|
Hip Flexor
In anatomy, flexor is a muscle that contracts to perform flexion (from the Latin verb ''flectere'', to bend), a movement that decreases the angle between the bones converging at a joint. For example, one's elbow joint flexes when one brings their hand closer to the shoulder, thus decreasing the angle between the upper arm and the forearm. Flexors Upper limb *of the humerus bone (the bone in the upper arm) at the shoulder ** Pectoralis major **Anterior deltoid **Coracobrachialis **Biceps brachii * of the forearm at the elbow **Brachialis **Brachioradialis **Biceps brachii *of carpus (the carpal bones) at the wrist **flexor carpi radialis **flexor carpi ulnaris **palmaris longus *of the hand **flexor pollicis longus muscle **flexor pollicis brevis muscle **flexor digitorum profundus muscle **flexor digitorum superficialis muscle Lower limb Hip The hip flexors are (in descending order of importance to the action of flexing the hip joint):Platzer (2004), p 246 *Collectively know ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anatomy
Anatomy () is the branch of morphology concerned with the study of the internal structure of organisms and their parts. Anatomy is a branch of natural science that deals with the structural organization of living things. It is an old science, having its beginnings in prehistoric times. Anatomy is inherently tied to developmental biology, embryology, comparative anatomy, evolutionary biology, and phylogeny, as these are the processes by which anatomy is generated, both over immediate and long-term timescales. Anatomy and physiology, which study the structure and function of organisms and their parts respectively, make a natural pair of related disciplines, and are often studied together. Human anatomy is one of the essential basic sciences that are applied in medicine, and is often studied alongside physiology. Anatomy is a complex and dynamic field that is constantly evolving as discoveries are made. In recent years, there has been a significant increase in the use of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Elbow
The elbow is the region between the upper arm and the forearm that surrounds the elbow joint. The elbow includes prominent landmarks such as the olecranon, the cubital fossa (also called the chelidon, or the elbow pit), and the lateral and the medial epicondyles of the humerus. The elbow joint is a hinge joint between the arm and the forearm; more specifically between the humerus in the upper arm and the radius and ulna in the forearm which allows the forearm and hand to be moved towards and away from the body. The term ''elbow'' is specifically used for humans and other primates, and in other vertebrates it is not used. In those cases, forelimb plus joint is used. The name for the elbow in Latin is ''cubitus'', and so the word cubital is used in some elbow-related terms, as in ''cubital nodes'' for example. Structure Joint The elbow joint has three different portions surrounded by a common joint capsule. These are joints between the three bones of the elbow, the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iliopsoas
The iliopsoas muscle (; ) refers to the joined psoas major and the iliacus muscles. The two muscles are separate in the abdomen, but usually merge in the thigh. They are usually given the common name ''iliopsoas''. The iliopsoas muscle joins to the femur at the lesser trochanter. It acts as the strongest flexor of the hip. The iliopsoas muscle is supplied by the lumbar spinal nerves L1– L3 (psoas) and parts of the femoral nerve (iliacus). Structure The iliopsoas muscle is a composite muscle formed from the psoas major muscle, and the iliacus muscle. The psoas major originates along the outer surfaces of the vertebral bodies of T12 and L1– L3 and their associated intervertebral discs. The iliacus originates in the iliac fossa of the pelvis. The psoas major unites with the iliacus at the level of the inguinal ligament. It crosses the hip joint to insert on the lesser trochanter of the femur. The iliopsoas is classified as an "anterior hip muscle" or "inner ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anterior Hip Muscles 2
Standard anatomical terms of location are used to describe unambiguously the anatomy of humans and other animals. The terms, typically derived from Latin or Greek roots, describe something in its standard anatomical position. This position provides a definition of what is at the front ("anterior"), behind ("posterior") and so on. As part of defining and describing terms, the body is described through the use of anatomical planes and axes. The meaning of terms that are used can change depending on whether a vertebrate is a biped or a quadruped, due to the difference in the neuraxis, or if an invertebrate is a non-bilaterian. A non-bilaterian has no anterior or posterior surface for example but can still have a descriptor used such as proximal or distal in relation to a body part that is nearest to, or furthest from its middle. International organisations have determined vocabularies that are often used as standards for subdisciplines of anatomy. For example, '' Terminologia A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flexor Digitorum Superficialis Muscle
Flexor digitorum superficialis (''flexor digitorum sublimis'') or flexor digitorum communis sublimis is an extrinsic flexor muscle of the fingers at the proximal interphalangeal joints. It is in the anterior compartment of the forearm. It is sometimes considered to be the deepest part of the superficial layer of this compartment, and sometimes considered to be a distinct, "intermediate layer" of this compartment. It is relatively common for the Flexor digitorum superficialis to be missing from the little finger, bilaterally and unilaterally, which can cause problems when diagnosing a little finger injury. Structure The muscle has two classically described heads – the humeroulnar and radial – and it is between these heads that the median nerve and ulnar artery pass. The ulnar collateral ligament of elbow joint gives its origin to part of this muscle. Four long tendons come off this muscle near the wrist and travel through the carpal tunnel formed by the flexor retinaculu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flexor Digitorum Profundus Muscle
The flexor digitorum profundus or flexor digitorum communis profundus is a muscle in the forearm of humans that flexes the fingers (also known as digits). It is considered an extrinsic hand muscle because it acts on the hand while its muscle belly is located in the forearm. Together the flexor pollicis longus, pronator quadratus, and flexor digitorum profundus form the deep layer of ventral forearm muscles.Platzer 2004, p 162 The muscle is named . Structure Flexor digitorum profundus originates in the upper 3/4 of the anterior and medial surfaces of the ulna, interosseous membrane and deep fascia of the forearm. The muscle fans out into four tendons (one to each of the second to fifth fingers) to the palmar base of the distal phalanx. Along with the flexor digitorum superficialis, it has long tendons that run down the arm and through the carpal tunnel and attach to the palmar side of the phalanges of the fingers. Flexor digitorum profundus lies deep to the superfici ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flexor Pollicis Brevis Muscle
The flexor pollicis brevis is a muscle in the hand that flexes the thumb. It is one of three thenar muscles. It has both a superficial part and a deep part. Origin and insertion The muscle's superficial head arises from the distal edge of the flexor retinaculum and the tubercle of the trapezium, the most lateral bone in the distal row of carpal bones. It passes along the radial side of the tendon of the flexor pollicis longus. The deeper (and medial) head "varies in size and may be absent."Gray's 37th British Edition, p. 630" It arises from the trapezoid and capitate bones on the floor of the carpal tunnel, as well as the ligaments of the distal carpal row. Both heads become tendinous and insert together into the radial side of the base of the proximal phalanx of the thumb; at the junction between the tendinous heads there is a sesamoid bone.''Gray's Anatomy'' 1918, see infobox Innervation The superficial head is usually innervated by the lateral terminal branch of the med ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flexor Pollicis Longus Muscle
The flexor pollicis longus (; FPL, Latin ''flexor'', bender; ''pollicis'', of the thumb; ''longus'', long) is a muscle in the forearm and hand that flexes the thumb. It lies in the same plane as the flexor digitorum profundus. This muscle is unique to humans, being either rudimentary or absent in other primates. A meta-analysis indicated accessory flexor pollicis longus is present in around 48% of the population. Human anatomy Origin and insertion It arises from the grooved anterior (side of palm) surface of the body of the radius, extending from immediately below the radial tuberosity and oblique line to within a short distance of the pronator quadratus muscle.Gray 1918, ''Flexor Pollicis Longus'', paras 20, 25 An occasionally present accessory long head of the flexor pollicis longus muscle is called 'Gantzer's muscle'. It may cause compression of the anterior interosseous nerve. It arises also from the adjacent part of the interosseous membrane of the forearm, and generall ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
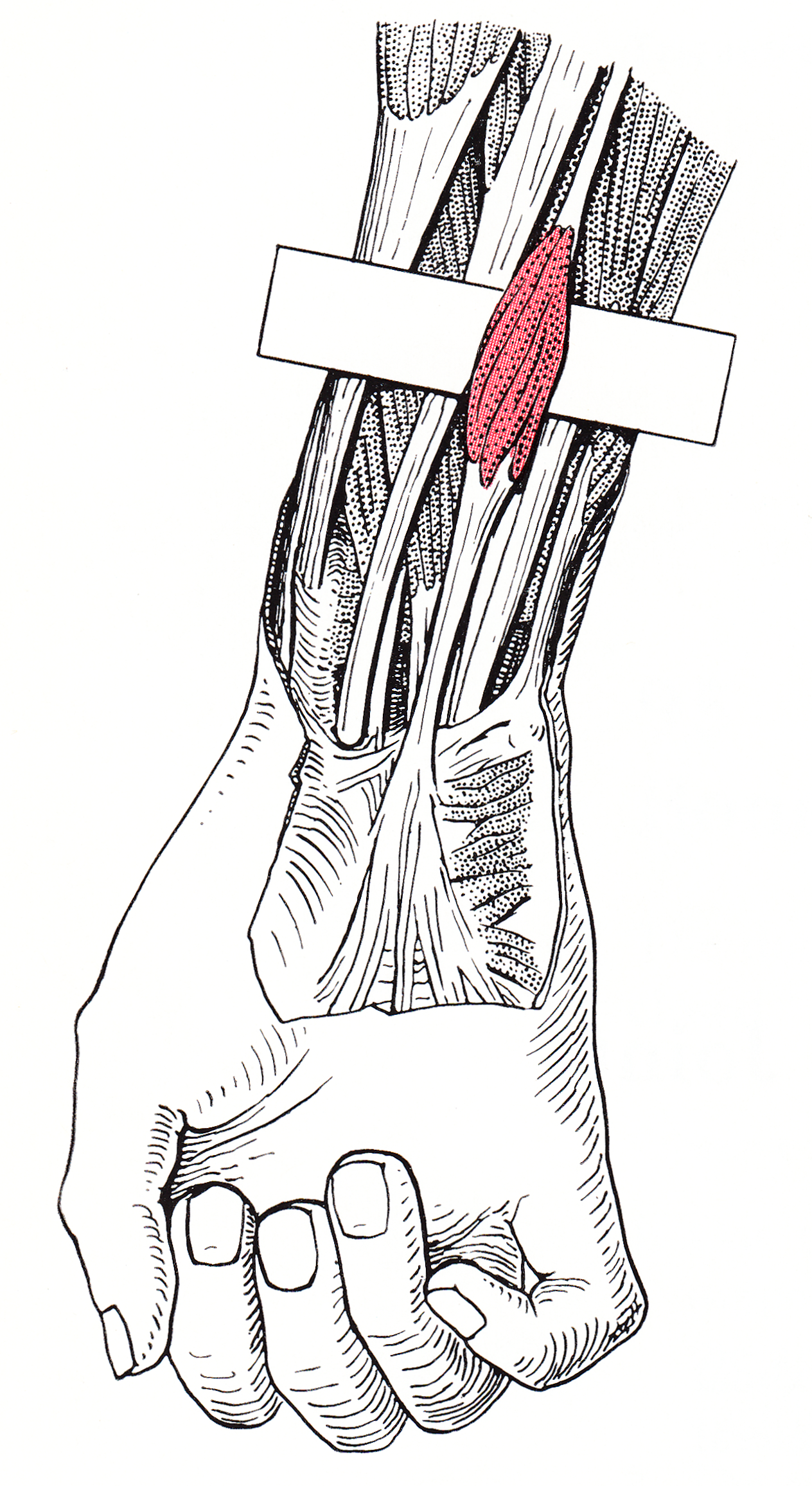
Palmaris Longus
The palmaris longus is a muscle visible as a small tendon located between the flexor carpi radialis and the flexor carpi ulnaris, although it is not always present. Reviews report rates of absence in the general population ranging from 10–20%; however, the rate varies in different ethnic groups. Absence of the palmaris longus does not have an effect on grip strength. The lack of palmaris longus muscle does result in decreased pinch strength in fourth and fifth fingers. The absence of palmaris longus muscle is more prevalent in females than males. The palmaris longus muscle can be observed by touching the pads of the fourth finger and thumb and flexing the wrist. The tendon, if present, will be visible in the midline of the anterior wrist. Structure Palmaris longus is a slender, elongated, spindle shaped muscle, lying on the medial side of the flexor carpi radialis. It is widest in the middle, and narrowest at the proximal and distal attachments.''Gray's Anatomy'' (1918), see in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flexor Carpi Ulnaris
The flexor carpi ulnaris (FCU) is a skeletal muscle, muscle of the forearm that flexion, flexes and Adduction, adducts at the wrist joint. Structure Origin The flexor carpi ulnaris has two heads; a humeral head and ulnar head. The humeral head originates from the medial epicondyle of the humerus via the common flexor tendon. The ulnar head originates from the medial margin of the olecranon of the ulna and the upper two-thirds of the dorsal border of the ulna by an aponeurosis. Between the two heads passes the ulnar nerve and ulnar artery. Insertion The flexor carpi ulnaris inserts onto the pisiform bone, pisiform, hook of the hamate (via the pisohamate ligament) and the anterior surface of the base of the fifth metacarpal bone, fifth metacarpal (via the pisometacarpal ligament). Action The flexor carpi ulnaris flexes and adducts at the Wrist, wrist joint. Innervation The flexor carpi ulnaris is innervated by the ulnar nerve. The corresponding spinal nerves are Cervical spinal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flexor Carpi Radialis
In anatomy, flexor carpi radialis is a muscle of the human forearm that acts to flex and (radially) abduct the hand. The Latin ''carpus'' means wrist; hence flexor carpi is a flexor of the wrist. Origin and insertion The flexor carpi radialis is one of four muscles in the superficial layer of the anterior compartment of the forearm. This muscle originates from the medial epicondyle of the humerus as part of the common flexor tendon. It runs just laterally of flexor digitorum superficialis and inserts on the anterior aspect of the base of the second metacarpal, and has small slips to both the third metacarpal and trapezium tuberosity. The tendon of the flexor carpi radialis is visible on the anterior surface of the forearm, just proximal to the wrist, when the wrist is flexed. It is the tendon seen most lateral, closest to the thumb. Nerve and artery Like most flexors of the anterior compartment of the forearm, FCR is innervated by the median nerve, specifically by axons fro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wrist
In human anatomy, the wrist is variously defined as (1) the carpus or carpal bones, the complex of eight bones forming the proximal skeletal segment of the hand; "The wrist contains eight bones, roughly aligned in two rows, known as the carpal bones." (2) the wrist joint or radiocarpal joint, the joint between the radius and the carpus and; (3) the anatomical region surrounding the carpus including the distal parts of the bones of the forearm and the proximal parts of the metacarpus or five metacarpal bones and the series of joints between these bones, thus referred to as ''wrist joints''. "With the large number of bones composing the wrist (ulna, radius, eight carpas, and five metacarpals), it makes sense that there are many, many joints that make up the structure known as the wrist." This region also includes the carpal tunnel, the anatomical snuff box, bracelet lines, the flexor retinaculum, and the extensor retinaculum. As a consequence of these various definitions, f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |