" (hence, ''acetate of lead'', ''acetate of aluminum'', etc.). The simplest of these is hydrogen acetate (called acetic acid) with corresponding salts, esters, and the polyatomic ion, polyatomic anion , or . Most of the approximately 5 billion kilograms of acetic acid produced annually in industry are used in the production of acetates, which usually take the form of polymers. In nature, acetate is the most common ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pyruvate
Pyruvic acid (CH3COCOOH) is the simplest of the alpha-keto acids, with a carboxylic acid and a ketone functional group. Pyruvate, the conjugate base, CH3COCOO−, is an intermediate in several metabolic pathways throughout the cell. Pyruvic acid can be made from glucose through glycolysis, converted back to carbohydrates (such as glucose) via gluconeogenesis, or to fatty acids through a reaction with acetyl-CoA. It can also be used to construct the amino acid alanine and can be converted into ethanol or lactic acid via fermentation. Pyruvic acid supplies energy to cells through the citric acid cycle (also known as the Krebs cycle) when oxygen is present (aerobic respiration), and alternatively ferments to produce lactate when oxygen is lacking. Chemistry In 1834, Théophile-Jules Pelouze distilled tartaric acid and isolated glutaric acid and another unknown organic acid. Jöns Jacob Berzelius characterized this other acid the following year and named pyruvic acid because it ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adenosine Triphosphate
Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) is an organic compound that provides energy to drive many processes in living cells, such as muscle contraction, nerve impulse propagation, condensate dissolution, and chemical synthesis. Found in all known forms of life, ATP is often referred to as the "molecular unit of currency" of intracellular energy transfer. When consumed in metabolic processes, it converts either to adenosine diphosphate (ADP) or to adenosine monophosphate (AMP). Other processes regenerate ATP. The human body recycles its own body weight equivalent in ATP each day. It is also a precursor to DNA and RNA, and is used as a coenzyme. From the perspective of biochemistry, ATP is classified as a nucleoside triphosphate, which indicates that it consists of three components: a nitrogenous base (adenine), the sugar ribose, and the Polyphosphate, triphosphate. Structure ATP consists of an adenine attached by the 9-nitrogen atom to the 1′ carbon atom of a sugar (ribose), which i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
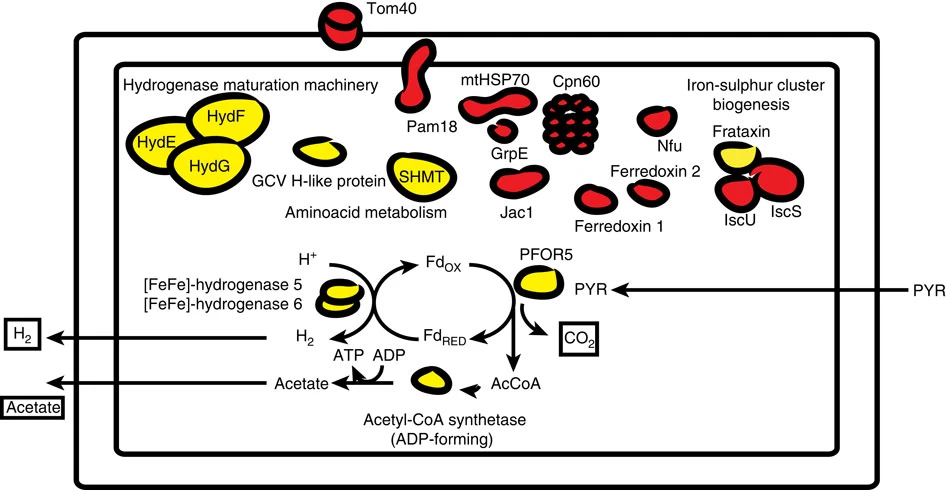
Hydrogenosome
A hydrogenosome is a membrane-enclosed organelle found in some anaerobic ciliates, flagellates, and fungi. Hydrogenosomes are highly variable organelles that have presumably evolved from protomitochondria to produce molecular hydrogen and ATP in anaerobic conditions. Hydrogenosomes were discovered in 1973 by D. G. Lindmark and M. Müller. Because hydrogenosomes hold evolutionary lineage significance for organisms living in anaerobic or oxygen-stressed environments, many research institutions have since documented their findings on how the organelle differs in various sources. History Hydrogenosomes were isolated, purified, biochemically characterized and named in the early 1970s by Lindmark and Müller at Rockefeller University. In addition to this seminal study on hydrogenosomes, they also demonstrated for the first time the presence of pyruvate:ferredoxin oxido-reductase and hydrogenase in eukaryotes. Further studies were subsequently conducted on the biochemical cytology a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Evolution
Evolution is change in the heritable characteristics of biological populations over successive generations. These characteristics are the expressions of genes, which are passed on from parent to offspring during reproduction. Variation tends to exist within any given population as a result of genetic mutation and recombination. Evolution occurs when evolutionary processes such as natural selection (including sexual selection) and genetic drift act on this variation, resulting in certain characteristics becoming more common or more rare within a population. The evolutionary pressures that determine whether a characteristic is common or rare within a population constantly change, resulting in a change in heritable characteristics arising over successive generations. It is this process of evolution that has given rise to biodiversity at every level of biological organisation, including the levels of species, individual organisms, and molecules. The theory of evolution by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bacterium
Bacteria (; singular: bacterium) are ubiquitous, mostly free-living organisms often consisting of one biological cell. They constitute a large domain of prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micrometres in length, bacteria were among the first life forms to appear on Earth, and are present in most of its habitats. Bacteria inhabit soil, water, acidic hot springs, radioactive waste, and the deep biosphere of Earth's crust. Bacteria are vital in many stages of the nutrient cycle by recycling nutrients such as the fixation of nitrogen from the atmosphere. The nutrient cycle includes the decomposition of dead bodies; bacteria are responsible for the putrefaction stage in this process. In the biological communities surrounding hydrothermal vents and cold seeps, extremophile bacteria provide the nutrients needed to sustain life by converting dissolved compounds, such as hydrogen sulphide and methane, to energy. Bacteria also live in symbiotic and parasitic relationshi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |