|
Human Computation
Human-based computation (HBC), human-assisted computation, ubiquitous human computing or distributed thinking (by analogy to distributed computing) is a computer science technique in which a machine performs its function by outsourcing certain steps to humans, usually as microwork. This approach uses differences in abilities and alternative costs between humans and computer agents to achieve symbiotic human–computer interaction. For computationally difficult tasks such as image recognition, human-based computation plays a central role in training Deep Learning-based Artificial Intelligence systems. In this case, human-based computation has been referred to as human-aided artificial intelligence. In traditional computation, a human employs a computer to solve a problem; a human provides a formalized problem description and an algorithm to a computer, and receives a solution to interpret. Human-based computation frequently reverses the roles; the computer asks a person or a lar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Distributed Computing
A distributed system is a system whose components are located on different networked computers, which communicate and coordinate their actions by passing messages to one another from any system. Distributed computing is a field of computer science that studies distributed systems. The components of a distributed system interact with one another in order to achieve a common goal. Three significant challenges of distributed systems are: maintaining concurrency of components, overcoming the lack of a global clock, and managing the independent failure of components. When a component of one system fails, the entire system does not fail. Examples of distributed systems vary from SOA-based systems to massively multiplayer online games to peer-to-peer applications. A computer program that runs within a distributed system is called a distributed program, and ''distributed programming'' is the process of writing such programs. There are many different types of implementations for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alan Turing
Alan Mathison Turing (; 23 June 1912 – 7 June 1954) was an English mathematician, computer scientist, logician, cryptanalyst, philosopher, and theoretical biologist. Turing was highly influential in the development of theoretical computer science, providing a formalisation of the concepts of algorithm and computation with the Turing machine, which can be considered a model of a general-purpose computer. He is widely considered to be the father of theoretical computer science and artificial intelligence. Born in Maida Vale, London, Turing was raised in southern England. He graduated at King's College, Cambridge, with a degree in mathematics. Whilst he was a fellow at Cambridge, he published a proof demonstrating that some purely mathematical yes–no questions can never be answered by computation and defined a Turing machine, and went on to prove that the halting problem for Turing machines is undecidable. In 1938, he obtained his PhD from the Department of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Digg
Digg, stylized in lowercase as digg, is an American news aggregator with a curated front page, aiming to select stories specifically for the Internet audience such as science, trending political issues, and viral Internet issues. It was launched in its current form on July 31, 2012, with support for sharing content to other social platforms such as Twitter and Facebook. It formerly had been a popular social news website, allowing people to vote web content up or down, called ''digging'' and ''burying'', respectively. In 2012, Quantcast estimated Digg's monthly U.S. unique visits at 3.8 million. Digg's popularity prompted the creation of similar sites such as Reddit. In July 2008, the former company took part in advanced acquisition talks with Google for a reported $200 million price tag, but the deal ultimately fell through. After a controversial 2010 redesign and the departure of co-founders Jay Adelson and Kevin Rose, in July 2012 Digg was sold in three parts: the Digg br ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Social Search
Social search is a behavior of retrieving and searching on a social searching engine that mainly searches user-generated content such as news, videos and images related search queries on social media like Facebook, LinkedIn, Twitter, Instagram and Flickr. It is an enhanced version of web search that combines traditional algorithms. The idea behind social search is that instead of ranking search results purely based on semantic relevance between a query and the results, a social search system also takes into account social relationships between the results and the searcher. The social relationships could be in various forms. For example, in LinkedIn people search engine, the social relationships include social connections between searcher and each result, whether or not they are in the same industries, work for the same companies, belong the same social groups, and go the same schools, etc. Social search may not be demonstrably better than algorithm-driven search. In the algorithmi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Wiki Way
''The Wiki Way: Quick Collaboration on the Web'' is a 2001 book about wikis by Bo Leuf and Ward Cunningham. It was the first major book published about using wikis. Cunningham invented wikis when he wrote WikiWikiWeb The WikiWikiWeb is the first wiki, or user-editable website. It was launched on 25 March 1995 by programmer Ward Cunningham to accompany the Portland Pattern Repository website discussing software design patterns. The name ''WikiWikiWeb'' orig ..., the first wiki website software. The book is about how to manage wiki systems, followed by a perspective on the nature of wiki-style online communication. References Leuf, Bo; Cunningham, Ward. The Wiki Way External linksBook homepage Wikis [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
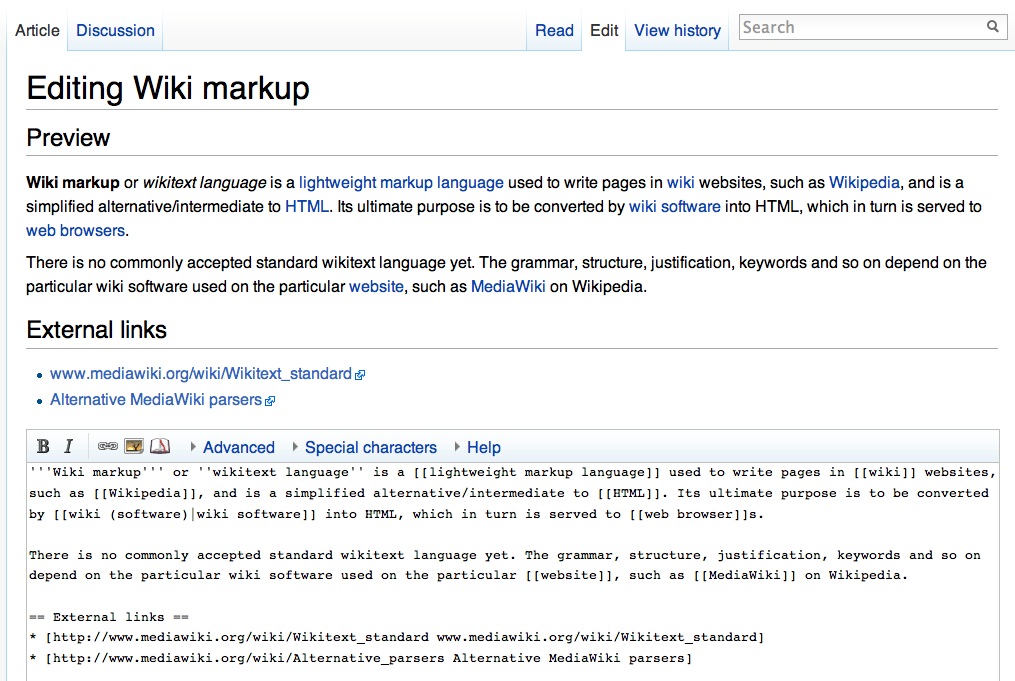
Wiki
A wiki ( ) is an online hypertext publication collaboratively edited and managed by its own audience, using a web browser. A typical wiki contains multiple pages for the subjects or scope of the project, and could be either open to the public or limited to use within an organization for maintaining its internal knowledge base. Wikis are enabled by wiki software, otherwise known as wiki engines. A wiki engine, being a form of a content management system, differs from other web-based systems such as blog software, in that the content is created without any defined owner or leader, and wikis have little inherent structure, allowing structure to emerge according to the needs of the users. Wiki engines usually allow content to be written using a simplified markup language and sometimes edited with the help of a rich-text editor. There are dozens of different wiki engines in use, both standalone and part of other software, such as bug tracking systems. Some wiki engines ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Core War
''Core War'' is a 1984 programming game created by D. G. Jones and A. K. Dewdney in which two or more battle programs (called "warriors") compete for control of a virtual computer. These battle programs are written in an abstract assembly language called ''Redcode''. The standards for the language and the virtual machine were initially set by the International Core Wars Society (ICWS), but later standards were determined by community consensus. Gameplay At the beginning of a game, each battle program is loaded into memory at a random location, after which each program executes one instruction in turn. The goal of the game is to cause the processes of opposing programs to terminate (which happens if they execute an invalid instruction), leaving the victorious program in sole possession of the machine. The earliest published version of Redcode defined only eight instructions. The ICWS-86 standard increased the number to 10 while the ICWS-88 standard increased it to 11. The curren ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Darwin (programming Game)
Darwin was a programming game invented in August 1961 by Victor A. Vyssotsky, Robert Morris Sr., and M. Douglas McIlroy. (Dennis Ritchie is sometimes incorrectly cited as a co-author, but was not involved.) The game was developed at Bell Labs, and played on an IBM 7090 mainframe there. The game was only played for a few weeks before Morris developed an "ultimate" program that eventually brought the game to an end, as no-one managed to produce anything that could defeat it. Description The game consisted of a program called the ''umpire'' and a designated section of the computer's memory known as the ''arena'', into which two or more small programs, written by the players, were loaded. The programs were written in 7090 machine code, and could call a number of functions provided by the umpire in order to probe other locations within the arena, kill opposing programs, and claim vacant memory for copies of themselves. The game ended after a set amount of time, or when copies ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wiki
A wiki ( ) is an online hypertext publication collaboratively edited and managed by its own audience, using a web browser. A typical wiki contains multiple pages for the subjects or scope of the project, and could be either open to the public or limited to use within an organization for maintaining its internal knowledge base. Wikis are enabled by wiki software, otherwise known as wiki engines. A wiki engine, being a form of a content management system, differs from other web-based systems such as blog software, in that the content is created without any defined owner or leader, and wikis have little inherent structure, allowing structure to emerge according to the needs of the users. Wiki engines usually allow content to be written using a simplified markup language and sometimes edited with the help of a rich-text editor. There are dozens of different wiki engines in use, both standalone and part of other software, such as bug tracking systems. Some wiki engines ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Interactive Genetic Algorithm
Interactive evolutionary computation (IEC) or aesthetic selection is a general term for methods of evolutionary computation that use human evaluation. Usually human evaluation is necessary when the form of fitness function is not known (for example, visual appeal or attractiveness; as in Dawkins, 1986) or the result of optimization should fit a particular user preference (for example, taste of coffee or color set of the user interface). IEC design issues The number of evaluations that IEC can receive from one human user is limited by user fatigue which was reported by many researchers as a major problem. In addition, human evaluations are slow and expensive as compared to fitness function computation. Hence, one-user IEC methods should be designed to converge using a small number of evaluations, which necessarily implies very small populations. Several methods were proposed by researchers to speed up convergence, like interactive constrain evolutionary search (user intervention) or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Computerized Adaptive Testing
Computerized adaptive testing (CAT) is a form of computer-based test that adapts to the examinee's ability level. For this reason, it has also been called tailored testing. In other words, it is a form of computer-administered test in which the next item or set of items selected to be administered depends on the correctness of the test taker's responses to the most recent items administered. How it works CAT successively selects questions for the purpose of maximizing the precision of the exam based on what is known about the examinee from previous questions. From the examinee's perspective, the difficulty of the exam seems to tailor itself to their level of ability. For example, if an examinee performs well on an item of intermediate difficulty, they will then be presented with a more difficult question. Or, if they performed poorly, they would be presented with a simpler question. Compared to static multiple choice tests that nearly everyone has experienced, with a fixed set of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genetic Algorithm
In computer science and operations research, a genetic algorithm (GA) is a metaheuristic inspired by the process of natural selection that belongs to the larger class of evolutionary algorithms (EA). Genetic algorithms are commonly used to generate high-quality solutions to optimization and search problems by relying on biologically inspired operators such as mutation, crossover and selection. Some examples of GA applications include optimizing decision trees for better performance, solving sudoku puzzles, hyperparameter optimization, etc. Methodology Optimization problems In a genetic algorithm, a population of candidate solutions (called individuals, creatures, organisms, or phenotypes) to an optimization problem is evolved toward better solutions. Each candidate solution has a set of properties (its chromosomes or genotype) which can be mutated and altered; traditionally, solutions are represented in binary as strings of 0s and 1s, but other encodings are also po ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |