|
Historian Of Mathematics
The history of mathematics deals with the origin of discoveries in mathematics and the mathematical methods and notation of the past. Before the modern age and the worldwide spread of knowledge, written examples of new mathematical developments have come to light only in a few locales. From 3000 BC the Mesopotamian states of Sumer, Akkad and Assyria, followed closely by Ancient Egypt and the Levantine state of Ebla began using arithmetic, algebra and geometry for purposes of taxation, commerce, trade and also in the patterns in nature, the field of astronomy and to record time and formulate calendars. The earliest mathematical texts available are from Mesopotamia and Egypt – '' Plimpton 322'' ( Babylonian c. 2000 – 1900 BC), the ''Rhind Mathematical Papyrus'' ( Egyptian c. 1800 BC) and the '' Moscow Mathematical Papyrus'' (Egyptian c. 1890 BC). All of these texts mention the so-called Pythagorean triples, so, by inference, the Pythagorean theorem seems to be the most ancie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plimpton 322
Plimpton 322 is a Babylonian clay tablet, notable as containing an example of Babylonian mathematics. It has number 322 in the G.A. Plimpton Collection at Columbia University. This tablet, believed to have been written about 1800 BC, has a table of four columns and 15 rows of numbers in the cuneiform script of the period. This table lists two of the three numbers in what are now called Pythagorean triples, i.e., integers , , and satisfying . From a modern perspective, a method for constructing such triples is a significant early achievement, known long before the Greek and Indian mathematicians discovered solutions to this problem. At the same time, one should recall the tablet's author was a scribe, rather than a professional mathematician; it has been suggested that one of his goals may have been to produce examples for school problems. There has been significant scholarly debate on the nature and purpose of the tablet. For readable popular treatments of this tablet see rec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Theoretical Mathematics
Pure mathematics is the study of mathematical concepts independently of any application outside mathematics. These concepts may originate in real-world concerns, and the results obtained may later turn out to be useful for practical applications, but pure mathematicians are not primarily motivated by such applications. Instead, the appeal is attributed to the intellectual challenge and aesthetic beauty of working out the logical consequences of basic principles. While pure mathematics has existed as an activity since at least Ancient Greece, the concept was elaborated upon around the year 1900, after the introduction of theories with counter-intuitive properties (such as non-Euclidean geometries and Cantor's theory of infinite sets), and the discovery of apparent paradoxes (such as continuous functions that are nowhere differentiable, and Russell's paradox). This introduced the need to renew the concept of mathematical rigor and rewrite all mathematics accordingly, with a syst ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mathematical Proof
A mathematical proof is an inferential argument for a mathematical statement, showing that the stated assumptions logically guarantee the conclusion. The argument may use other previously established statements, such as theorems; but every proof can, in principle, be constructed using only certain basic or original assumptions known as axioms, along with the accepted rules of inference. Proofs are examples of exhaustive deductive reasoning which establish logical certainty, to be distinguished from empirical arguments or non-exhaustive inductive reasoning which establish "reasonable expectation". Presenting many cases in which the statement holds is not enough for a proof, which must demonstrate that the statement is true in ''all'' possible cases. A proposition that has not been proved but is believed to be true is known as a conjecture, or a hypothesis if frequently used as an assumption for further mathematical work. Proofs employ logic expressed in mathematical symbols ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mathematical Rigor
Rigour (British English) or rigor (American English; see spelling differences) describes a condition of stiffness or strictness. These constraints may be environmentally imposed, such as "the rigours of famine"; logically imposed, such as mathematical proofs which must maintain consistent answers; or socially imposed, such as the process of defining ethics and law. Etymology "Rigour" comes to English through old French (13th c., Modern French '' rigueur'') meaning "stiffness", which itself is based on the Latin ''rigorem'' (nominative ''rigor'') "numbness, stiffness, hardness, firmness; roughness, rudeness", from the verb ''rigere'' "to be stiff". The noun was frequently used to describe a condition of strictness or stiffness, which arises from a situation or constraint either chosen or experienced passively. For example, the title of the book ''Theologia Moralis Inter Rigorem et Laxitatem Medi'' roughly translates as "mediating theological morality between rigour and lax ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Greek Mathematics
Greek mathematics refers to mathematics texts and ideas stemming from the Archaic through the Hellenistic and Roman periods, mostly extant from the 7th century BC to the 4th century AD, around the shores of the Eastern Mediterranean. Greek mathematicians lived in cities spread over the entire Eastern Mediterranean from Italy to North Africa but were united by Greek culture and the Greek language. The word "mathematics" itself derives from the grc, , máthēma , meaning "subject of instruction". The study of mathematics for its own sake and the use of generalized mathematical theories and proofs is an important difference between Greek mathematics and those of preceding civilizations. Origins of Greek mathematics The origin of Greek mathematics is not well documented. The earliest advanced civilizations in Greece and in Europe were the Minoan and later Mycenaean civilizations, both of which flourished during the 2nd millennium BCE. While these civilizations possessed writing and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Greek Language
Greek ( el, label=Modern Greek, Ελληνικά, Elliniká, ; grc, Ἑλληνική, Hellēnikḗ) is an independent branch of the Indo-European family of languages, native to Greece, Cyprus, southern Italy (Calabria and Salento), southern Albania, and other regions of the Balkans, the Black Sea coast, Asia Minor, and the Eastern Mediterranean. It has the longest documented history of any Indo-European language, spanning at least 3,400 years of written records. Its writing system is the Greek alphabet, which has been used for approximately 2,800 years; previously, Greek was recorded in writing systems such as Linear B and the Cypriot syllabary. The alphabet arose from the Phoenician script and was in turn the basis of the Latin, Cyrillic, Armenian, Coptic, Gothic, and many other writing systems. The Greek language holds a very important place in the history of the Western world. Beginning with the epics of Homer, ancient Greek literature includes many works of lasting impo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pythagoreans
Pythagoreanism originated in the 6th century BC, based on and around the teachings and beliefs held by Pythagoras and his followers, the Pythagoreans. Pythagoras established the first Pythagorean community in the ancient Greek colony of Kroton, in modern Calabria (Italy). Early Pythagorean communities spread throughout Magna Graecia. Pythagoras' death and disputes about his teachings led to the development of two philosophical traditions within Pythagoreanism. The ''akousmatikoi'' were superseded in the 4th century BC as a significant mendicant school of philosophy by the Cynics. The ''mathēmatikoi'' philosophers were absorbed into the Platonic school in the 4th century BC. Following political instability in Magna Graecia, some Pythagorean philosophers fled to mainland Greece while others regrouped in Rhegium. By about 400 BC the majority of Pythagorean philosophers had left Italy. Pythagorean ideas exercised a marked influence on Plato and through him, on all of Western phi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
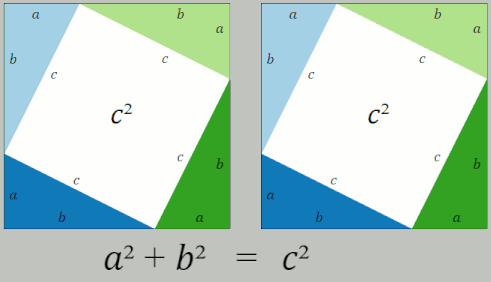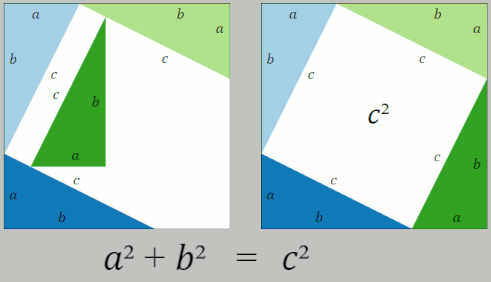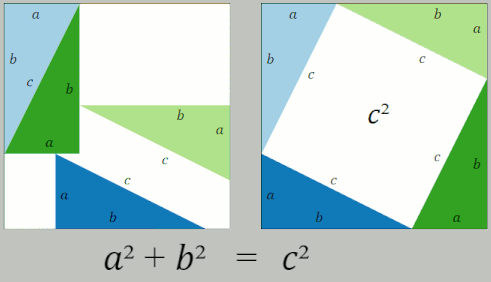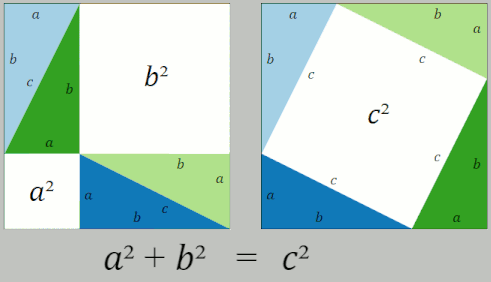
Pythagorean Theorem
In mathematics, the Pythagorean theorem or Pythagoras' theorem is a fundamental relation in Euclidean geometry between the three sides of a right triangle. It states that the area of the square whose side is the hypotenuse (the side opposite the right angle) is equal to the sum of the areas of the squares on the other two sides. This theorem can be written as an equation relating the lengths of the sides ''a'', ''b'' and the hypotenuse ''c'', often called the Pythagorean equation: :a^2 + b^2 = c^2 , The theorem is named for the Greek philosopher Pythagoras, born around 570 BC. The theorem has been proven numerous times by many different methods – possibly the most for any mathematical theorem. The proofs are diverse, including both geometric proofs and algebraic proofs, with some dating back thousands of years. When Euclidean space is represented by a Cartesian coordinate system in analytic geometry, Euclidean distance satisfies the Pythagorean relation: the squared dist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pythagorean Triple
A Pythagorean triple consists of three positive integers , , and , such that . Such a triple is commonly written , and a well-known example is . If is a Pythagorean triple, then so is for any positive integer . A primitive Pythagorean triple is one in which , and are coprime (that is, they have no common divisor larger than 1). For example, is a primitive Pythagorean triple whereas is not. A triangle whose sides form a Pythagorean triple is called a Pythagorean triangle, and is necessarily a right triangle. The name is derived from the Pythagorean theorem, stating that every right triangle has side lengths satisfying the formula a^2+b^2=c^2; thus, Pythagorean triples describe the three integer side lengths of a right triangle. However, right triangles with non-integer sides do not form Pythagorean triples. For instance, the triangle with sides a=b=1 and c=\sqrt2 is a right triangle, but (1,1,\sqrt2) is not a Pythagorean triple because \sqrt2 is not an integer. Moreover, 1 and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moscow Mathematical Papyrus
The Moscow Mathematical Papyrus, also named the Golenishchev Mathematical Papyrus after its first non-Egyptian owner, Egyptologist Vladimir Golenishchev, is an ancient Egyptian mathematical papyrus containing several problems in arithmetic, geometry, and algebra. Golenishchev bought the papyrus in 1892 or 1893 in Thebes. It later entered the collection of the Pushkin State Museum of Fine Arts in Moscow, where it remains today. Based on the palaeography and orthography of the hieratic text, the text was most likely written down in the 13th Dynasty and based on older material probably dating to the Twelfth Dynasty of Egypt, roughly 1850 BC.Clagett, Marshall. 1999. Ancient Egyptian Science: A Source Book. Volume 3: Ancient Egyptian Mathematics. Memoirs of the American Philosophical Society 232. Philadelphia: American Philosophical Society. Approximately 5½ m (18 ft) long and varying between wide, its format was divided by the Soviet Orientalist Vasily Vasilievich Stru ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dover Publications
Dover Publications, also known as Dover Books, is an American book publisher founded in 1941 by Hayward and Blanche Cirker. It primarily reissues books that are out of print from their original publishers. These are often, but not always, books in the public domain. The original published editions may be scarce or historically significant. Dover republishes these books, making them available at a significantly reduced cost. Classic reprints Dover reprints classic works of literature, classical sheet music, and public-domain images from the 18th and 19th centuries. Dover also publishes an extensive collection of mathematical, scientific, and engineering texts. It often targets its reprints at a niche market, such as woodworking. Starting in 2015, the company branched out into graphic novel reprints, overseen by Dover acquisitions editor and former comics writer and editor Drew Ford. Most Dover reprints are photo facsimiles of the originals, retaining the original pagination and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |