|
Helix Turn Helix
Helix-turn-helix is a DNA-binding protein (DBP). The helix-turn-helix (HTH) is a major structural motif capable of binding DNA. Each monomer incorporates two α helices, joined by a short strand of amino acids, that bind to the major groove of DNA. The HTH motif occurs in many proteins that regulate gene expression. It should not be confused with the helix–loop–helix motif. Discovery The discovery of the helix-turn-helix motif was based on similarities between several genes encoding transcription regulatory proteins from bacteriophage lambda and ''Escherichia coli'': Cro, CAP, and λ repressor, which were found to share a common 20–25 amino acid sequence that facilitates DNA recognition. Function The helix-turn-helix motif is a DNA-binding motif. The recognition and binding to DNA by helix-turn-helix proteins is done by the two α helices, one occupying the N-terminal end of the motif, the other at the C-terminus. In most cases, such as in the Cro repressor, the second h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lambda Repressor 1LMB
Lambda (}, ''lám(b)da'') is the 11th letter of the Greek alphabet, representing the voiced alveolar lateral approximant . In the system of Greek numerals, lambda has a value of 30. Lambda is derived from the Phoenician Lamed . Lambda gave rise to the Latin L and the Cyrillic El (Л). The ancient grammarians and dramatists give evidence to the pronunciation as () in Classical Greek times. In Modern Greek, the name of the letter, Λάμδα, is pronounced . In early Greek alphabets, the shape and orientation of lambda varied. Most variants consisted of two straight strokes, one longer than the other, connected at their ends. The angle might be in the upper-left, lower-left ("Western" alphabets) or top ("Eastern" alphabets). Other variants had a vertical line with a horizontal or sloped stroke running to the right. With the general adoption of the Ionic alphabet, Greek settled on an angle at the top; the Romans put the angle at the lower-left. The HTML 4 character entity re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MYB (gene)
Myb genes are part of a large gene family of transcription factors found in animals and plants. In humans, it includes Myb proto-oncogene like 1 and Myb-related protein B in addition to MYB proper. Members of the extended SANT/Myb family also include the SANT domain and other similar all-helical homeobox-like domains. Function Viral The Myb gene family is named after the eponymous gene in Avian myeloblastosis virus. The viral Myb (v-Myb, ) recognizes the sequence 5'-YAACKG-3'. It causes myeloblastosis (myeloid leukemia) in chickens. Compared to the normal animal cellular Myb (c-myb), v-myb contains deletions in the C-terminal regulatory domain, leading to aberrant activation of other oncogenes. Animals Myb proto-oncogene protein is a member of the MYB (myeloblastosis) family of transcription factors. The protein contains three domains, an N-terminal DNA-binding domain, a central transcriptional activation domain and a C-terminal domain involved in transcriptional re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
EMBL
The European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) is an intergovernmental organization dedicated to molecular biology research and is supported by 27 member states, two prospect states, and one associate member state. EMBL was created in 1974 and is funded by public research money from its member states. Research at EMBL is conducted by approximately 110 independent research and service groups and teams covering the spectrum of molecular biology and bioinformatics. The list of Groups and Teams at EMBL can be found at . The Laboratory operates from six sites: the main laboratory in Heidelberg, and sites in Hinxton (the European Bioinformatics Institute (EBI), in England), Grenoble (France), Hamburg (Germany), Rome (Italy) and Barcelona (Spain). EMBL groups and laboratories perform basic research in molecular biology and molecular medicine as well as train scientists, students, and visitors. The organization aids in the development of services, new instruments and methods, and techno ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zinc Finger
A zinc finger is a small protein structural motif that is characterized by the coordination of one or more zinc ions (Zn2+) in order to stabilize the fold. It was originally coined to describe the finger-like appearance of a hypothesized structure from the African clawed frog (''Xenopus laevis'') transcription factor IIIA. However, it has been found to encompass a wide variety of differing protein structures in eukaryotic cells. ''Xenopus laevis'' TFIIIA was originally demonstrated to contain zinc and require the metal for function in 1983, the first such reported zinc requirement for a gene regulatory protein followed soon thereafter by the Krüppel factor in ''Drosophila''. It often appears as a metal-binding domain in multi-domain proteins. Proteins that contain zinc fingers (zinc finger proteins) are classified into several different structural families. Unlike many other clearly defined supersecondary structures such as Greek keys or β hairpins, there are a number of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Secondary Structure
Protein secondary structure is the three dimensional conformational isomerism, form of ''local segments'' of proteins. The two most common Protein structure#Secondary structure, secondary structural elements are alpha helix, alpha helices and beta sheets, though beta turns and omega loops occur as well. Secondary structure elements typically spontaneously form as an intermediate before the protein protein folding, folds into its three dimensional protein tertiary structure, tertiary structure. Secondary structure is formally defined by the pattern of hydrogen bonds between the Amine, amino hydrogen and carboxyl oxygen atoms in the peptide backbone chain, backbone. Secondary structure may alternatively be defined based on the regular pattern of backbone Dihedral angle#Dihedral angles of proteins, dihedral angles in a particular region of the Ramachandran plot regardless of whether it has the correct hydrogen bonds. The concept of secondary structure was first introduced by Kaj Ulrik ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DNA-binding Domain
A DNA-binding domain (DBD) is an independently folded protein domain that contains at least one structural motif that recognizes double- or single-stranded DNA. A DBD can recognize a specific DNA sequence (a recognition sequence) or have a general affinity to DNA. Some DNA-binding domains may also include nucleic acids in their folded structure. Function One or more DNA-binding domains are often part of a larger protein consisting of further protein domains with differing function. The extra domains often regulate the activity of the DNA-binding domain. The function of DNA binding is either structural or involves transcription regulation, with the two roles sometimes overlapping. DNA-binding domains with functions involving DNA structure have biological roles in DNA replication, repair, storage, and modification, such as methylation. Many proteins involved in the regulation of gene expression contain DNA-binding domains. For example, proteins that regulate transcription by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Multiple Antibiotic Resistance
Multiple drug resistance (MDR), multidrug resistance or multiresistance is antimicrobial resistance shown by a species of microorganism to at least one antimicrobial drug in three or more antimicrobial categories. Antimicrobial categories are classifications of antimicrobial agents based on their mode of action and specific to target organisms. The MDR types most threatening to public health are MDR bacteria that resist multiple antibiotics; other types include MDR viruses, parasites (resistant to multiple antifungal, antiviral, and antiparasitic drugs of a wide chemical variety). Recognizing different degrees of MDR in bacteria, the terms extensively drug-resistant (XDR) and pandrug-resistant (PDR) have been introduced. Extensively drug-resistant (XDR) is the non-susceptibility of one bacteria species to all antimicrobial agents except in two or less antimicrobial categories. Within XDR, pandrug-resistant (PDR) is the non-susceptibility of bacteria to all antimicrobial agents i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MarR
Marr (Scottish Gaelic: ''Màrr'') is one of six committee areas in Aberdeenshire, Scotland. It has a population of 34,038 (2001 Census). Someone from Marr is called a ''Màrnach'' in Scottish Gaelic. Etymology The genesis of the name ''Marr'' is uncertain. ''Mar'', a Brittonic personal name, may be involved. Further possibilities include a connection with the ethnic names ''Marsi'' and ''Marsigni'' of Italy and Bohemia, or a derivation from Old Norse ''marr'' meaning "sea, marsh, fen". American academic Thomas Clancy has noted cautiously the similarity between the territory names ''Buchan'' and ''Marr'' to those of the Welsh commotes ''Cantref Bychan'' and ''Cantref Mawr'', meaning "large-" and "small-commote", respectively. Linguist Guto Rhys adjudged the proposal "appealing" but "questionable", on the basis that the form ''Marr'' conflicts with the expected development of ''mawr''. Features To the west, the mountain environment of the Cairngorms National Park sustains ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ETS Transcription Factor Family
In the field of molecular biology, the ETS (E26 transformation-specific or E-twenty-six. (Erythroblast Transformation Specific)) family is one of the largest families of transcription factors and is unique to animals. There are 29 genes in humans, 28 in the mouse, 10 in ''Caenorhabditis elegans'' and 9 in ''Drosophila.'' The founding member of this family was identified as a gene transduced by the leukemia virus, E26. The members of the family have been implicated in the development of different tissues as well as cancer progression. Subfamilies The ETS (Erythroblast Transformation Specific)family is divided into 12 subfamilies, which are listed below: Structure All ETS (Erythroblast Transformation Specific) family members are identified through a highly conserved DNA binding domain, the ETS domain, which is a winged helix-turn-helix structure that binds to DNA sites with a central GGA(A/T) DNA sequence. As well as DNA-binding functions, evidence suggests that the ETS doma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beta Sheet
The beta sheet, (β-sheet) (also β-pleated sheet) is a common motif of the regular protein secondary structure. Beta sheets consist of beta strands (β-strands) connected laterally by at least two or three backbone hydrogen bonds, forming a generally twisted, pleated sheet. A β-strand is a stretch of polypeptide chain typically 3 to 10 amino acids long with backbone in an extended conformation. The supramolecular association of β-sheets has been implicated in the formation of the fibrils and protein aggregates observed in amyloidosis, notably Alzheimer's disease. History The first β-sheet structure was proposed by William Astbury in the 1930s. He proposed the idea of hydrogen bonding between the peptide bonds of parallel or antiparallel extended β-strands. However, Astbury did not have the necessary data on the bond geometry of the amino acids in order to build accurate models, especially since he did not then know that the peptide bond was planar. A refined versi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beta-sheet
The beta sheet, (β-sheet) (also β-pleated sheet) is a common motif of the regular protein secondary structure. Beta sheets consist of beta strands (β-strands) connected laterally by at least two or three backbone hydrogen bonds, forming a generally twisted, pleated sheet. A β-strand is a stretch of polypeptide chain typically 3 to 10 amino acids long with backbone in an extended conformation. The supramolecular association of β-sheets has been implicated in the formation of the fibrils and protein aggregates observed in amyloidosis, notably Alzheimer's disease. History The first β-sheet structure was proposed by William Astbury in the 1930s. He proposed the idea of hydrogen bonding between the peptide bonds of parallel or antiparallel extended β-strands. However, Astbury did not have the necessary data on the bond geometry of the amino acids in order to build accurate models, especially since he did not then know that the peptide bond was planar. A refined versi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
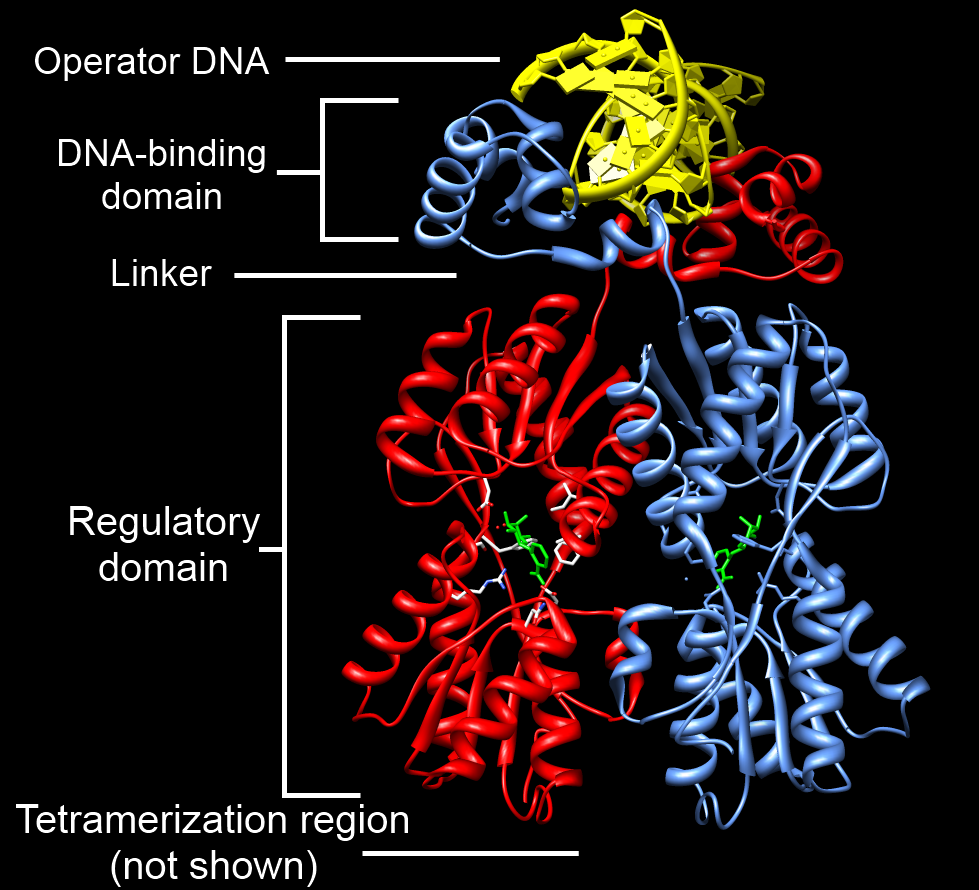
TetR
Tet Repressor proteins (otherwise known as TetR) are proteins playing an important role in conferring antibiotic resistance to large categories of bacterial species. Tetracycline (Tc) is a broad family of antibiotics to which bacteria have evolved resistance. Tc normally kills bacteria by binding to the bacterial ribosome and halting protein synthesis. The expression of Tc resistance genes is regulated by the repressor TetR. TetR represses the expression of TetA, a membrane protein that pumps out substances toxic to the bacteria like Tc, by binding the ''tetA'' operator. In Tc-resistant bacteria, TetA will pump out Tc before it can bind to the ribosome because the repressive action of TetR on TetA is halted by binding of Tc to TetR. Therefore, TetR may have an important role in helping scientists to better understand mechanisms of antibiotic resistance and how to treat antibiotic resistant bacteria. TetR is one of many proteins in the TetR protein family, which is so named becaus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |





.png)