|
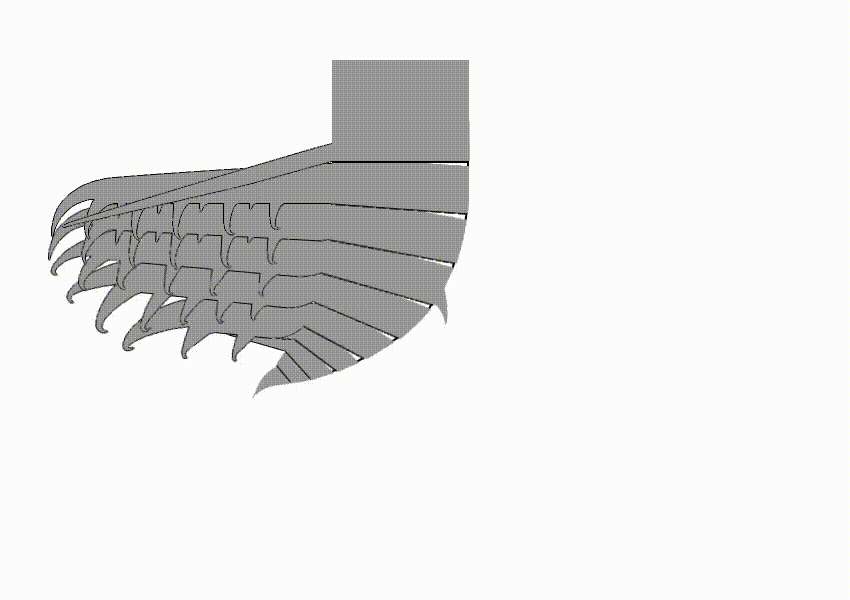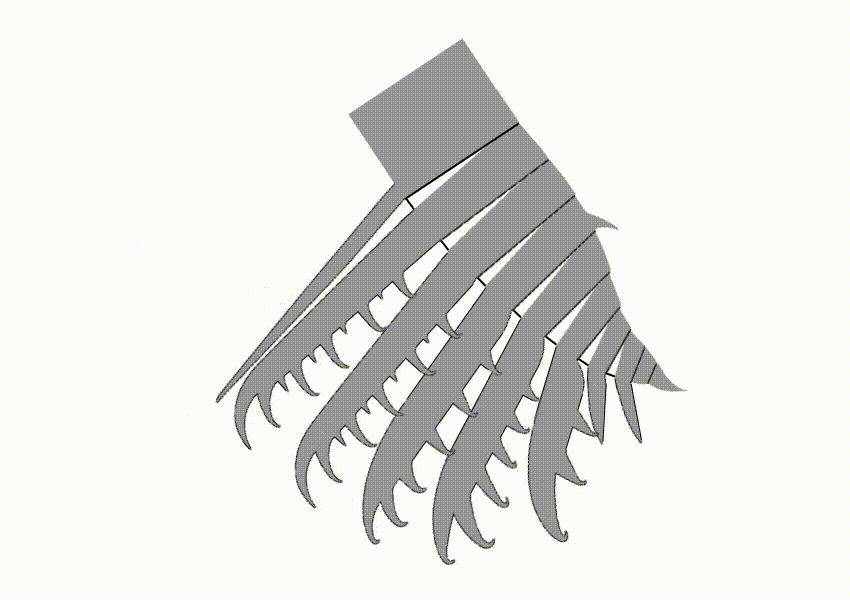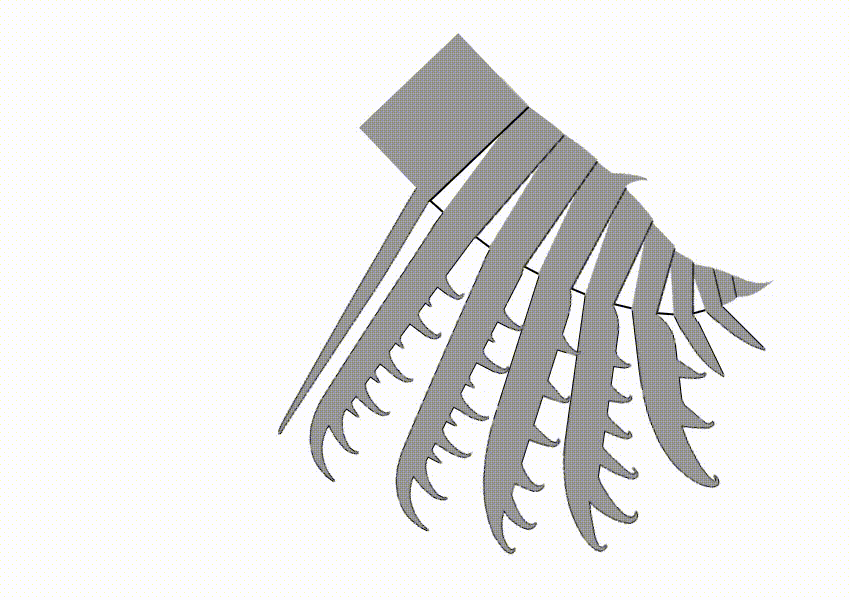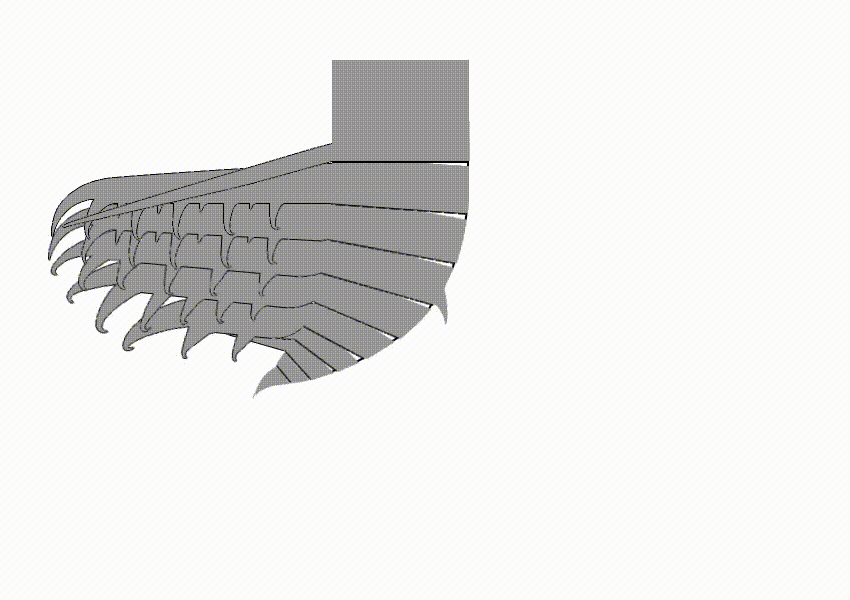
Hurdiidae
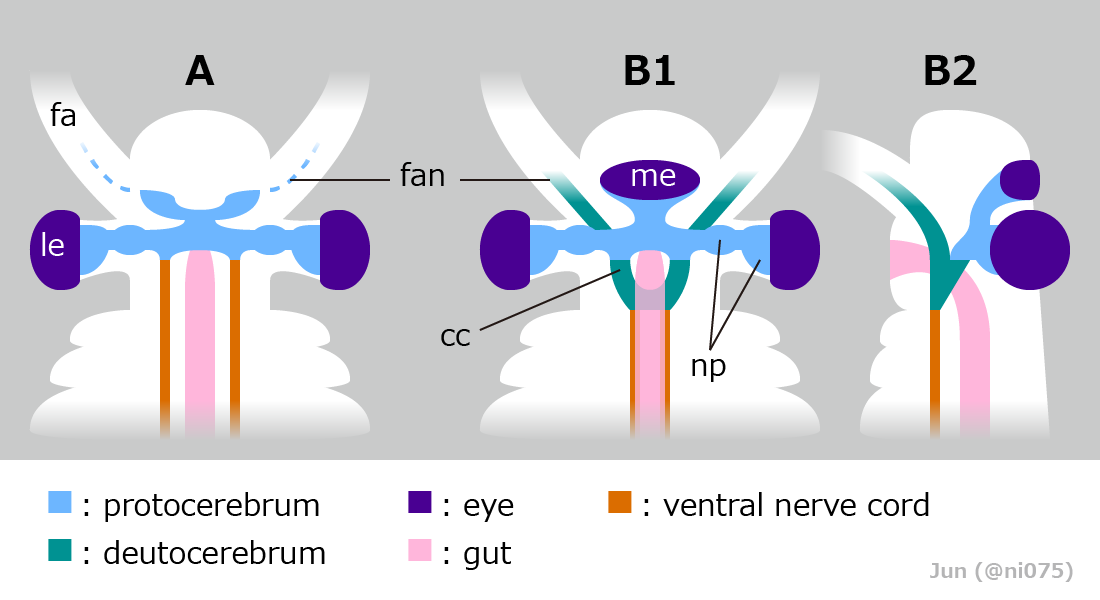
Hurdiidae is an extinct cosmopolitan distribution, cosmopolitan Family (biology), family of radiodonts, a group of Crown group#Stem groups, stem-group arthropods, which lived during the Paleozoic Era. It is the most long-lived radiodont clade, lasting from the Cambrian period to the Devonian period. Description Hurdiidae is characterized by Radiodonta#Frontal appendage, frontal appendages with distal region composed of 5 subequal blade-like endites, alongside the enlarged head carapaces and tetraradial mouthpart (Radiodonta#Oral cone, oral cone). The Radiodonta#Frontal appendage, frontal appendages of hurdiids have a distinctive morphology, with the appendage of most species bearing five equally-sized elongate blade-like ventral spines known as endites. Subsequent podomeres were reduced in size and with only small endites or none. Each podomere bore only a single endite, unlike other radiodonts, in which the endites were paired. In most species, the endites were curved med ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radiodonta
Radiodonta is an extinct Order (biology), order of stem-group arthropods that was successful worldwide during the Cambrian period. They may be referred to as radiodonts, radiodontans, radiodontids, anomalocarids, or anomalocaridids, although the last two originally refer to the family Anomalocarididae, which previously included all species of this order but is now restricted to only a few species. Radiodonts are distinguished by their distinctive frontal appendages, which are morphologically diverse and used for a variety of functions. Radiodonts included the earliest large predators known, but they also included sediment sifters and filter feeders. Some of the most famous species of radiodonts are the Cambrian taxa ''Anomalocaris, Anomalocaris canadensis'', ''Hurdia, Hurdia victoria'', ''Peytoia nathorsti'', ''Titanokorys gainesii, Titanokorys gainessii, Cambroraster, Cambroraster falcatus'' and ''Amplectobelua, Amplectobelua symbrachiata'', the Ordovician ''Aegirocassis, Aegiroca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radiodont
Radiodonta is an extinct Order (biology), order of stem-group arthropods that was successful worldwide during the Cambrian period. They may be referred to as radiodonts, radiodontans, radiodontids, anomalocarids, or anomalocaridids, although the last two originally refer to the family Anomalocarididae, which previously included all species of this order but is now restricted to only a few species. Radiodonts are distinguished by their distinctive frontal appendages, which are morphologically diverse and used for a variety of functions. Radiodonts included the earliest large predators known, but they also included sediment sifters and filter feeders. Some of the most famous species of radiodonts are the Cambrian taxa ''Anomalocaris, Anomalocaris canadensis'', ''Hurdia, Hurdia victoria'', ''Peytoia nathorsti'', ''Titanokorys gainesii, Titanokorys gainessii, Cambroraster, Cambroraster falcatus'' and ''Amplectobelua, Amplectobelua symbrachiata'', the Ordovician ''Aegirocassis, Aegiroca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stanleycaris
''Stanleycaris'' is an extinct, monotypic genus of hurdiid radiodont from the middle Cambrian (Miaolingian). The type species is ''Stanleycaris hirpex''. ''Stanleycaris'' was described from the Stephen Formation near the Stanley Glacier and Burgess Shale locality of Canada, as well as Wheeler Formation of United States. The genus was characterized by the rake-like frontal appendages with robust inner spines. ''Stanleycaris'' was originally described only from frontal appendages and oral cone. However, in 2022, 268 specimens of ''Stanleycaris'', many of which were complete, were studied, making ''Stanleycaris'' a well documented radiodont. ''Stanleycaris'' had three eyes, a bizarre configuration previously unknown among other radiodont genera; yet this head anatomy supports early differentiation among arthropod head and trunk segmentation. The original description of the taxon appeared in an online supplement to the article published by Jean-Bernard Caron, Robert R. Gaines, M. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peytoia
''Peytoia'' is a genus of hurdiid radiodont that lived in the Cambrian period, containing two species, ''Peytoia nathorsti'' from the Miaolingian of Canada and ''Peytoia infercambriensis'' from Poland, dating to Cambrian Stage 3. Its two frontal appendages had long bristle-like spines, it had no fan tail, and its short stalked eyes were behind its large head. 108 specimens of ''Peytoia'' are known from the Greater Phyllopod bed, where they comprise 0.21% of the community. ''Peytoia nathorsti'' and its junior synonym ''Laggania cambria'' played a major role in the discovery of the radiodont body plan. Initially interpreted as a jellyfish and a sea cucumber respectively, they were eventually shown to be the mouthparts and body of a single animal, which bore ''Anomalocaris''-like appendages. ''Peytoia infercambriensis'' is the geologically oldest known radiodont species. Classification ''Peytoia'' belongs to the clade Hurdiidae, and is closely related to the contemporary genus ' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Schinderhannes Bartelsi
''Schinderhannes bartelsi'' is a species of hurdiid radiodont (anomalocaridid) known from one specimen from the lower Devonian Hunsrück Slates. Its discovery was astonishing because previously, radiodonts were known only from exceptionally well-preserved fossil beds (Lagerstätten) from the Cambrian, 100 million years earlier. Discovery The single specimen was discovered in the Eschenbach-Bocksberg Quarry in Bundenbach, and is named after the outlaw Schinderhannes who frequented the area. Its specific epithet ''bartelsi'' honours Christoph Bartels, a Hunsrück Slate expert. The specimen is now housed in the Naturhistorisches Museum, Mainz. Morphology ''Schinderhannes'' is about long in full body length (6.8cm long excluding telson). Like other radiodonts, the head bears a pair of spiny frontal appendages, a radially-arranged ventral mouthpart ( oral cone), and a pair of large lateral compound eyes. Detailed morphology of the frontal appendages and oral cone are equivocal due ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hurdia
''Hurdia'' is an extinct genus of hurdiid radiodont that lived 505 million years ago during the Cambrian Period. As a radiodont like ''Peytoia'' and ''Anomalocaris'', it is part of the ancestral lineage that led to euarthropods. Description ''Hurdia'' was one of the largest organisms in the Cambrian oceans, ''H. victoria'' reached approximately in length, while ''H. triangulata'' reached up to just . Its head bore a pair of rake-like frontal appendages which shovelled food into its pineapple-ring-like mouth (oral cone). Like other hurdiids, ''Hurdia'' bore a large frontal carapace protruding from its head composed of three sclerites: a central component known as the H-element and two lateral components known as P-elements. The function of this organ remains mysterious; it cannot have been protective as there was no underlying soft tissue. Originally, it is estimated that body flaps ran along the sides of the organisms, from which large gills were suspended. However, anatomy of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peytoia Infercambriensis
''Peytoia infercambriensis'' is a species of hurdiid radiodont in the genus ''Peytoia''. ''P. infercambriensis'' is the geologically oldest known radiodont; its remains date to the third age of the Cambrian. The type and only known specimen, a partial appendage, was found in a core sample from a borehole nearly five kilometers deep in northern Poland. ''P. infercambriensis'' was previously regarded as belonging to a separate genus, ''Cassubia'', named after the historical region of Kashubia in which the specimen was found, but ''Cassubia'' is now considered a junior synonym of ''Peytoia''. History of study Discovery and naming The holotype—and only—specimen was recovered from the Kościerzyna borehole, in the Cambrian Stage 3 aged Zawiszyn Formation. It was found in the Fallotaspis Zone making it older than the Chengjiang biota. It was described by Kazimiera Lendzion in 1975 and given the name ''Pomerania infercambriensis'', in reference to its Lower Cambrian provenance a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ursulinacaris
''Ursulinacaris'' is a genus of hurdiid radiodont from the Cambrian of North America. It contains one known species, ''Ursulinacaris grallae''. It was described in 2019, based on fossils of the frontal appendages discovered in the 1990s and thereafter. Unlike all other hurdiids, but like non-hurdiid radiodont, the frontal appendages of ''Ursulinacaris'' have two rows of ventral spines called endites instead of one. The endites of ''Ursulinacaris'' were very slender, unlike other hurdiids such as ''Peytoia'' or ''Hurdia''. ''Ursulinacaris'' helps resolve the evolution of hurdiid anatomy, showing what order characteristics of the frontal appendages evolved in by showing that the distinctive shape of hurdiid endites evolved before they transitioned from two rows to one row of endites. Discovery and naming ''Ursulinacaris'' fossils have been found in the Northwest Territories and Nevada. Most specimens come from the Little Bear biota of the Mount Cap Formation, though one referred s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hurdia Victoria
''Hurdia'' is an extinct genus of hurdiid radiodont that lived 505 million years ago during the Cambrian Period. As a radiodont like ''Peytoia'' and ''Anomalocaris'', it is part of the ancestral lineage that led to euarthropods. Description ''Hurdia'' was one of the largest organisms in the Cambrian oceans, ''H. victoria'' reached approximately in length, while ''H. triangulata'' reached up to just . Its head bore a pair of rake-like frontal appendages which shovelled food into its pineapple-ring-like mouth (oral cone). Like other hurdiids, ''Hurdia'' bore a large frontal carapace protruding from its head composed of three sclerites: a central component known as the H-element and two lateral components known as P-elements. The function of this organ remains mysterious; it cannot have been protective as there was no underlying soft tissue. Originally, it is estimated that body flaps ran along the sides of the organisms, from which large gills were suspended. However, anatomy of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anomalocaris Canadensis
''Anomalocaris'' ("unlike other shrimp", or "abnormal shrimp") is an extinct genus of radiodont, an order of early-diverging stem-group arthropods. The first fossils of ''Anomalocaris'' were discovered in the ''Ogygopsis'' Shale of the Stephen Formation in British Columbia, Canada by Joseph Frederick Whiteaves, with more examples found by Charles Doolittle Walcott in the Burgess Shale unit of the Stephen Formation. Other closely related fossils have been found in the older Emu Bay Shale of Australia, as well as possibly elsewhere. Originally several fossilized parts discovered separately (the mouth, frontal appendages and trunk) were thought to be three separate creatures, a misapprehension corrected by Harry B. Whittington and Derek Briggs in a 1985 journal article. With a body length close to 40 centimetres, ''A. canadensis'' is thought to be one of the earliest examples of an apex predator, though others have been found in older Cambrian lagerstätten deposits. Discovery ''A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cambroraster
''Cambroraster'' is an extinct monotypic genus of hurdiid radiodont, dating to the middle Cambrian, and represented by the single formally described species ''Cambroraster falcatus''. Hundreds of specimens were found in the Burgess Shale, and described in 2019. A large animal (for its era) at up to 30cm long (but not as long as ''Titanokorys'' at 50 cm), it is characterized by a significantly enlarged horseshoe-shaped dorsal carapace (H-element), and presumably fed by sifting through the sediment with its well-developed tooth plates ( oral cone) and short frontal appendages with hooked spines. It is named partially after the fictional Millennium Falcon, which its dorsal carapace resembles. File:20200329 Cambroraster falcatus.png, Reconstruction File:20210516 Radiodonta head sclerites Cambroraster falcatus.png, Head sclerites File:20191229 Radiodonta frontal appendage Cambroraster falcatus.png, Frontal appendage File:20210813 Cambroraster falcatus frontal appendage mobility. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aegirocassis
''Aegirocassis'' is an extinct genus of radiodont arthropod belonging to the family Hurdiidae that lived 480 million years ago during the early Ordovician. It is known by a single species, ''Aegirocassis benmoulai''. Van Roy initiated scientific study of the fossil, the earliest known of a "giant" filter-feeder discovered to date. ''Aegirocassis'' is considered to have evolved from early predatory radiodonts. Description File:20210221 Aegirocassis size.png, Size estimation File:YPM 527123 Aegirocassis benmoulai frontal appendage.png, Fossil of frontal appendage File:20191229 Radiodonta frontal appendage Aegirocassis benmoulai Aegirocassis benmoulae.png, Reconstruction of frontal appendage ''A. benmoulai'' was the largest known radiodont and largest animal existed in this period, and the length was described as exceeding in the scientific journal ''Nature''. The fossil was preserved with exceptional three-dimensional detail, unlike most other radiodont fossils, in which the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |