|
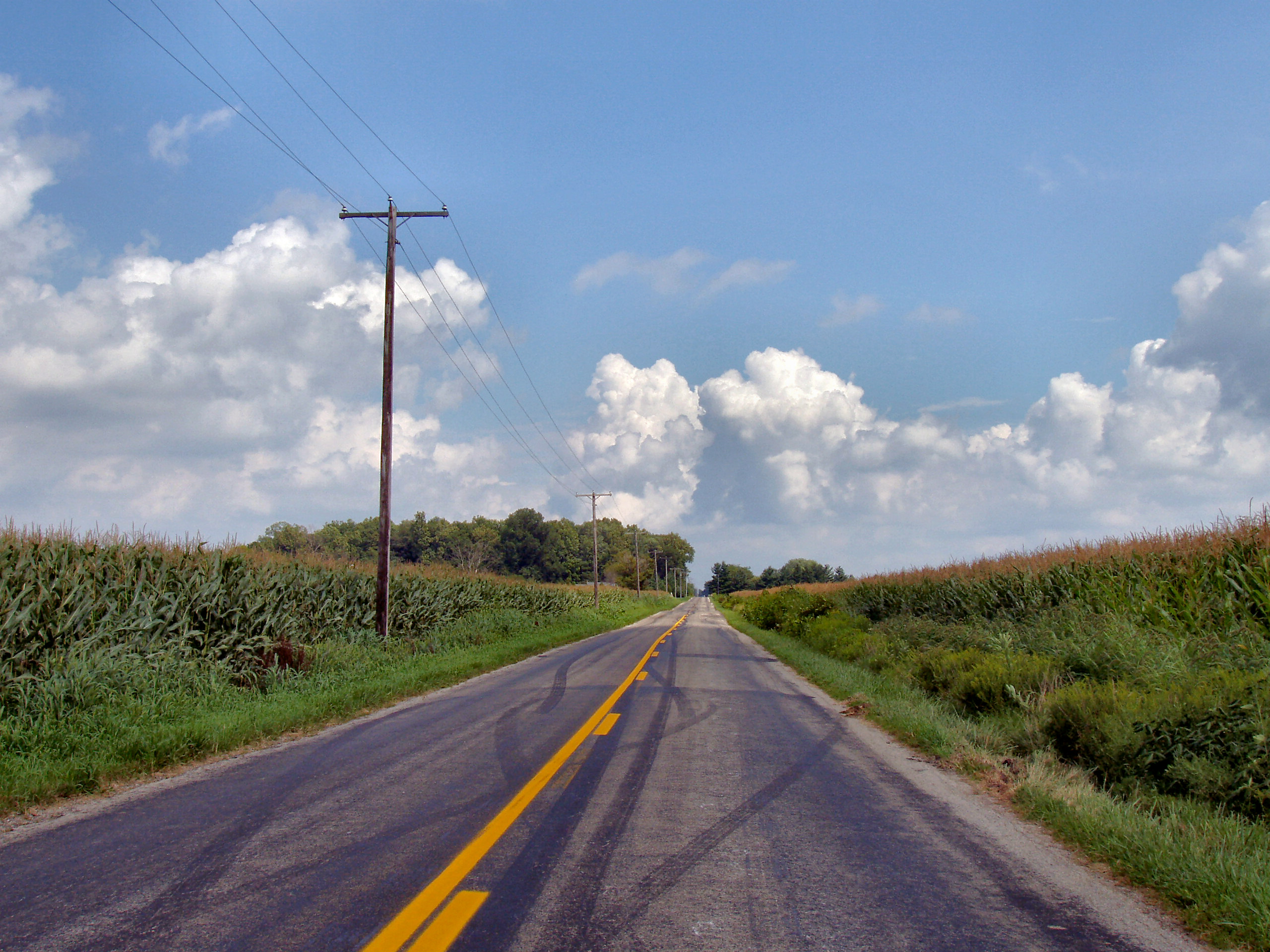
Highway Hypnosis
Highway hypnosis, also known as white line fever, is an altered mental state in which a person can drive a car, truck, or other automobile great distances, responding to external events in the expected, safe, and correct manner with no recollection of having consciously done so. In this state, the driver's conscious mind is apparently fully focused elsewhere, while seemingly still processing the information needed to drive safely. Highway hypnosis is a manifestation of the common process of automaticity. The concept was first described in a 1921 article that mentioned the phenomenon of "road hypnotism": driving in a trance-like state while gazing at a fixed point. A 1929 study, ''Sleeping with the Eyes Open'' by Walter Miles, also dealt with the subject, suggesting that it was possible for motorists to fall asleep with their eyes open and continuing to steer. The idea that the unaccountable automobile accidents could be explained by this phenomenon became popular in the 1950s. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amnesia
Amnesia is a deficit in memory caused by brain damage or disease,Gazzaniga, M., Ivry, R., & Mangun, G. (2009) Cognitive Neuroscience: The biology of the mind. New York: W.W. Norton & Company. but it can also be caused temporarily by the use of various sedatives and hypnotic drugs. The memory can be either wholly or partially lost due to the extent of damage that was caused. There are two main types of amnesia: retrograde amnesia and anterograde amnesia. Retrograde amnesia is the inability to retrieve information that was acquired before a particular date, usually the date of an accident or operation. In some cases the memory loss can extend back decades, while in others the person may lose only a few months of memory. Anterograde amnesia is the inability to transfer new information from the short-term store into the long-term store. People with anterograde amnesia cannot remember things for long periods of time. These two types are not mutually exclusive; both can occur simu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sleep-deprived Driving
Sleep-deprived driving (commonly known as tired driving, drowsy driving, or fatigued driving) is the operation of a motor vehicle while being cognitively impaired by a lack of sleep. Sleep deprivation is a major cause of motor vehicle accidents, and it can impair the human brain as much as inebriation can. According to a 1998 survey, 23% of adults have fallen asleep while driving.Peters, Robert D"Effects of Partial and Total Sleep Deprivation on Driving Performance" US Department of Transportation, February 1999. According to the United States Department of Transportation, male drivers admit to have fallen asleep while driving twice as much as female drivers. In the United States, 250,000 drivers fall asleep at the wheel every day, according to the Division of Sleep Medicine at Harvard Medical School and in a national poll by the National Sleep Foundation, 54% of adult drivers said they had driven while drowsy during the past year with 28% saying they had actually fallen asleep whil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Selective Hearing
Selective auditory attention or selective hearing is a type of selective attention and involves the auditory system. Selective hearing is characterized as the action in which people focus their attention intentionally on a specific source of a sound or spoken words. When people use selective hearing, noise from the surrounding environment is heard by the auditory system but only certain parts of the auditory information are chosen to be processed by the brain. Most often, auditory attention is directed at things people are most interested in hearing. Selective hearing is not a physiological disorder but rather it is the capability of humans to block out sounds and noise. It is the notion of ignoring certain things in the surrounding environment. The dividing line between preference and utility is not clear cut. Selective auditory attention differs from selective perception, in that the filtering in the latter case is mediated by cognitive dissonance. Background In an artic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microsleep
A microsleep is a sudden temporary episode of sleep or drowsiness which may last for a few seconds where an individual fails to respond to some arbitrary sensory input and becomes unconscious.International Classification of Sleep Disorders, , page 343Poudel, G. R., Innes, C. R., Bones, P. J., Watts, R., & Jones, R. D. (2012) Losing the struggle to stay awake: Divergent thalamic and cortical activity during microsleeps. Human Brain Mapping: 00:000-000 MSs occur when an individual loses and regains awareness after a brief lapse in consciousness, often without warning, or when there are sudden shifts between states of wakefulness and sleep. In behavioural terms, MSs may manifest as droopy eyes, slow eyelid-closure, and head nodding. In electrical terms, microsleeps are often classified as a shift in electroencephalography (EEG) during which 4–7 Hz (theta wave) activity replaces the waking 8–13 Hz (alpha wave) background rhythm. MSs frequently occur as a result of slee ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Muscle Memory
Muscle memory is a form of procedural memory that involves consolidating a specific motor task into memory through repetition, which has been used synonymously with motor learning. When a movement is repeated over time, the brain creates a long-term muscle memory for that task, eventually allowing it to be performed with little to no conscious effort. This process decreases the need for attention and creates maximum efficiency within the motor and memory systems. Muscle memory is found in many everyday activities that become automatic and improve with practice, such as riding bikes, driving motor vehicles, playing ball sports, typing on keyboards, entering PINs, playing musical instruments, poker, martial arts, and dancing. History The origins of research for the acquisition of motor skills stem from philosophers such as Plato, Aristotle and Galen. After the break from tradition of the pre-1900s view of introspection, psychologists emphasized research and more scientific metho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Automatism (law)
In criminal law, automatism is a rarely used criminal defence. It is one of the mental condition defences that relate to the mental state of the defendant. Automatism can be seen variously as lack of voluntariness, lack of culpability (unconsciousness) or excuse. Automatism means that the defendant was not aware of his or her actions when making the particular movements that constituted the illegal act. For example, Esther Griggs in 1858 threw her child out of a first floor window believing that the house was on fire, while having a sleep terror. In 2002, Peter Buck, lead guitarist of the band R.E.M., was cleared of several charges, including assault, which resulted from automatism brought on by a bad interaction between alcohol and sleeping pills. In a 2009 case in Aberporth in west Wales, Brian Thomas strangled his wife in their camper van, also during a sleep terror, when he mistook his wife for an intruder. The defence of automatism is denying that the person was acting ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Automaticity
Automaticity is the ability to do things without occupying the mind with the low-level details required, allowing it to become an automatic response pattern or habit. It is usually the result of learning, repetition, and practice. Examples of tasks carried out by 'muscle memory' often involve some degree of automaticity. Examples of automaticity are common activities such as walking, speaking, bicycle-riding, assembly-line work, and driving a car (the last of these sometimes being termed "highway hypnosis"). After an activity is sufficiently practiced, it is possible to focus the mind on other activities or thoughts while undertaking an automatized activity (for example, holding a conversation or planning a speech while driving a car). Characteristics John Bargh (1994), based on over a decade of research, suggested that four characteristics usually accompany automatic behavior: ;Awareness :A person may be unaware of the mental process that is occurring. ;Intentionality :A perso ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dissociation (psychology)
Dissociation, as a concept that has been developed over time, is a wide array of experiences, ranging from a mild emotional detachment from the immediate surroundings, to a more severe disconnection from physical and emotional experiences. The major characteristic of all dissociative phenomena involves a detachment from reality, rather than a loss of reality as in psychosis. The phenomena are diagnosable under the ''DSM-5'' as a group of disorders as well as a symptom of other disorders through various diagnostic tools. Its cause is believed to be related to neurobiological mechanisms, trauma, anxiety, and psychoactive drugs. Research has further related it to suggestibility and hypnosis, and it is inversely related to mindfulness, which is a potential treatment. History French philosopher and psychologist Pierre Janet (1859–1947) is considered to be the author of the concept of dissociation. Contrary to some conceptions of dissociation, Janet did not believe that dissocia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Altered State Of Consciousness
An altered state of consciousness (ASC), also called altered state of mind or mind alteration, is any condition which is significantly different from a normal waking state. By 1892, the expression was in use in relation to hypnosis, though there is an ongoing debate as to whether hypnosis is to be identified as an ASC according to its modern definition. The next retrievable instance, by Dr Max Mailhouse from his 1904 presentation to conference, however, is unequivocally identified as such, as it was in relation to epilepsy, and is still used today. In academia, the expression was used as early as 1966 by Arnold M. Ludwig and brought into common usage from 1969 by Charles Tart. It describes induced changes in one's mental state, almost always temporary. A synonymous phrase is "altered state of awareness". Definitions There is no general definition of an altered state of consciousness, as any definitional attempt would first have to rely on a definition of a normal state of consci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Consciousness
Consciousness, at its simplest, is sentience and awareness of internal and external existence. However, the lack of definitions has led to millennia of analyses, explanations and debates by philosophers, theologians, linguisticians, and scientists. Opinions differ about what exactly needs to be studied or even considered consciousness. In some explanations, it is synonymous with the mind, and at other times, an aspect of mind. In the past, it was one's "inner life", the world of introspection, of private thought, imagination and volition. Today, it often includes any kind of cognition, experience, feeling or perception. It may be awareness, awareness of awareness, or self-awareness either continuously changing or not. The disparate range of research, notions and speculations raises a curiosity about whether the right questions are being asked. Examples of the range of descriptions, definitions or explanations are: simple wakefulness, one's sense of selfhood or sou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Awareness
Awareness is the state of being conscious of something. More specifically, it is the ability to directly know and perceive, to feel, or to be cognizant of events. Another definition describes it as a state wherein a subject is aware of some information when that information is directly available to bring to bear in the direction of a wide range of behavioral actions. The concept is often synonymous to consciousness and is also understood as being consciousness itself. The states of awareness are also associated with the states of experience so that the structure represented in awareness is mirrored in the structure of experience. Concept Awareness is a relative concept. It may be focused on an internal state, such as a visceral feeling, or on external events by way of sensory perception. It is analogous to sensing something, a process distinguished from observing and perceiving (which involves a basic process of acquainting with the items we perceive). Awareness or "to sense" can ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |