|
Heterologous
The term heterologous has several meanings in biology. Gene expression In cell biology and protein biochemistry, heterologous expression means that a protein is experimentally put into a cell that does not normally make (i.e., express) that protein. Heterologous (meaning 'derived from a different organism') refers to the fact that often the transferred protein was initially cloned from or derived from a different cell type or a different species from the recipient. Typically the protein itself is not transferred, but instead the 'correctly edited' genetic material coding for the protein (the complementary DNA or cDNA) is added to the recipient cell. The genetic material that is transferred typically must be within a format that encourages the recipient cell to express the cDNA as a protein (i.e., it is put in an expression vector). Methods for transferring foreign genetic material into a recipient cell include transfection and transduction. The choice of recipient cell ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heterogeneous
Homogeneity and heterogeneity are concepts often used in the sciences and statistics relating to the uniformity of a substance or organism. A material or image that is homogeneous is uniform in composition or character (i.e. color, shape, size, weight, height, distribution, texture, language, income, disease, temperature, radioactivity, architectural design, etc.); one that is heterogeneous is distinctly nonuniform in at least one of these qualities. Heterogeneous Mixtures, in chemistry, is where certain elements are unwillingly combined and, when given the option, will separate. Etymology and spelling The words ''homogeneous'' and ''heterogeneous'' come from Medieval Latin ''homogeneus'' and ''heterogeneus'', from Ancient Greek ὁμογενής (''homogenēs'') and ἑτερογενής (''heterogenēs''), from ὁμός (''homos'', “same”) and ἕτερος (''heteros'', “other, another, different”) respectively, followed by γένος (''genos'', “kind”); - ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transduction (genetics)
Transduction is the process by which foreign DNA is introduced into a cell by a virus or viral vector. An example is the viral transfer of DNA from one bacterium to another and hence an example of horizontal gene transfer. Transduction does not require physical contact between the cell donating the DNA and the cell receiving the DNA (which occurs in conjugation), and it is DNase resistant ( transformation is susceptible to DNase). Transduction is a common tool used by molecular biologists to stably introduce a foreign gene into a host cell's genome (both bacterial and mammalian cells). Discovery (bacterial transduction) Transduction was discovered by Norton Zinder and Joshua Lederberg at the University of Wisconsin–Madison in 1952 in Salmonella. In the lytic and lysogenic cycles Transduction happens through either the lytic cycle or the lysogenic cycle. When bacteriophages (viruses that infect bacteria) that are lytic infect bacterial cells, they harness the replicat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Homology (biology)
In biology, homology is similarity due to shared ancestry between a pair of structures or genes in different taxa. A common example of homologous structures is the forelimbs of vertebrates, where the wings of bats and birds, the arms of primates, the front flippers of whales and the forelegs of four-legged vertebrates like dogs and crocodiles are all derived from the same ancestral tetrapod structure. Evolutionary biology explains homologous structures adapted to different purposes as the result of descent with modification from a common ancestor. The term was first applied to biology in a non-evolutionary context by the anatomist Richard Owen in 1843. Homology was later explained by Charles Darwin's theory of evolution in 1859, but had been observed before this, from Aristotle onwards, and it was explicitly analysed by Pierre Belon in 1555. In developmental biology, organs that developed in the embryo in the same manner and from similar origins, such as from matc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Homology (other)
Homology may refer to: Sciences Biology *Homology (biology), any characteristic of biological organisms that is derived from a common ancestor *Sequence homology, biological homology between DNA, RNA, or protein sequences *Homologous chromosomes, chromosomes in a biological cell that pair up (synapse) during meiosis *Homologous recombination, genetic recombination in which nucleotide sequences are exchanged between molecules of DNA *Homologous desensitization, a receptor decreases its response to a signalling molecule when that agonist is in high concentration *Homology modeling, a method of protein structure prediction Chemistry *Homology (chemistry), the relationship between compounds in a homologous series *Homologous series, a series of organic compounds having different quantities of a repeated unit *Homologous temperature, the temperature of a material as a fraction of its absolute melting point *Homologation reaction, a chemical reaction which produces the next lo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Autologous
Autotransplantation is the organ transplantation, transplantation of Organ (anatomy), organs, Biological tissue, tissues, or even particular proteins from one part of the body to another in the same person (''wikt:auto-, auto-'' meaning "self" in Ancient Greek, Greek). The autologous tissue (also called autogenous, autogeneic, or autogenic tissue) transplanted by such a procedure is called an autograft or autotransplant. It is contrasted with allotransplantation (from other individual of the same species), Syngenic, syngeneic transplantation (grafts transplanted between two genetically identical individuals of the same species) and xenotransplantation (from other species). A common example is the removal of a piece of bone (usually from the hip) and its being ground into a paste for the reconstruction of another portion of bone. Autotransplantation, although most common with blood, bone, or skin, can be used for a wide variety of organs. One of the rare examples is autotransp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
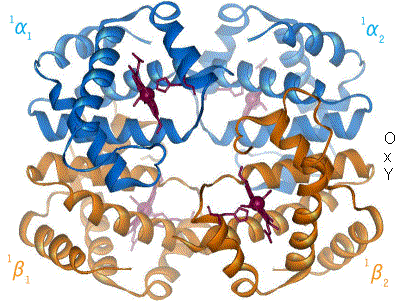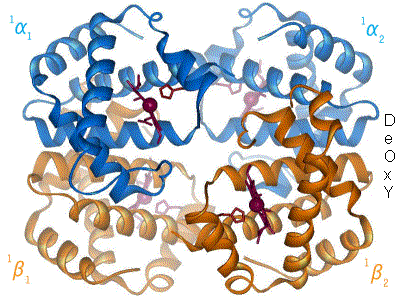
Protomer
In structural biology, a protomer is the structural unit of an oligomeric protein. It is the smallest unit composed of at least two different protein chains that form a larger hetero-oligomer by association of two or more copies of this unit. The term was introduced by Chetverin to make nomenclature in the Na/K-ATPase enzyme unambiguous. This enzyme is composed of two subunits: a large, catalytic α subunit, and a smaller glycoprotein β subunit (plus a proteolipid, called γ-subunit). At the time it was unclear how many of each work together. In addition, when people spoke of a dimer, it was unclear whether they were referring to αβ or to (αβ)2. Chetverin suggested to call αβ a protomer and (αβ)2 a diprotomer. Protomers usually arrange in cyclic symmetry to form closed point group symmetries. In chemistry, a so-called protomer is a molecule which displays tautomerism due to position of a proton. Examples Hemoglobin is a heterotetramer consisting of four subunits ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Structural Biology
Structural biology is a field that is many centuries old which, and as defined by the Journal of Structural Biology, deals with structural analysis of living material (formed, composed of, and/or maintained and refined by living cells) at every level of organization. Early structural biologists throughout the 19th and early 20th centuries were primarily only able to study structures to the limit of the naked eye's visual acuity and through magnifying glasses and light microscopes. In the 20th century, a variety of experimental techniques were developed to examine the 3D structures of biological molecules. The most prominent techniques are X-ray crystallography, nuclear magnetic resonance, and electron microscopy. Through the discovery of X-rays and its applications to protein crystals, structural biology was revolutionized, as now scientists could obtain the three-dimensional structures of biological molecules in atomic detail. Likewise, NMR spectroscopy allowed information about ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Allogenic
In ecology, allogenic succession is succession driven by the abiotic components of an ecosystem. In contrast, autogenic succession is driven by the biotic components of the ecosystem. An allogenic succession can be brought about in a number of ways which can include: *Volcanic eruptions *Meteor or comet strike *Flooding *Drought *Earthquakes * Non-anthropogenic climate change Allogenic succession can happen on a time scale that is proportionate with the disturbance. For example, allogenic succession that is the result of non-anthropogenic climate change can happen over thousands of years. Example The majority of Salt Marsh development comes from allogenic succession. The constant exposure to water in the intertidal zone causes the soil of a salt marsh to change over time. This results in sedimentation and nutrient buildup that also slowly raises the level of the land. What started as a sandy soil with a slightly high pH level, eventually becomes a loamy soil with a more ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Autologous
Autotransplantation is the organ transplantation, transplantation of Organ (anatomy), organs, Biological tissue, tissues, or even particular proteins from one part of the body to another in the same person (''wikt:auto-, auto-'' meaning "self" in Ancient Greek, Greek). The autologous tissue (also called autogenous, autogeneic, or autogenic tissue) transplanted by such a procedure is called an autograft or autotransplant. It is contrasted with allotransplantation (from other individual of the same species), Syngenic, syngeneic transplantation (grafts transplanted between two genetically identical individuals of the same species) and xenotransplantation (from other species). A common example is the removal of a piece of bone (usually from the hip) and its being ground into a paste for the reconstruction of another portion of bone. Autotransplantation, although most common with blood, bone, or skin, can be used for a wide variety of organs. One of the rare examples is autotransp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stem Cell Biology
In multicellular organisms, stem cells are Cellular differentiation, undifferentiated or partially differentiated Cell (biology), cells that can differentiate into various types of cells and Cell proliferation, proliferate indefinitely to produce more of the same stem cell. They are the earliest type of cell in a cell lineage. They are found in both embryonic and adult organisms, but they have slightly different properties in each. They are usually distinguished from progenitor cells, which cannot divide indefinitely, and Precursor cell, precursor or blast cells, which are usually committed to differentiating into one cell type. In mammals, roughly 50–150 cells make up the inner cell mass during the blastocyst stage of embryonic development, around days 5–14. These have stem-cell capability. ''In vivo'', they eventually differentiate into all of the body's cell types (making them pluripotent). This process starts with the differentiation into the three germ layers – the ect ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Medicine
Medicine is the science and Praxis (process), practice of caring for a patient, managing the diagnosis, prognosis, Preventive medicine, prevention, therapy, treatment, Palliative care, palliation of their injury or disease, and Health promotion, promoting their health. Medicine encompasses a variety of health care practices evolved to maintain and restore health by the prevention (medical), prevention and therapy, treatment of illness. Contemporary medicine applies biomedical sciences, biomedical research, medical genetics, genetics, and medical technology to diagnosis (medical), diagnose, treat, and prevent injury and disease, typically through pharmaceuticals or surgery, but also through therapies as diverse as psychotherapy, splint (medicine), external splints and traction, medical devices, biologic medical product, biologics, and Radiation (medicine), ionizing radiation, amongst others. Medicine has been practiced since Prehistoric medicine, prehistoric times, and for most o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cell Biology
Cell biology (also cellular biology or cytology) is a branch of biology that studies the structure, function, and behavior of cells. All living organisms are made of cells. A cell is the basic unit of life that is responsible for the living and functioning of organisms. Cell biology is the study of structural and functional units of cells. Cell biology encompasses both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells and has many subtopics which may include the study of cell metabolism, cell communication, cell cycle, biochemistry, and cell composition. The study of cells is performed using several microscopy techniques, cell culture, and cell fractionation. These have allowed for and are currently being used for discoveries and research pertaining to how cells function, ultimately giving insight into understanding larger organisms. Knowing the components of cells and how cells work is fundamental to all biological sciences while also being essential for research in biomedical fields ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |