|
Heightfield
In computer graphics, a heightmap or heightfield is a raster image used mainly as Discrete Global Grid in secondary elevation modeling. Each pixel stores values, such as surface elevation data, for display in 3D computer graphics. A heightmap can be used in bump mapping to calculate where this 3D data would create shadow in a material, in displacement mapping to displace the actual geometric position of points over the textured surface, or for terrain where the heightmap is converted into a 3D mesh. A heightmap contains one channel interpreted as a distance of displacement or "height" from the "floor" of a surface and sometimes visualized as luma of a grayscale image, with black representing minimum height and white representing maximum height. When the map is rendered, the designer can specify the amount of displacement for each unit of the height channel, which corresponds to the “contrast” of the image. Heightmaps can be stored by themselves in existing grayscale i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Daylon Leveller
{{Infobox software , name = Daylon Leveller , logo = , screenshot = , caption = , collapsible = , author = Ray Gardener , developer = Daylon Graphics Ltd. , released = , latest release version = 4.2 , latest release date = {{release_date, 2019, 10, 14 , latest preview version = , latest preview date = , programming language = C++ , operating system = Microsoft Windows , platform = , size = , language = , status = , genre = 3D computer graphics , license = Commercial per-seat , website Daylon Leveller is a terrain/ heightfield modeling program made by Daylon Graphics Ltd. of British Columbia, Canada. It was written by Ray Gardener in 1998 and is now at version 4.2. Leveller began as a fork of Gardener's earlier NavCam utility ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heightmap
In computer graphics, a heightmap or heightfield is a raster image used mainly as Discrete Global Grid in secondary elevation modeling. Each pixel stores values, such as surface elevation data, for display in 3D computer graphics. A heightmap can be used in bump mapping to calculate where this 3D data would create shadow in a material, in displacement mapping to displace the actual geometric position of points over the textured surface, or for terrain where the heightmap is converted into a 3D mesh. A heightmap contains one channel interpreted as a distance of displacement or "height" from the "floor" of a surface and sometimes visualized as luma of a grayscale image, with black representing minimum height and white representing maximum height. When the map is rendered, the designer can specify the amount of displacement for each unit of the height channel, which corresponds to the “contrast” of the image. Heightmaps can be stored by themselves in existing graysca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
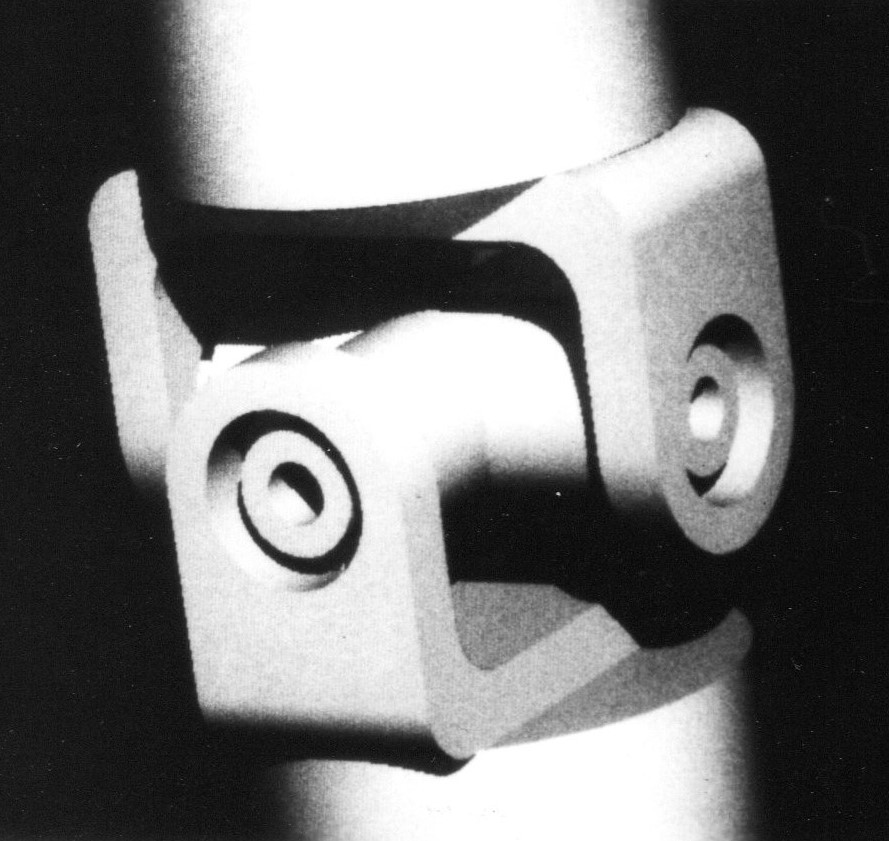
Ray Casting
Ray casting is the methodological basis for 3D CAD/CAM solid modeling and image rendering. It is essentially the same as ray tracing for computer graphics where virtual light rays are "cast" or "traced" on their path from the focal point of a camera through each pixel in the camera sensor to determine what is visible along the ray in the 3D scene. The term "Ray Casting" was introduced by Scott Roth while at the General Motors Research Labs from 1978–1980. His paper, "Ray Casting for Modeling Solids", describes modeled solid objects by combining primitive solids, such as blocks and cylinders, using the set operators union (+), intersection (&), and difference (-). The general idea of using these binary operators for solid modeling is largely due to Voelcker and Requicha's geometric modelling group at the University of Rochester. See Solid modeling for a broad overview of solid modeling methods. This figure on the right shows a U-Joint modeled from cylinders and blocks in a binary ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Voxel
In 3D computer graphics, a voxel represents a value on a regular grid in three-dimensional space. As with pixels in a 2D bitmap, voxels themselves do not typically have their position (i.e. coordinates) explicitly encoded with their values. Instead, rendering systems infer the position of a voxel based upon its position relative to other voxels (i.e., its position in the data structure that makes up a single volumetric image). In contrast to pixels and voxels, polygons are often explicitly represented by the coordinates of their vertices (as points). A direct consequence of this difference is that polygons can efficiently represent simple 3D structures with much empty or homogeneously filled space, while voxels excel at representing regularly sampled spaces that are non-homogeneously filled. Voxels are frequently used in the visualization and analysis of medical and scientific data (e.g. geographic information systems (GIS)). Some volumetric displays use voxels to desc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Normal Mapping
In 3D computer graphics, normal mapping, or Dot3 bump mapping, is a texture mapping technique used for faking the lighting of bumps and dents – an implementation of bump mapping. It is used to add details without using more polygons. A common use of this technique is to greatly enhance the appearance and details of a low polygon model by generating a normal map from a high polygon model or height map. Normal maps are commonly stored as regular RGB images where the RGB components correspond to the X, Y, and Z coordinates, respectively, of the surface normal. History In 1978 Jim Blinn described how the normals of a surface could be perturbed to make geometrically flat faces have a detailed appearance. The idea of taking geometric details from a high polygon model was introduced in "Fitting Smooth Surfaces to Dense Polygon Meshes" by Krishnamurthy and Levoy, Proc. SIGGRAPH 1996, where this approach was used for creating displacement maps over nurbs. In 1998, two papers we ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Video Game
Video games, also known as computer games, are electronic games that involves interaction with a user interface or input device such as a joystick, game controller, controller, computer keyboard, keyboard, or motion sensing device to generate visual feedback. This feedback mostly commonly is shown on a video display device, such as a TV set, computer monitor, monitor, touchscreen, or virtual reality headset. Some computer games do not always depend on a graphics display, for example List of text-based computer games, text adventure games and computer chess can be played through teletype printers. Video games are often augmented with audio feedback delivered through loudspeaker, speakers or headphones, and sometimes with other types of feedback, including haptic technology. Video games are defined based on their computing platform, platform, which include arcade video games, console games, and PC game, personal computer (PC) games. More recently, the industry has expanded on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Terrain Rendering
Terrain cartography or relief mapping is the depiction of the shape of the surface of the Earth on a map, using one or more of several techniques that have been developed. Terrain or relief is an essential aspect of physical geography, and as such its portrayal presents a central problem in cartographic design, and more recently geographic information systems and geovisualization. Hill profiles The most ancient form of relief depiction in cartography, hill profiles are simply illustrations of mountains and hills in profile, placed as appropriate on generally small-scale (broad area of coverage) maps. They are seldom used today except as part of an "antique" styling. Physiographic illustration In 1921, A.K. Lobeck published ''A Physiographic Diagram of the United States'', using an advanced version of the hill profile technique to illustrate the distribution of landforms on a small-scale map.Lobeck, A.K. (1921''A Physiographic Diagram of the United States'' A.J. Nystrom & Co., ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Synthetic Aperture Radar
Synthetic-aperture radar (SAR) is a form of radar that is used to create two-dimensional images or three-dimensional reconstructions of objects, such as landscapes. SAR uses the motion of the radar antenna over a target region to provide finer spatial resolution than conventional stationary beam-scanning radars. SAR is typically mounted on a moving platform, such as an aircraft or spacecraft, and has its origins in an advanced form of side looking airborne radar (SLAR). The distance the SAR device travels over a target during the period when the target scene is illuminated creates the large ''synthetic'' antenna aperture (the ''size'' of the antenna). Typically, the larger the aperture, the higher the image resolution will be, regardless of whether the aperture is physical (a large antenna) or synthetic (a moving antenna) – this allows SAR to create high-resolution images with comparatively small physical antennas. For a fixed antenna size and orientation, objects which a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
3D Reconstruction
In computer vision and computer graphics, 3D reconstruction is the process of capturing the shape and appearance of real objects. This process can be accomplished either by active or passive methods. If the model is allowed to change its shape in time, this is referred to as non-rigid or spatio-temporal reconstruction. Motivation and applications The research of 3D reconstruction has always been a difficult goal. By Using 3D reconstruction one can determine any object's 3D profile, as well as knowing the 3D coordinate of any point on the profile. The 3D reconstruction of objects is a generally scientific problem and core technology of a wide variety of fields, such as Computer Aided Geometric Design ( CAGD), computer graphics, computer animation, computer vision, medical imaging, computational science, virtual reality, digital media, etc. For instance, the lesion information of the patients can be presented in 3D on the computer, which offers a new and accurate approach in d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diffusion-limited Aggregation
Diffusion-limited aggregation (DLA) is the process whereby particles undergoing a random walk due to Brownian motion cluster together to form aggregates of such particles. This theory, proposed by T.A. Witten Jr. and L.M. Sander in 1981, is applicable to aggregation in any system where diffusion is the primary means of transport in the system. DLA can be observed in many systems such as electrodeposition, Hele-Shaw flow, mineral deposits, and dielectric breakdown. The clusters formed in DLA processes are referred to as Brownian trees. These clusters are an example of a fractal. In 2D these fractals exhibit a dimension of approximately 1.71 for free particles that are unrestricted by a lattice, however computer simulation of DLA on a lattice will change the fractal dimension slightly for a DLA in the same embedding dimension. Some variations are also observed depending on the geometry of the growth, whether it be from a single point radially outward or from a plane o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Simplex Noise
Simplex noise is the result of an ''n''-dimensional noise function comparable to Perlin noise ("classic" noise) but with fewer directional artifacts and, in higher dimensions, a lower computational overhead. Ken Perlin designed the algorithm in 2001 to address the limitations of his classic noise function, especially in higher dimensions. The advantages of simplex noise over Perlin noise: * Simplex noise has lower computational complexity and requires fewer multiplications. * Simplex noise scales to higher dimensions (4D, 5D) with much less computational cost: the complexity is O(n^2) for n dimensions instead of the O(n\,2^n) of classic noise. * Simplex noise has no noticeable directional artifacts (is visually isotropic), though noise generated for different dimensions is visually distinct (e.g. 2D noise has a different look than 2D slices of 3D noise, and it looks increasingly worse for higher dimensions). * Simplex noise has a well-defined and continuous gradient (almost) eve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geographic Information System
A geographic information system (GIS) is a type of database containing geographic data (that is, descriptions of phenomena for which location is relevant), combined with software tools for managing, analyzing, and visualizing those data. In a broader sense, one may consider such a system to also include human users and support staff, procedures and workflows, body of knowledge of relevant concepts and methods, and institutional organizations. The uncounted plural, ''geographic information systems'', also abbreviated GIS, is the most common term for the industry and profession concerned with these systems. It is roughly synonymous with geoinformatics and part of the broader geospatial field, which also includes GPS, remote sensing, etc. Geographic information science, the academic discipline that studies these systems and their underlying geographic principles, may also be abbreviated as GIS, but the unambiguous GIScience is more common. GIScience is often considered a subdi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |