|
Head On A Spike
A head on a spike (also described as a head on a pike, a head on a stake, or a head on a spear) is a severed head that has been vertically impaled for display. This has been a custom in a number of cultures, typically either as part of a criminal penalty following execution or as a war trophy following a violent conflict. The symbolic value may change over time. It may give a warning to spectators. The head may be a human head or an animal head. History The earliest known archeological evidence for mounting heads on stakes has been identified in Sweden, at a Mesolithic site in Kanaljorden, in the floor of a dried lake, dating to 8,000 years ago.Gummeson ''et al.'' 2018. There, archeologists recovered human crania with the remnants of wooden stakes still in place within the two crania. The crania exhibited evidence of blunt force trauma that looked to have resulted from a violent confrontation. Archeologists interpreted the wooden stakes as evidence that the heads had been ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oliver Cromwell's Head, Late 1700s
Oliver may refer to: Arts, entertainment and literature Books * ''Oliver the Western Engine'', volume 24 in ''The Railway Series'' by Rev. W. Awdry * ''Oliver Twist'', a novel by Charles Dickens Fictional characters * Ariadne Oliver, in the novels of Agatha Christie * Oliver (Disney character) * Oliver Fish, a gay police officer on the American soap opera ''One Life to Live'' * Oliver Hampton, in the American television series ''How to Get Away with Murder'' * Oliver Jones (''The Bold and the Beautiful''), on the American soap opera ''The Bold and the Beautiful'' * Oliver Lightload, in the movie ''Cars'' * Oliver Oken, from ''Hannah Montana'' * Oliver (paladin), a paladin featured in the Matter of France * Oliver Queen, DC Comic book hero also known as the Green Arrow * Oliver (Thomas and Friends character), a locomotive in the Thomas and Friends franchise * Oliver Trask, a controversial minor character from the first season of ''The O.C.'' * Oliver Twist (characte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Simon Fraser (died 1306)
Sir Simon Fraser of Oliver and Neidpath was a Scottish knight who fought in the Wars of Scottish Independence, for which he was hanged, drawn, and quartered in 1306. Life Simon Fraser was the son of Simon Fraser (died 1291) and Maria. Fraser was captured during the Battle of Dunbar on 27 April 1296 and was sent to a prison in England. He was forfeited of his lands. He was released to serve King Edward I of England's expedition in Flanders in 1297. Fraser was made a household knight – effectively, a member of the royal bodyguard – and gifted a horse by Edward before the Battle of Falkirk. Fraser was thus among the English cavalry divisions that defeated the army of William Wallace. On 27 March 1299, in recognition of his good service, he was restored his lands and titles. He was the Keeper of Selkirk Forest, and was at the Siege of Caerlaverock on the side of the English in 1300. He switched to the Scottish side in mid-1301 and led the Scottish victory at the Battle of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bernard-René Jourdan De Launay
Bernard René Jourdan, marquis de Launay (8/9 April 1740 – 14 July 1789) was the French governor of the Bastille. He was the son of a previous governor, and commander of the Bastille's garrison when the prison-fortress in Paris was stormed on 14 July 1789. Early life The marquis Bernard-René Jordan de Launay was born on the night of 8/9 April 1740 in the Bastille where his father, René Jourdan de Launay, was governor. At the age of eight he was appointed to an honorary position in the King's Musketeers (''mousquetaires du roi''). He subsequently entered the French Guards (''gardes-françaises''), a regiment permanently stationed in Paris except in time of war. In 1776 de Launay succeeded M. de Jumilhac as Governor of the Bastille. As was the custom with many senior positions under the Ancien Régime, the marquis purchased the office of governor from his predecessor as a form of investment. The thirteen years that he spent in this position were uneventful, though on 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jacques De Flesselles
Jacques de Flesselles (; 11 November 173014 July 1789) was a French official and one of the early victims of the French Revolution. Early life Jacques de Flesselles was born in Paris in 1730 of a family of middle-class origins, which had recently achieved nobility status. His father, also Jacques de Flesselles, was a financial official who had served as a royal adviser. The younger Jacques de Flesselles followed a similar career path. Career Following appointments as Intendant of Moulins in 1762 and of Rennes in 1765, de Flesselles served as Intendant of Lyon (1768–1784) where he won respect as a reform-minded royal official. Motivated by a personal interest in scientific development, he sponsored a Montgolfier balloon in 1784, named the Flesselles in his honour. On 21 April 1789, de Flesselles became the last provost of the merchants of Paris, a post roughly equivalent to mayor. Three months later he faced a chaotic situation as widespread disturbances broke out and t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Éamonn An Chnoic
"Éamonn an Chnoic" ("Ned of the Hill") is a popular Sean nos song in traditional Irish music. It is a slow, mournful ballad with a somber theme and no chorus. The song is attributed to Éamonn Ó Riain (Edmund O'Ryan) (d.c.1724), an early 18th century County Tipperary folk hero, composer of Irish bardic poetry, and rapparee; an outlawed member of the Gaelic nobility of Ireland who still held to the code of conduct of the traditional chiefs of the Irish clans. Folk song researcher Donal O'Sullivan has written that Captain Edmund O'Ryan's, "gay chivalry, daring exploits, and 'moving accidents by flood and field' would indeed make fine material for a historical novel." Life According to James Clarence Mangan, O'Ryan was born in Shanbohy, in the civil parish of Templebeg ( ga, An Teampall Beag), in the half-barony of Kilnamanagh Upper in Tipperary, "previous to the wars of 1690". Stephen Dunford, however, gives his birthplace as Atshanbohy, in the same civil parish. Donal O' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Redmond O'Hanlon (outlaw)
Count Redmond O'Hanlon ( ga, Réamonn Ó hAnluain), (c. 1640 – 25 April 1681) was a 17th-century Irish tóraidhe or rapparee; an outlawed member of the Gaelic nobility of Ireland who still held to the code of conduct of the traditional chiefs of the Irish clans. Historian John J. Marshall has called Redmond O'Hanlon Ireland's answer to Robin Hood and Rob Roy MacGregor. Stephen Dunford has further dubbed O'Hanlon, "The Irish Skanderbeg." Family background Although born in impoverished circumstances, Redmond was part of the ''Derbfine'' of the last O'Hanlon Chief of the Name, Lord of Airgíalla, and Master of Tandragee Castle. During the Nine Years' War, Sir Oghie O'Hanlon had allied the Clan with Queen Elizabeth I of England against Hugh O'Neill and Red Hugh O'Donnell. In 1606, Sir Oghie received his Clan's lands under the policy of Surrender and regrant. According to Royal decree, the family's manor was to be passed on to Sir Oghie's heirs under Primogeniture, rather tha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
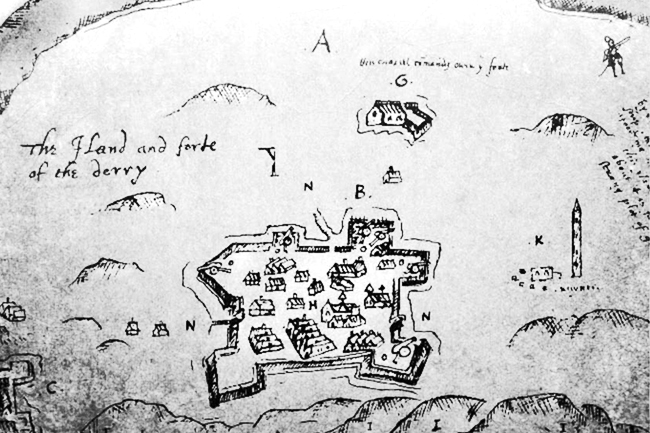
Cahir O'Doherty
Sir Cahir O'Doherty ( ga, Cathaoir Ó Dochartaigh or ga, label=none, Caṫaoir Ó Doċartaiġ; 1587–5 July 1608) was the last Gaelic Chief of the Name of Clan O'Doherty and Lord of Inishowen, in what is now County Donegal. O'Doherty was a noted loyalist during Tyrone's Rebellion and became known as the Queen's O'Doherty for his service on the Crown's side during the fighting. After the war O'Doherty had ambitions to become a courtier and applied for a position in the household of Henry Frederick, Prince of Wales, but he increasingly came into dispute with Irish-based officials such as the Viceroy Sir Arthur Chichester and the Governor of Derry Sir George Paulet. In 1608 he launched a rebellion, seizing Derry from Paulet and burning it to the ground. O'Doherty was subsequently killed in a battle at Kilmacrennan, and the rebellion swiftly collapsed. Early life Cahir was the son of Sir John O'Doherty, the head of the O'Dohertys and effective ruler of Inishowen. One of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Muiris Mac Ionrachtaigh
Muiris Mac Ionrachtaigh, anglicised as Maurice MacKenraghty (executed 30 April 1585, Clonmel, County Tipperary) was an Irish Roman Catholic priest and one of the Irish Catholic Martyrs. He was beatified in 1992. Life Although the exact date of his birth remains unknown, Muiris Mac Ionrachtaigh, was born at Kilmallock ( ga, Cill Mocheallóg), which was "a prosperous walled town in the Desmond lands in County Limerick". His father, Tomás Mac Ionrachtaigh ("Thomas MacKenraghty"), was a goldsmith and silversmith who was originally from the civil barony of Irraghticonnor. The MacKenraghty family were full citizens of the town of Kilmallock and probably also enjoyed the patronage of the Earl of Desmond. Edited by Patrick J. Cornish and Benignus Millet (2005), ''The Irish Martyrs'', Four Courts Press, Dublin. Page 86. Mac Ionrachtaigh embraced the ecclesiastical state, studied abroad, and graduated bachelor in theology. Returning to Ireland, he became chaplain to Gerald FitzGerald, 15 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Richard Gwyn
Richard Gwyn (ca. 1537 – 15 October 1584), also known by his anglicised name, Richard White, was a Welsh teacher at illegal and underground schools and a Bard who wrote both Christian and satirical poetry in the Welsh language. A Roman Catholic during the reign of Queen Elizabeth I of England, Gwyn was martyred by being hanged, drawn and quartered for high treason at Wrexham in 1584. He was canonised by Pope Paul VI in 1970 as one of the Forty Martyrs of England and Wales. Since its creation in 1987, St. Richard Gwyn has been the Patron Saint of the Roman Catholic Diocese of Wrexham. Along with fellow lay martyr St. Margaret Clitherow, Gwyn is the co-patron of the Latin Mass Society of England and Wales. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thomas Cromwell
Thomas Cromwell (; 1485 – 28 July 1540), briefly Earl of Essex, was an English lawyer and statesman who served as List of English chief ministers, chief minister to King Henry VIII from 1534 to 1540, when he was beheaded on orders of the king, who later blamed false charges for the execution. Cromwell was one of the most powerful proponents of the English Reformation, and the creator of true English governance. He helped to engineer an annulment of the king's marriage to Catherine of Aragon so that Henry could lawfully marry Anne Boleyn. Henry failed to obtain the approval of Pope Clement VII for the annulment in 1533, so Parliament endorsed the king's claim to be Supreme Head of the Church of England, giving him the authority to annul his own marriage. Cromwell subsequently charted an evangelical and reformist course for the Church of England from the unique posts of Vicegerent in Spirituals and Vicar-general (the two titles refer to the same position). During his rise to p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thomas More
Sir Thomas More (7 February 1478 – 6 July 1535), venerated in the Catholic Church as Saint Thomas More, was an English lawyer, judge, social philosopher, author, statesman, and noted Renaissance humanist. He also served Henry VIII as Lord High Chancellor of England from October 1529 to May 1532. He wrote ''Utopia'', published in 1516, which describes the political system of an imaginary island state. More opposed the Protestant Reformation, directing polemics against the theology of Martin Luther, Huldrych Zwingli, John Calvin and William Tyndale. More also opposed Henry VIII's separation from the Catholic Church, refusing to acknowledge Henry as supreme head of the Church of England and the annulment of his marriage to Catherine of Aragon. After refusing to take the Oath of Supremacy, he was convicted of treason and executed. On his execution, he was reported to have said: "I die the King's good servant, and God's first". Pope Pius XI canonised More in 1935 as a martyr. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Fisher
John Fisher (c. 19 October 1469 – 22 June 1535) was an English Catholic bishop, cardinal, and theologian. Fisher was also an academic and Chancellor of the University of Cambridge. He was canonized by Pope Pius XI. Fisher was executed by order of Henry VIII during the English Reformation for refusing to accept him as the supreme head of the Church of England and for upholding the Catholic Church's doctrine of papal supremacy. He was named a cardinal shortly before his death. He is honoured as a martyr and saint by the Catholic Church. He shares his feast day with Thomas More on 22 June in the Catholic calendar of saints and on 6 July in that of the Church of England. Early life John Fisher was born in Beverley, Yorkshire, in 1469, the eldest son of Robert Fisher, a modestly prosperous merchant of Beverley, and Agnes, his wife. He was one of four children. His father died when John was eight. His mother remarried and had five more children by her second husband, William ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |