|
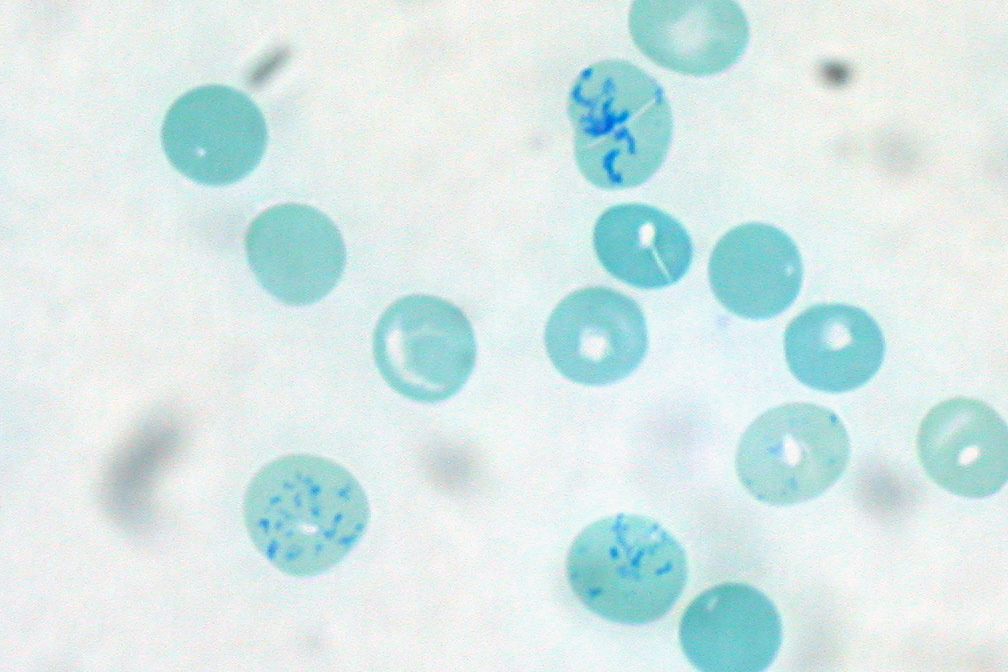
Hereditary Spherocytosis
Hereditary spherocytosis (HS) is a congenital hemolytic disorder, wherein a genetic mutation coding for a structural membrane protein phenotype leads to a spherical shaping of erythrocytic cellular morphology. As erythrocytes are sphere-shaped (spherocytosis), rather than the normal biconcave disk-shaped, their morphology interferes with these cells' abilities to be flexible during circulation throughout the entirety of the body - arteries, arterioles, capillaries, venules, veins, and organs. This difference in shape also makes the red blood cells more prone to rupture under osmotic and/or mechanical stress. Cells with these dysfunctional proteins are degraded in the spleen, which leads to a shortage of erythrocytes resulting in hemolytic anemia. HS was first described in 1871, and is the most common cause of inherited hemolysis in populations of northern European descent, with an incidence of 1 in 5000 births. The clinical severity of HS varies from mild (symptom-free carrier), t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hematology
Hematology ( always spelled haematology in British English) is the branch of medicine concerned with the study of the cause, prognosis, treatment, and prevention of diseases related to blood. It involves treating diseases that affect the production of blood and its components, such as blood cells, hemoglobin, blood proteins, bone marrow, platelets, blood vessels, spleen, and the mechanism of coagulation. Such diseases might include hemophilia, blood clots (thrombus), other bleeding disorders, and blood cancers such as leukemia, multiple myeloma, and lymphoma. The laboratory analysis of blood is frequently performed by a medical technologist or medical laboratory scientist. Specialization Physicians specialized in hematology are known as hematologists or haematologists. Their routine work mainly includes the care and treatment of patients with hematological diseases, although some may also work at the hematology laboratory viewing blood films and bone marrow slides under the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gallbladder
In vertebrates, the gallbladder, also known as the cholecyst, is a small hollow organ where bile is stored and concentrated before it is released into the small intestine. In humans, the pear-shaped gallbladder lies beneath the liver, although the structure and position of the gallbladder can vary significantly among animal species. It receives and stores bile, produced by the liver, via the common hepatic duct, and releases it via the common bile duct into the duodenum, where the bile helps in the digestion of fats. The gallbladder can be affected by gallstones, formed by material that cannot be dissolved – usually cholesterol or bilirubin, a product of haemoglobin breakdown. These may cause significant pain, particularly in the upper-right corner of the abdomen, and are often treated with removal of the gallbladder (called a cholecystectomy). Cholecystitis, inflammation of the gallbladder, has a wide range of causes, including result from the impaction of gallstones, inf ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Band 3 Anion Transport Protein
Band 3 anion transport protein, also known as anion exchanger 1 (AE1) or band 3 or solute carrier family 4 member 1 (SLC4A1), is a protein that is encoded by the gene in humans. Band 3 anion transport protein is a phylogenetically-preserved Membrane transport protein, transport protein responsible for mediating the Active transport#Antiport, exchange of chloride (Cl−) with bicarbonate (HCO3−) across plasma membranes. Functionally similar members of the AE clade are SLC4A2, AE2 and SLC4A3, AE3. Function Band 3 is present in the basolateral face of the Collecting duct system#Intercalated cells, α-intercalated cells of the collecting ducts of the nephron, which are the main acid-secreting cells of the kidney. They generate hydrogen ions and bicarbonate ions from carbon dioxide and water – a reaction catalysed by carbonic anhydrase. The hydrogen ions are pumped into the collecting duct tubule by V-ATPase, vacuolar H+ ATPase, the apical proton pump, which thus excretes ac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
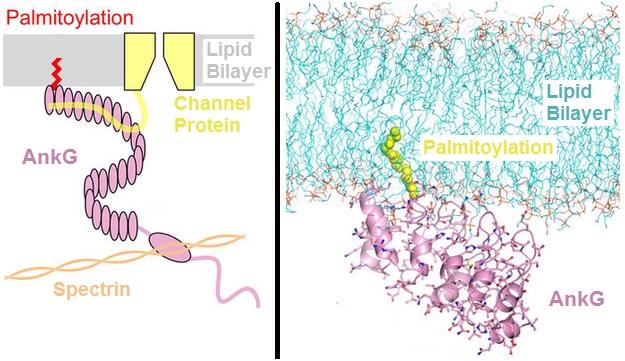
Ankyrin
Ankyrins are a family of proteins that mediate the attachment of integral membrane proteins to the spectrin-actin based membrane cytoskeleton. Ankyrins have binding sites for the beta subunit of spectrin and at least 12 families of integral membrane proteins. This linkage is required to maintain the integrity of the plasma membranes and to anchor specific ion channels, ion exchangers and ion transporters in the plasma membrane. The name is derived from the Greek word ἄγκυρα (''ankyra'') for "anchor". Structure Ankyrins contain four functional domains: an N-terminal domain that contains 24 tandem ankyrin repeats, a central domain that binds to spectrin, a death domain that binds to proteins involved in apoptosis, and a C-terminal regulatory domain that is highly variable between different ankyrin proteins. Membrane protein recognition The 24 tandem ankyrin repeats are responsible for the recognition of a wide range of membrane proteins. These 24 repeats contain 3 struc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spectrin
Spectrin is a cytoskeletal protein that lines the intracellular side of the plasma membrane in eukaryotic cells. Spectrin forms pentagonal or hexagonal arrangements, forming a scaffold and playing an important role in maintenance of plasma membrane integrity and cytoskeletal structure. The hexagonal arrangements are formed by tetramers of spectrin subunits associating with short actin filaments at either end of the tetramer. These short actin filaments act as junctional complexes allowing the formation of the hexagonal mesh. The protein is named spectrin since it was first isolated as a major protein component of human red blood cells which had been treated with mild detergents; the detergents lysed the cells and the hemoglobin and other cytoplasmic components were washed out. In the light microscope the basic shape of the red blood cell could still be seen as the spectrin-containing submembranous cytoskeleton preserved the shape of the cell in outline. This became known as a red ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mutation
In biology, a mutation is an alteration in the nucleic acid sequence of the genome of an organism, virus, or extrachromosomal DNA. Viral genomes contain either DNA or RNA. Mutations result from errors during DNA or viral replication, mitosis, or meiosis or other types of damage to DNA (such as pyrimidine dimers caused by exposure to ultraviolet radiation), which then may undergo error-prone repair (especially microhomology-mediated end joining), cause an error during other forms of repair, or cause an error during replication (translesion synthesis). Mutations may also result from insertion or deletion of segments of DNA due to mobile genetic elements. Mutations may or may not produce detectable changes in the observable characteristics (phenotype) of an organism. Mutations play a part in both normal and abnormal biological processes including: evolution, cancer, and the development of the immune system, including junctional diversity. Mutation is the ultimate source o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Harrison's Principles Of Internal Medicine
''Harrison's Principles of Internal Medicine'' is an American textbook of internal medicine. First published in 1950, it is in its 21st edition (published in 2022 by McGraw-Hill Professional ) and comes in two volumes. Although it is aimed at all members of the medical profession, it is mainly used by internists and junior doctors in this field, as well as medical students. It is widely regarded as one of the most authoritative books on internal medicine and has been described as the "most recognized book in all of medicine." The work is named after Tinsley R. Harrison of Birmingham, Alabama, who served as editor-in-chief of the first five editions and established the format of the work: a strong basis of clinical medicine interwoven with an understanding of pathophysiology. History It was published in 1950 by Blakiston. Creator and editor Tinsley Harrison's quotation appeared on the first edition of this book in 1950: Blakiston was acquired by McGraw-Hill in 1954. The 17th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gallstone
A gallstone is a calculus (medicine), stone formed within the gallbladder from precipitated bile components. The term cholelithiasis may refer to the presence of gallstones or to any disease caused by gallstones, and choledocholithiasis refers to the presence of migrated gallstones within bile ducts. Most people with gallstones (about 80%) are asymptomatic. However, when a gallstone obstructs the bile duct and causes acute cholestasis, a reflexive smooth muscle spasm often occurs, resulting in an intense cramp-like visceral pain in the quadrant (abdomen), right upper part of the abdomen known as a biliary colic (or "gallbladder attack"). This happens in 1–4% of those with gallstones each year. Complications from gallstones may include inflammation of the gallbladder (cholecystitis), inflammation of the pancreas (pancreatitis), Jaundice#Post-hepatic, obstructive jaundice, and infection in bile ducts (ascending cholangitis, cholangitis). Symptoms of these complications may include ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reticulocyte
Reticulocytes are immature red blood cells (RBCs). In the process of erythropoiesis (red blood cell formation), reticulocytes develop and mature in the bone marrow and then circulatory system, circulate for about a day in the blood stream before developing into mature red blood cells. Like mature red blood cells, in mammals, reticulocytes do not have a cell nucleus. They are called reticulocytes because of a reticular (mesh-like) network of ribosome, ribosomal RNA that becomes visible under a microscope with certain staining, stains such as new methylene blue and Romanowsky stain. Clinical significance To accurately measure reticulocyte counts, automated flow cytometry, counters use a combination of laser excitation, detectors and a fluorophore, fluorescent dye that marks RNA and DNA (such as titan yellow or polymethine). Reticulocytes appear slightly bluer than other red cells when looked at with the normal Romanowsky stain. Reticulocytes are also relatively large, a character ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hemoglobin
Hemoglobin (haemoglobin BrE) (from the Greek word αἷμα, ''haîma'' 'blood' + Latin ''globus'' 'ball, sphere' + ''-in'') (), abbreviated Hb or Hgb, is the iron-containing oxygen-transport metalloprotein present in red blood cells (erythrocytes) of almost all vertebrates (the exception being the fish family Channichthyidae) as well as the tissues of some invertebrates. Hemoglobin in blood carries oxygen from the respiratory organs (''e.g.'' lungs or gills) to the rest of the body (''i.e.'' tissues). There it releases the oxygen to permit aerobic respiration to provide energy to power functions of an organism in the process called metabolism. A healthy individual human has 12to 20grams of hemoglobin in every 100mL of blood. In mammals, the chromoprotein makes up about 96% of the red blood cells' dry content (by weight), and around 35% of the total content (including water). Hemoglobin has an oxygen-binding capacity of 1.34mL O2 per gram, which increases the total blood oxygen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Splenectomy
A splenectomy is the surgical procedure that partially or completely removes the spleen. The spleen is an important organ in regard to immunological function due to its ability to efficiently destroy encapsulated bacteria. Therefore, removal of the spleen runs the risk of overwhelming post-splenectomy infection, a medical emergency and rapidly fatal disease caused by the inability of the body's immune system to properly fight infection following splenectomy or asplenia. Common indications for splenectomy include trauma, tumors, splenomegaly or for hematological disease such as sickle cell anemia or thalassemia. Indications The spleen is an organ located in the abdomen next to the stomach. It is composed of red pulp which filters the blood, removing foreign material, damaged and worn out red blood cells. It also functions as a storage site for iron, red blood cells and platelets. The rest (~25%) of the spleen is known as the white pulp and functions like a large lymph node bein ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |