|
Henohenomoheji
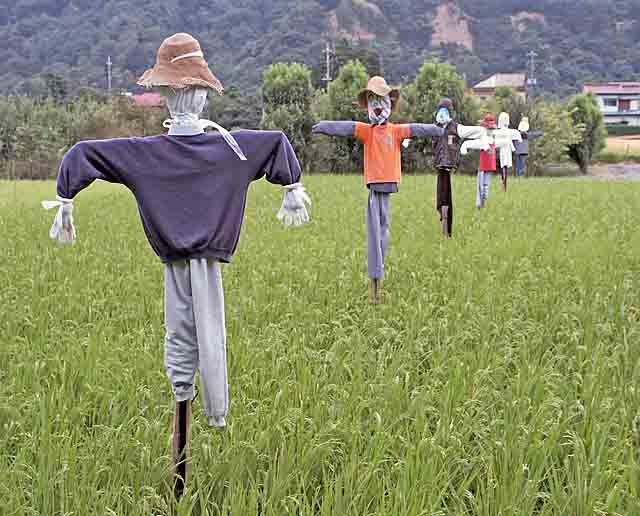
''Henohenomoheji'' ( ja, へのへのもへじ ) or ''hehenonomoheji'' () is a face known to be drawn by Japanese schoolchildren using hiragana characters. It became a popular drawing during the Edo period. The word breaks down into seven hiragana characters: ''he'' (), ''no'' (), ''he'' (), ''no'' (), ''mo'' (), ''he'' (), and ''ji'' (). The first two ''he'' are the eyebrows, the two ''no'' are the eyes, the ''mo'' is a nose, and the last ''he'' is the mouth. The outline of the face is made by the character ''ji'', its two short strokes (''dakuten'') forming the ear or cheek. Henohenomoheji is often used to symbolize a nondescript or generic human face, such as the faces of ''kakashi'' (scarecrows) and teru teru bōzu. The characters are often sung as they are drawn, making the an . File:Henohenomoheji graffiti Oct 04 2020 02-52PM.jpeg , As a graffiti へのへのもへ (19559421992).jpg , On a Face of Japanese scarecrow.jpg , On a scarecrow File:MET 10 211 1816 d.jpg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Henohenomoheji
''Henohenomoheji'' ( ja, へのへのもへじ ) or ''hehenonomoheji'' () is a face known to be drawn by Japanese schoolchildren using hiragana characters. It became a popular drawing during the Edo period. The word breaks down into seven hiragana characters: ''he'' (), ''no'' (), ''he'' (), ''no'' (), ''mo'' (), ''he'' (), and ''ji'' (). The first two ''he'' are the eyebrows, the two ''no'' are the eyes, the ''mo'' is a nose, and the last ''he'' is the mouth. The outline of the face is made by the character ''ji'', its two short strokes (''dakuten'') forming the ear or cheek. Henohenomoheji is often used to symbolize a nondescript or generic human face, such as the faces of ''kakashi'' (scarecrows) and teru teru bōzu. The characters are often sung as they are drawn, making the an . File:Henohenomoheji graffiti Oct 04 2020 02-52PM.jpeg , As a graffiti へのへのもへ (19559421992).jpg , On a Face of Japanese scarecrow.jpg , On a scarecrow File:MET 10 211 1816 d.jpg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tête à Toto
The tête à Toto is a French typographical design and children's game, well known to French schoolchildren. It consists of the equation "0+0=0", written with the first two "0"s for eyes, the "+" for a nose, the "=" for a mouth, and the final "0" surrounding, as a stylized face or skull. It is drawn while reciting: Translated: As his head equals zero, it means that his intelligence is null. The name, or character, of Toto is a common stock character in French culture; he is the generic child used in jokes ("Toto asks his mother..."). See Blague de Toto (Toto joke). Other uses *A circumlocution for "zero" *In prostitution, slang for a prostitute – or rather, prospective prostitute – who has not had a single client ( i.e., who has had zero clients). See also *Henohenomoheji ''Henohenomoheji'' ( ja, へのへのもへじ ) or ''hehenonomoheji'' () is a face known to be drawn by Japanese schoolchildren using hiragana characters. It became a popular drawing during the Ed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Emoticon
An emoticon (, , rarely , ), short for "emotion icon", also known simply as an emote, is a pictorial representation of a facial expression using Character (symbol), characters—usually punctuation marks, numbers, and letters—to express a person's feelings, mood or reaction, or as a time-saving method. The first ASCII emoticons are generally credited to computer scientist Scott Fahlman, who proposed what came to be known as "smileys":-) and :-(in a message on the bulletin board system (BBS) of Carnegie Mellon University in 1982. In Western countries, emoticons are usually written at a right angle to the direction of the text. Users from Japan popularized a kind of emoticon called kaomoji, utilizing the larger character sets required for Japanese, that can be understood without tilting one's head to the left. This style arose on ASCII NET of Japan in 1986. As SMS mobile text messaging and the Internet became widespread in the late 1990s, emoticons became increasingly popula ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cool S
The Cool S (also known as the Stussy S, Super S, Superman S, Universal S, Pointy S, Middle School S, Graffiti S, and by many other names) is a graffiti sign in popular culture that is typically doodled on children's notebooks or graffitied on walls. The exact origin of the Cool S is unknown, but an instance was found in a late 1800s geometry textbook and it became prevalent around the early 1970s as a part of graffiti culture. Contrary to popular belief, the symbol neither originated from nor was used by the U.S. clothing brand Stüssy or the character Superman, though Stüssy did conduct an interview in 2010 with Jon Naar, a pioneer graffiti photographer with many works including this S, dating back to the 1970s. This symbol and other nearly-identical S-shaped motifs have appeared for at least hundreds of years. A similar pattern can be seen in 14th-century tilework at the central courtyard of the Sultan Hassan Mosque in Cairo, as well as in the background of the 1533 painting ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scarecrow
A scarecrow is a decoy or mannequin, often in the shape of a human. Humanoid scarecrows are usually dressed in old clothes and placed in open fields to discourage birds from disturbing and feeding on recently cast seed and growing crops.Lesley Brown (ed.). (2007). "Shorter Oxford English Dictionary on Historical Principles". 6th ed. Oxford: Oxford University Press. . Scarecrows are used around the world by farmers, and are a notable symbol of farms and the countryside in popular culture. Design The common form of a scarecrow is a humanoid figure dressed in old clothes and placed in open fields to discourage birds such as Corvus, crows or Old World sparrow, sparrows from disturbing and feeding on recently cast seed and growing crops. Machinery such as windmills have been employed as scarecrows, but the effectiveness lessens as animals become familiar with the structures. Since the invention of the humanoid scarecrow, more effective methods have been developed. On California far ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cheek
The cheeks ( la, buccae) constitute the area of the face below the eyes and between the nose and the left or right ear. "Buccal" means relating to the cheek. In humans, the region is innervated by the buccal nerve. The area between the inside of the cheek and the teeth and gums is called the vestibule or buccal pouch or buccal cavity and forms part of the mouth. In other animals the cheeks may also be referred to as jowls. Structure Humans Cheeks are fleshy in humans, the skin being suspended by the chin and the jaws, and forming the lateral wall of the human mouth, visibly touching the cheekbone below the eye. The inside of the cheek is lined with a mucous membrane (buccal mucosa, part of the oral mucosa). During mastication (chewing), the cheeks and tongue between them serve to keep the food between the teeth. Other animals The cheeks are covered externally by hairy skin, and internally by stratified squamous epithelium. This is mostly smooth, but may have caudally di ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ASCII Art
ASCII art is a graphic design technique that uses computers for presentation and consists of pictures pieced together from the 95 printable (from a total of 128) characters defined by the ASCII Standard from 1963 and ASCII compliant character sets with proprietary extended characters (beyond the 128 characters of standard 7-bit ASCII). The term is also loosely used to refer to text-based visual art in general. ASCII art can be created with any text editor, and is often used with free-form languages. Most examples of ASCII art require a fixed-width font (non-proportional fonts, as on a traditional typewriter) such as Courier for presentation. Among the oldest known examples of ASCII art are the creations by computer-art pioneer Kenneth Knowlton from around 1966, who was working for Bell Labs at the time. "Studies in Perception I" by Ken Knowlton and Leon Harmon from 1966 shows some examples of their early ASCII art. "1966 Studies in Perception I by Ken Knowlton and Leon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Netsuke
A is a miniature sculpture, originating in 17th century Japan. Initially a simply-carved button fastener on the cords of an box, later developed into ornately sculpted objects of craftsmanship. History Traditionally, Japanese clothing – first the and its later evolution, the kimono – did not have pockets. Though the sleeves of the kimono could be used to store small items, the men who wore kimono needed a larger and stronger container in which to store personal belongings, such as pipes, tobacco, money and seals, resulting in the development of containers known as , which were hung by cords from the robes' sashes (). These containers may have been pouches or small woven baskets, but the most popular were crafted boxes () held shut by , sliding beads on cords. Whatever the form of the container, the fastener that secured the cord at the top of the sash was a carved, button-like toggle called a . , like and , evolved over time from being strictly utilitarian into object ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Graffiti
Graffiti (plural; singular ''graffiti'' or ''graffito'', the latter rarely used except in archeology) is art that is written, painted or drawn on a wall or other surface, usually without permission and within public view. Graffiti ranges from simple written words to elaborate wall paintings, and has existed Graffito (archaeology), since ancient times, with examples dating back to ancient Egypt, ancient Greece, and the Roman Empire. Graffiti is a controversial subject. In most countries, marking or painting property without permission is considered by property owners and civic authorities as defacement and vandalism, which is a punishable crime, citing the use of graffiti by street gangs to mark territory or to serve as an indicator of gang-related activities. Graffiti has become visualized as a growing urban "problem" for many cities in industrialized nations, spreading from the New York City Subway nomenclature, New York City subway system and Philadelphia in the early 1970s to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Teru Teru Bōzu
A is a small traditional handmade that originated from the Edo period in Japan, made from white paper or cloth, Japanese farmers began hanging outside of their window by a string. This talisman is supposed to have magical powers to bring good weather and to stop or prevent a rainy day. ''Teru'' is a Japanese verb that describes sunshine, and a ''bōzu'' is a Buddhist monk (compare the word bonze), or in modern slang, "bald-headed"; ''bōzu'' is also used as a term of endearment for addressing little boys. ''Teru Teru bōzu'' became popular during the Edo period among urban dwellers, whose children would make them the day before the good weather was desired and chant, "Fine-weather priest, please let the weather be good tomorrow." Traditionally, if the weather does turn out well, a libation of holy sake is poured over them, and they are washed away in the river. Today, children make ''teru teru bōzu'' out of tissue paper or cotton and string and hang them from a window when t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dakuten
The , colloquially , is a diacritic most often used in the Japanese kana syllabaries to indicate that the consonant of a syllable should be pronounced voiced, for instance, on sounds that have undergone rendaku (sequential voicing). The , colloquially , is a diacritic used with the kana for syllables starting with ''h'' to indicate that they should instead be pronounced with . History The ''kun'yomi'' pronunciation of the character is ''nigori''; hence the ''daku-ten'' may also be called the ''nigori-ten''. This character, meaning ''muddy'' or ''turbid'', stems from historical Chinese phonology, where consonants were traditionally classified as ''clear'' ( "voiceless"), ''lesser-clear'' ( " aspirated") and ''muddy'' ( "voiced"). (See: Middle Chinese § Initials) ''Dakuten'' were used sporadically since the start of written Japanese; their use tended to become more common as time went on. The modern practice of using dakuten in all cases of voicing in all writing only came ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Japanese Person
The are an East Asian ethnic group native to the Japanese archipelago."人類学上は,旧石器時代あるいは縄文時代以来,現在の北海道〜沖縄諸島(南西諸島)に住んだ集団を祖先にもつ人々。" () Japanese people constitute 97.9% of the population of the country of Japan. Worldwide, approximately 129 million people are of Japanese descent; of these, approximately 122.5 million are residents of Japan. People of Japanese ancestry who live outside Japan are referred to as , the Japanese diaspora. Depending on the context, the term may be limited or not to mainland Japanese people, specifically the Yamato (as opposed to Ryukyuan and Ainu people). Japanese people are one of the largest ethnic groups in the world. In recent decades, there has also been an increase in the number of multiracial people with both Japanese and non-Japanese roots, including half Japanese people. History Theories of origins Archaeological evidence in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |