|
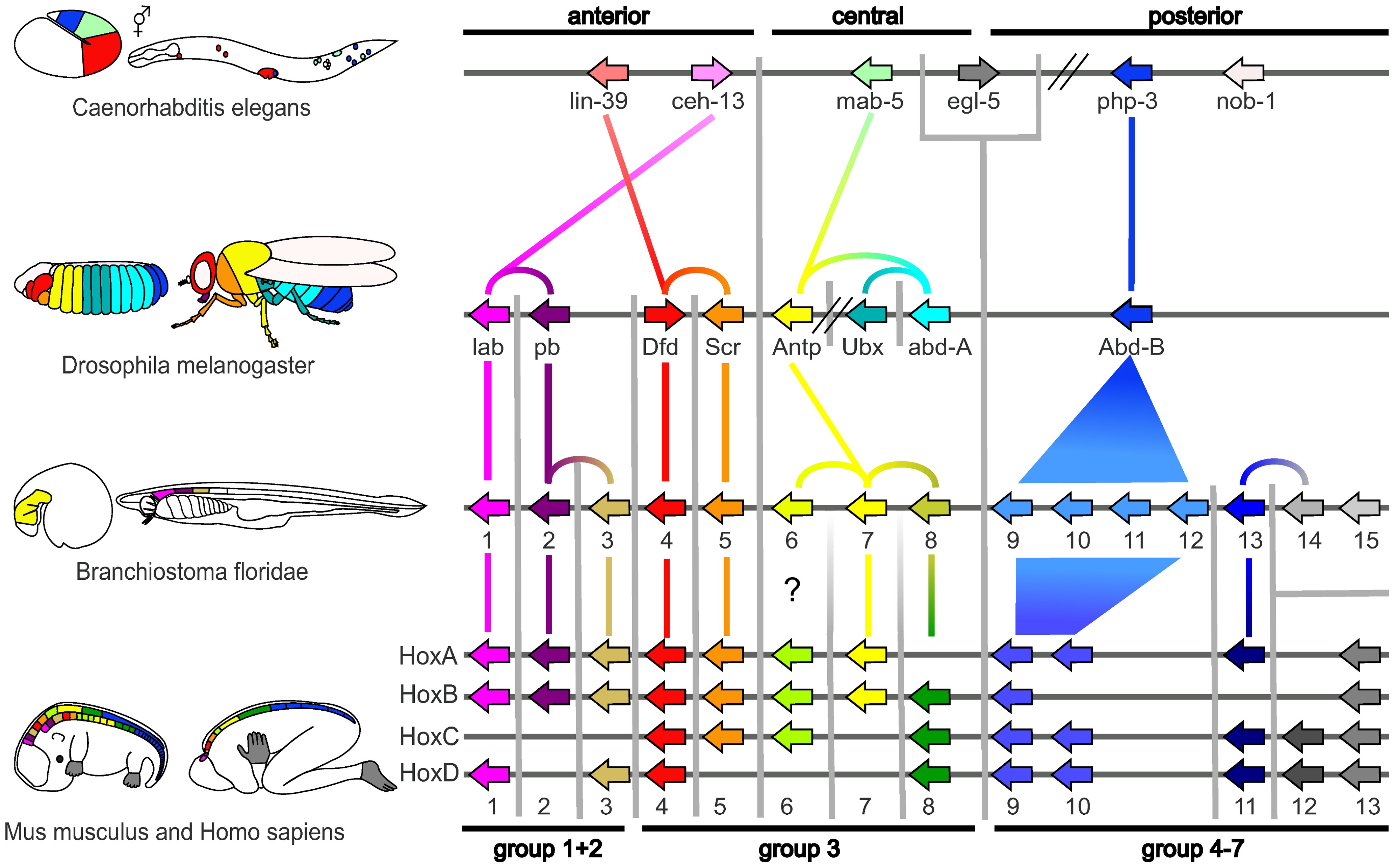
Homeotic Gene
In evolutionary developmental biology, homeotic genes are genes which regulate the development of anatomical structures in various organisms such as echinoderms, insects, mammals, and plants. Homeotic genes often encode transcription factor proteins, and these proteins affect development by regulating downstream gene networks involved in body patterning. Mutations in homeotic genes cause displaced body parts ( homeosis), such as antennae growing at the posterior of the fly instead of at the head. Mutations that lead to development of ectopic structures are usually lethal. Types There are several subsets of homeotic genes. They include many of the Hox and ParaHox genes that are important for segmentation. Hox genes are found in bilateral animals, including ''Drosophila'' (in which they were first discovered) and humans. Hox genes are a subset of the homeobox genes. The Hox genes are often conserved across species, so some of the Hox genes of ''Drosophila'' are homologous to tho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Evolutionary Developmental Biology
Evolutionary developmental biology (informally, evo-devo) is a field of biological research that compares the developmental processes of different organisms to infer how developmental processes evolved. The field grew from 19th-century beginnings, where embryology faced a mystery: zoologists did not know how embryonic development was controlled at the molecular level. Charles Darwin noted that having similar embryos implied common ancestry, but little progress was made until the 1970s. Then, recombinant DNA technology at last brought embryology together with molecular genetics. A key early discovery was of homeotic genes that regulate development in a wide range of eukaryotes. The field is composed of multiple core evolutionary concepts. One is deep homology, the finding that dissimilar organs such as the eyes of insects, vertebrates and cephalopod molluscs, long thought to have evolved separately, are controlled by similar genes such as ''pax-6'', from the evo-devo gene ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Homeotic Selector Gene Complexes
In evolutionary developmental biology, homeosis is the transformation of one organ into another, arising from mutation in or misexpression of certain developmentally critical genes, specifically homeotic genes. In animals, these developmental genes specifically control the development of organs on their anteroposterior axis. In plants, however, the developmental genes affected by homeosis may control anything from the development of a stamen or petals to the development of chlorophyll. Homeosis may be caused by mutations in Hox genes, found in animals, or others such as the MADS-box family in plants. Homeosis is a characteristic that has helped insects become as successful and diverse as they are. Homeotic mutations work by changing segment identity during development. For example, the ''Ultrabithorax'' genotype gives a phenotype wherein metathoracic and first abdominal segments become mesothoracic segments. Another well-known example is ''Antennapedia'': a gain-of-function allel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Homeobox
A homeobox is a DNA sequence, around 180 base pairs long, that regulates large-scale anatomical features in the early stages of embryonic development. For instance, mutations in a homeobox may change large-scale anatomical features of the full-grown organism. Homeoboxes are found within genes that are involved in the regulation of patterns of anatomical development (morphogenesis) in animals, fungi, plants, and numerous single cell eukaryotes. Homeobox genes encode homeodomain protein products that are transcription factors sharing a characteristic protein fold structure that binds DNA to regulate expression of target genes. Homeodomain proteins regulate gene expression and cell differentiation during early embryonic development, thus mutations in homeobox genes can cause developmental disorders. Homeosis is a term coined by William Bateson to describe the outright replacement of a discrete body part with another body part, e.g. antennapedia—replacement of the antenna ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carcinogen
A carcinogen is any substance, radionuclide, or radiation that promotes carcinogenesis (the formation of cancer). This may be due to the ability to damage the genome or to the disruption of cellular metabolic processes. Several radioactive substances are considered carcinogens, but their carcinogenic activity is attributed to the radiation, for example gamma rays and alpha particles, which they emit. Common examples of non-radioactive carcinogens are inhaled asbestos, certain dioxins, and tobacco smoke. Although the public generally associates carcinogenicity with synthetic chemicals, it is equally likely to arise from both natural and synthetic substances. Carcinogens are not necessarily immediately toxic; thus, their effect can be insidious. Carcinogens, as mentioned, are agents in the environment capable of contributing to cancer growth. Carcinogens can be categorized into two different types: activation-dependent and activation-independent, and each nature impacts their ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tumor Suppressor
A tumor suppressor gene (TSG), or anti-oncogene, is a gene that regulates a cell during cell division and replication. If the cell grows uncontrollably, it will result in cancer. When a tumor suppressor gene is mutated, it results in a loss or reduction in its function. In combination with other genetic mutations, this could allow the cell to grow abnormally. The loss of function for these genes may be even more significant in the development of human cancers, compared to the activation of oncogenes. TSGs can be grouped into the following categories: caretaker genes, gatekeeper genes, and more recently landscaper genes. Caretaker genes ensure stability of the genome via DNA repair and subsequently when mutated allow mutations to accumulate. Meanwhile, gatekeeper genes directly regulate cell growth by either inhibiting cell cycle progression or inducing apoptosis. Lastly landscaper genes regulate growth by contributing to the surrounding environment, when mutated can cause an e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blastoderm
A blastoderm ( germinal disc, blastodisc) is a single layer of embryonic epithelial tissue that makes up the blastula. It encloses the fluid filled blastocoel. Gastrulation follows blastoderm formation, where the tips of the blastoderm begins the formation of the ectoderm, mesoderm, and endoderm. Formation The blastoderm is formed when the oocyte plasma membrane begins cleaving by invagination, creating multiple cells that arrange themselves into an outer sleeve to the blastocoel. In oviparous In chicken eggs, the blastoderm represents a flat disc after embryonic fertilization. At the edge of the blastoderm is the site of active migration by most cells.{{cite book, last1=Bellairs, first1=Ruth, last2=Osmond, first2=Mark, title=Atlas of Chick Development, publisher=Atlas Press, page=15–28, edition=3 See also *Blastodisc *Embryology * Cleavage *Gastrulation Gastrulation is the stage in the early embryonic development of most animals, during which the blastula (a single-layere ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proboscipedia (pb Gene)
Proboscipedia (pb) is a protein coding gene in ''Drosophila melanogaster'', the fruit fly. Function This hox gene participates in the development of the labial and maxillary palps and mouthparts in the Drosophila fly. The pb gene is known to regulate the location of the antenna, maxillary palp, tarsus and proboscis identities. Taxonomy Proboscipedia belongs to the Antennapedia (Antp) homeobox family and the Proboscipedia subfamily. A homeobox gene is a transcription factor in which a region known as a homeodomain binds to a target gene promoter and controls the differentiation and development of cells. The pb gene is evidenced to be associated with the Sex combs reduced (Scr) gene. Both of these are essential for determination of the proboscis, a long flexible mouthpart in many insects used for the purpose of sucking. Mutations Mutated In biology, a mutation is an alteration in the nucleic acid sequence of the genome of an organism, virus, or extrachromosomal D ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
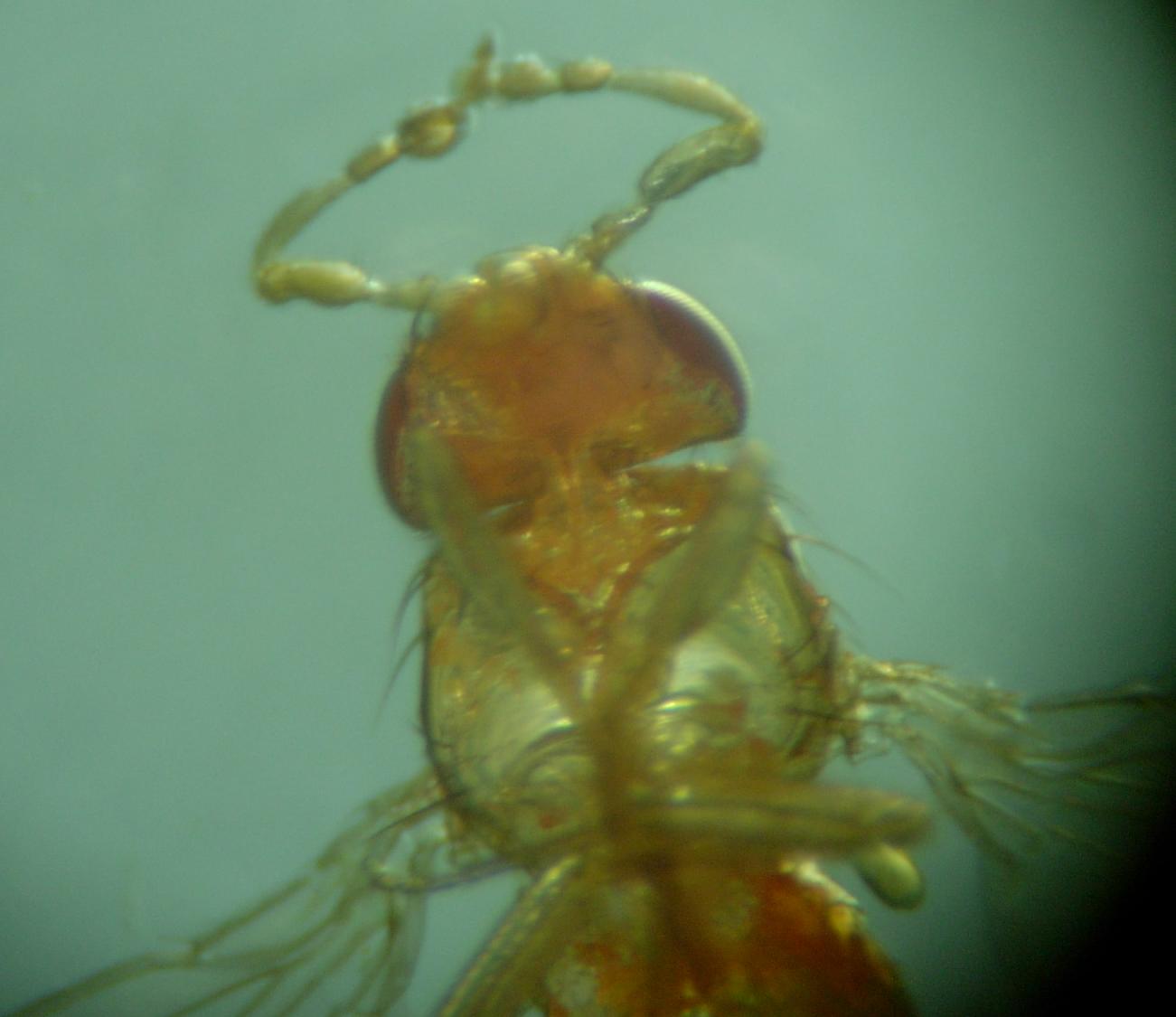
Antennapedia
''Antennapedia'' (abbreviated ''Antp'') is a Hox gene first discovered in ''Drosophila'' which controls the formation of legs during development. Loss-of-function mutations in the regulatory region of this gene result in the development of the second leg pair into ectopic antennae. By contrast gain-of-function alleles convert antennae into ectopic legs. This is just one illustration of the tendency of organisms to exhibit variations on a theme: modulated repetition. Legs and antennae are related to one another as much as molars are to incisors, fingers are to toes, and arms are to legs. ''Antp'' also refers to a gene complex (ANT-C) in ''Drosophila'' ending with the ''Antp'' gene. It is responsible for formation and differentiation of the thoracic and head segments of the fly's body. Origin of ''Antennapedia''-class homeobox gene The origin of the ancestor homeobox gene is an important aspect of the evolution of the ''Antp''-class ''Hox'' genes. Early evolution of the ' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Edward B
Edward is an English given name. It is derived from the Anglo-Saxon name ''Ēadweard'', composed of the elements '' ēad'' "wealth, fortune; prosperous" and '' weard'' "guardian, protector”. History The name Edward was very popular in Anglo-Saxon England, but the rule of the Norman and Plantagenet dynasties had effectively ended its use amongst the upper classes. The popularity of the name was revived when Henry III named his firstborn son, the future Edward I, as part of his efforts to promote a cult around Edward the Confessor, for whom Henry had a deep admiration. Variant forms The name has been adopted in the Iberian peninsula since the 15th century, due to Edward, King of Portugal, whose mother was English. The Spanish/Portuguese forms of the name are Eduardo and Duarte. Other variant forms include French Édouard, Italian Edoardo and Odoardo, German, Dutch, Czech and Romanian Eduard and Scandinavian Edvard. Short forms include Ed, Eddy, Eddie, Ted, Teddy a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Drosophila Melanogaster
''Drosophila melanogaster'' is a species of fly (the taxonomic order Diptera) in the family Drosophilidae. The species is often referred to as the fruit fly or lesser fruit fly, or less commonly the " vinegar fly" or " pomace fly". Starting with Charles W. Woodworth's 1901 proposal of the use of this species as a model organism, ''D. melanogaster'' continues to be widely used for biological research in genetics, physiology, microbial pathogenesis, and life history evolution. As of 2017, five Nobel Prizes have been awarded to drosophilists for their work using the insect. ''D. melanogaster'' is typically used in research owing to its rapid life cycle, relatively simple genetics with only four pairs of chromosomes, and large number of offspring per generation. It was originally an African species, with all non-African lineages having a common origin. Its geographic range includes all continents, including islands. ''D. melanogaster'' is a common pest in homes, restaurants, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



_en_rotate_05.jpg)