|
Histone-modifying Enzymes
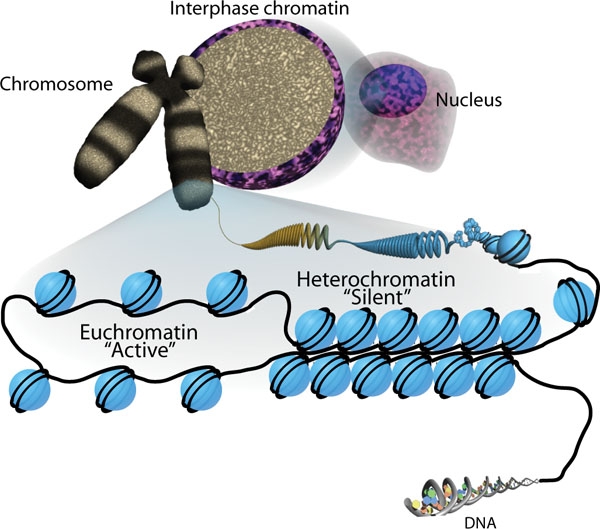
Histone-modifying enzymes are enzymes involved in the modification of histone substrates after protein translation and affect cellular processes including gene expression. To safely store the eukaryotic genome, DNA is wrapped around four core histone proteins (H3, H4, H2A, H2B), which then join to form nucleosomes. These nucleosomes further fold together into highly condensed chromatin, which renders the organism's genetic material far less accessible to the factors required for gene transcription, DNA replication, recombination and repair. Subsequently, eukaryotic organisms have developed intricate mechanisms to overcome this repressive barrier imposed by the chromatin through histone modification, a type of post-translational modification which typically involves covalently attaching certain groups to histone residues. Once added to the histone, these groups (directly or indirectly) elicit either a loose and open histone conformation, euchromatin, or a tight and closed histone ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Basic Unit Of Chromatin Organization Is The Nucleosome, Which Comprises 147 Bp Of DNA Wrapped Ar
''The'' () is a grammatical article in English, denoting persons or things that are already or about to be mentioned, under discussion, implied or otherwise presumed familiar to listeners, readers, or speakers. It is the definite article in English. ''The'' is the most frequently used word in the English language; studies and analyses of texts have found it to account for seven percent of all printed English-language words. It is derived from gendered articles in Old English which combined in Middle English and now has a single form used with nouns of any gender. The word can be used with both singular and plural nouns, and with a noun that starts with any letter. This is different from many other languages, which have different forms of the definite article for different genders or numbers. Pronunciation In most dialects, "the" is pronounced as (with the voiced dental fricative followed by a schwa) when followed by a consonant sound, and as (homophone of the archaic pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Covalent Bond
A covalent bond is a chemical bond that involves the sharing of electrons to form electron pairs between atoms. These electron pairs are known as shared pairs or bonding pairs. The stable balance of attractive and repulsive forces between atoms, when they share electrons, is known as covalent bonding. For many molecules, the sharing of electrons allows each atom to attain the equivalent of a full valence shell, corresponding to a stable electronic configuration. In organic chemistry, covalent bonding is much more common than ionic bonding. Covalent bonding also includes many kinds of interactions, including σ-bonding, π-bonding, metal-to-metal bonding, agostic interactions, bent bonds, three-center two-electron bonds and three-center four-electron bonds. The term ''covalent bond'' dates from 1939. The prefix ''co-'' means ''jointly, associated in action, partnered to a lesser degree, '' etc.; thus a "co-valent bond", in essence, means that the atoms share "valence" ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proline Isomerization
In epigenetics, proline isomerization is the effect that ''cis-trans'' isomerization of the amino acid proline has on the regulation of gene expression. Similar to aspartic acid, the amino acid proline has the rare property of being able to occupy both ''cis'' and ''trans'' isomers of its prolyl peptide bonds with ease. Peptidyl-prolyl isomerase, or PPIase, is an enzyme very commonly associated with proline isomerization due to their ability to catalyze the isomerization of prolines. PPIases are present in three types: cyclophilins, FK507-binding proteins, and the parvulins. PPIase enzymes catalyze the transition of proline between ''cis'' and ''trans'' isomers and are essential to the numerous biological functions controlled and affected by prolyl isomerization (i.e. cell signalling, protein folding, and epigenetic modifications) Without PPIases, prolyl peptide bonds will slowly switch between ''cis'' and ''trans'' isomers, a process that can lock proteins in a nonnative structur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Citrullination
Citrullination or deimination is the conversion of the amino acid arginine in a protein into the amino acid citrulline. Citrulline is not one of the 20 standard amino acids encoded by DNA in the genetic code. Instead, it is the result of a post-translational modification. Citrullination is distinct from the formation of the free amino acid citrulline as part of the urea cycle or as a byproduct of enzymes of the nitric oxide synthase family. Enzymes called arginine deiminases (ADIs) catalyze the deimination of free arginine, while protein arginine deiminases or peptidylarginine deiminases (PADs) replace the primary ketimine group (>C=NH) by a ketone group (>C=O). Arginine is positively charged at a neutral pH, whereas citrulline has no net charge. This increases the hydrophobicity of the protein, which can lead to changes in protein folding, affecting the structure and function. The immune system can attack citrullinated proteins, leading to autoimmune diseases such as rheumato ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ADP-ribosylation ADP-ribosylation is the addition of one or more ADP-ribose moieties to a protein. It is a reversible post-translational modification that is involved in many cellular processes, including cell signaling, DNA repair, gene regulation and apoptosis. Improper ADP-ribosylation has been implicated in some forms of cancer. It is also the basis for the toxicity of bacterial compounds such as cholera toxin, diphtheria toxin, and others. History The first suggestion of ADP-ribosylation surfaced during the early 1960s. At this time, Pierre Chambon and coworkers observed the incorporation of ATP into hen liver nuclei extract. After extensive studies on the acid insoluble fraction, several different research laboratories were able to identify ADP-ribose, derived from NAD+, as the incorporated group. Several years later, the enzymes responsible for this incorporation were identified and given the name poly(ADP-ribose)polymerase. Originally, this group was thought to be a linear sequence of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] |
.png)
