|
Halberd
A halberd (also called halbard, halbert or Swiss voulge) is a two-handed pole weapon that came to prominent use during the 13th, 14th, 15th, and 16th centuries. The word ''halberd'' is cognate with the German word ''Hellebarde'', deriving from Middle High German ''halm'' (handle) and ''barte'' (battleaxe) joined to form ''helmbarte''. Troops that used the weapon were called halberdiers. The halberd consists of an axe blade topped with a spike mounted on a long shaft. It always has a hook or thorn on the back side of the axe blade for grappling mounted combatants. It is very similar to certain forms of the voulge in design and usage. The halberd was usually 1.5 to 1.8 metres (5 to 6 feet) long. The word has also been used to describe a weapon of the Early Bronze Age in Western Europe. This consisted of a blade mounted on a pole at a right angle. History The halberd was inexpensive to produce and very versatile in battle. As the halberd was eventually refined, its point was mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pole Weapon
A polearm or pole weapon is a close combat weapon in which the main fighting part of the weapon is fitted to the end of a long shaft, typically of wood, thereby extending the user's effective range and striking power. Polearms are predominantly melee weapons, with a subclass of spear-like designs fit for both thrusting and throwing. Because many polearms were adapted from agricultural implements or other fairly abundant tools, and contained relatively little metal, they were cheap to make and readily available. When warfare would break out and the belligerents had a poorer class who could not pay for dedicated military weapons, leaders would often appropriate tools as cheap weapons. The cost of training was comparatively minimal, since these conscripted farmers had spent most of their lives using these "weapons" in the fields. This made polearms the favored weapon of peasant levies and peasant rebellions the world over. Polearms can be divided into three broad categories: those ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pike (weapon)
A pike is a very long thrusting spear formerly used in European warfare from the Late Middle Ages and most of the Early Modern Period, and were wielded by foot soldiers deployed in pike square formation, until it was largely replaced by bayonet-equipped muskets. The pike was particularly well-known as the primary weapon of Swiss mercenary and German Landsknecht units. A similar weapon, the sarissa, had been used in antiquity by Alexander the Great's Macedonian phalanx infantry. Design The pike was a long weapon, varying considerably in size, from long. Generally, a spear becomes a pike when it is too long to be wielded with one hand in combat. It was approximately in weight, with the 16th century military writer Sir John Smythe recommending lighter rather than heavier pikes. It had a wooden shaft with an iron or steel spearhead affixed. The shaft near the head was often reinforced with metal strips called "cheeks" or langets. When the troops of opposing armies both c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Landsknecht
The (singular: , ), also rendered as Landsknechts or Lansquenets, were Germanic mercenaries used in pike and shot formations during the early modern period. Consisting predominantly of pikemen and supporting foot soldiers, their front line was formed by ''Doppelsöldner'' ("double-pay men") renowned for their use of ''Zweihänder'' and arquebus. Originally organized by Emperor Maximilian I and Georg von Frundsberg, they formed the bulk of the Holy Roman Empire's Imperial Army from the late 1400s to the early 1600s, fighting in the Habsburg-Valois wars, the Habsburg-Ottoman wars, and the European wars of religion. Although prone to mutiny if unpaid and divided within their ranks between Catholics and Lutherans, the ''Landsknechte'' were well-armed, experienced, and fierce warriors. In addition, they were recruitable in large numbers throughout Germany and Austria by the Holy Roman Emperor and thus guaranteed both quantity and quality to the Imperial military for a century a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spear
A spear is a pole weapon consisting of a shaft, usually of wood, with a pointed head. The head may be simply the sharpened end of the shaft itself, as is the case with fire hardened spears, or it may be made of a more durable material fastened to the shaft, such as bone, flint, obsidian, iron, steel, or bronze. The most common design for hunting or combat spears since ancient times has incorporated a metal spearhead shaped like a triangle, lozenge, or leaf. The heads of fishing spears usually feature barbs or serrated edges. The word '' spear'' comes from the Old English '' spere'', from the Proto-Germanic ''speri'', from a Proto-Indo-European root ''*sper-'' "spear, pole". Spears can be divided into two broad categories: those designed for thrusting as a melee weapon and those designed for throwing as a ranged weapon (usually referred to as javelins or darts). The spear has been used throughout human history both as a hunting and fishing tool and as a weapon. Along ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
King Richard III
Richard III (2 October 145222 August 1485) was King of England and Lord of Ireland from 26 June 1483 until his death in 1485. He was the last king of the House of York and the last of the Plantagenet dynasty. His defeat and death at the Battle of Bosworth Field, the last decisive battle of the Wars of the Roses, marked the end of the Middle Ages in England. Richard was created Duke of Gloucester in 1461 after the accession of his brother King Edward IV. In 1472, he married Anne Neville, daughter of Richard Neville, 16th Earl of Warwick. He governed northern England during Edward's reign, and played a role in the invasion of Scotland in 1482. When Edward IV died in April 1483, Richard was named Lord Protector of the realm for Edward's eldest son and successor, the 12-year-old Edward V. Arrangements were made for Edward V's coronation on 22 June 1483. Before the king could be crowned, the marriage of his parents was declared bigamous and therefore invalid. Now officially illeg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Bosworth
The Battle of Bosworth or Bosworth Field was the last significant battle of the Wars of the Roses, the civil war between the houses of Lancaster and York that extended across England in the latter half of the 15th century. Fought on 22 August 1485, the battle was won by an alliance of Lancastrians and disaffected Yorkists. Their leader Henry Tudor, Earl of Richmond, became the first English monarch of the Tudor dynasty by his victory and subsequent marriage to a Yorkist princess. His opponent Richard III, the last king of the House of York, was killed during the battle, the last English monarch to die in combat. Historians consider Bosworth Field to mark the end of the Plantagenet dynasty, making it one of the defining moments of English history. Richard's reign began in 1483 when he seized the throne from his twelve-year-old nephew Edward V. The boy and his younger brother Richard soon disappeared, to the consternation of many, and Richard's support was further eroded by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bill (weapon)
A bill is a class of agricultural implement used for trimming tree limbs, which was often repurposed for use as an infantry polearm. In English, the term 'Italian bill' is applied to the similar roncone or roncola, but the Italian version tended to have a long thrusting spike in addition to the cutting blade. The English distinguished among several varieties of bill, including the black, brown and forest bills, but the differences between them are currently not fully understood. Bills were adapted to military use through addition of various projecting blades. Other variants include the bill hook and bill-guisarme. Disambiguation The bill is similar in size, function and appearance to the halberd, and might be said to represent convergent evolution to fill a common niche: a pole-arm with a point to thrust with, a hook to drag with, and a spike/axe to cut with. The bill should not be conflated with a war-scythe, another pole-arm adapted from an agricultural implement, the scythe. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
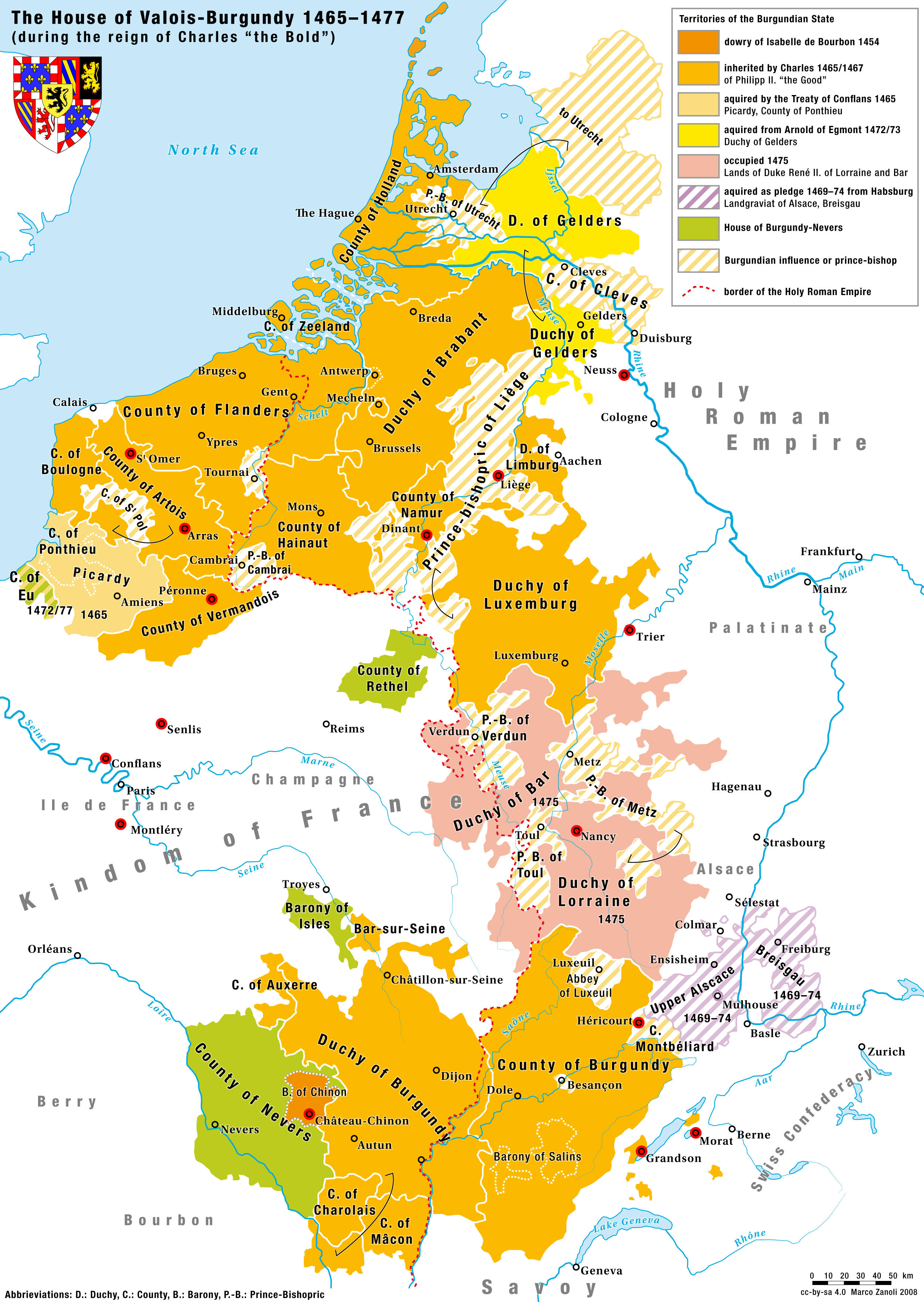
Charles The Bold
Charles I (Charles Martin; german: Karl Martin; nl, Karel Maarten; 10 November 1433 – 5 January 1477), nicknamed the Bold (German: ''der Kühne''; Dutch: ''de Stoute''; french: le Téméraire), was Duke of Burgundy from 1467 to 1477. Charles's main objective was to be crowned king by turning the growing Burgundian State into a territorially continuous kingdom. He declared himself and his lands independent, bought Upper Alsace and conquered Zutphen, Guelders and Lorraine, uniting at last Burgundian northern and southern possessions. This caused the enmity of several European powers and triggered the Burgundian Wars. Charles's early death at the Battle of Nancy at the hands of Swiss mercenaries fighting for René II, Duke of Lorraine, was of great consequence in European history. The Burgundian domains, long wedged between the Kingdom of France and the Habsburg Empire, were divided, but the precise disposition of the vast and disparate territorial possessions involved ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
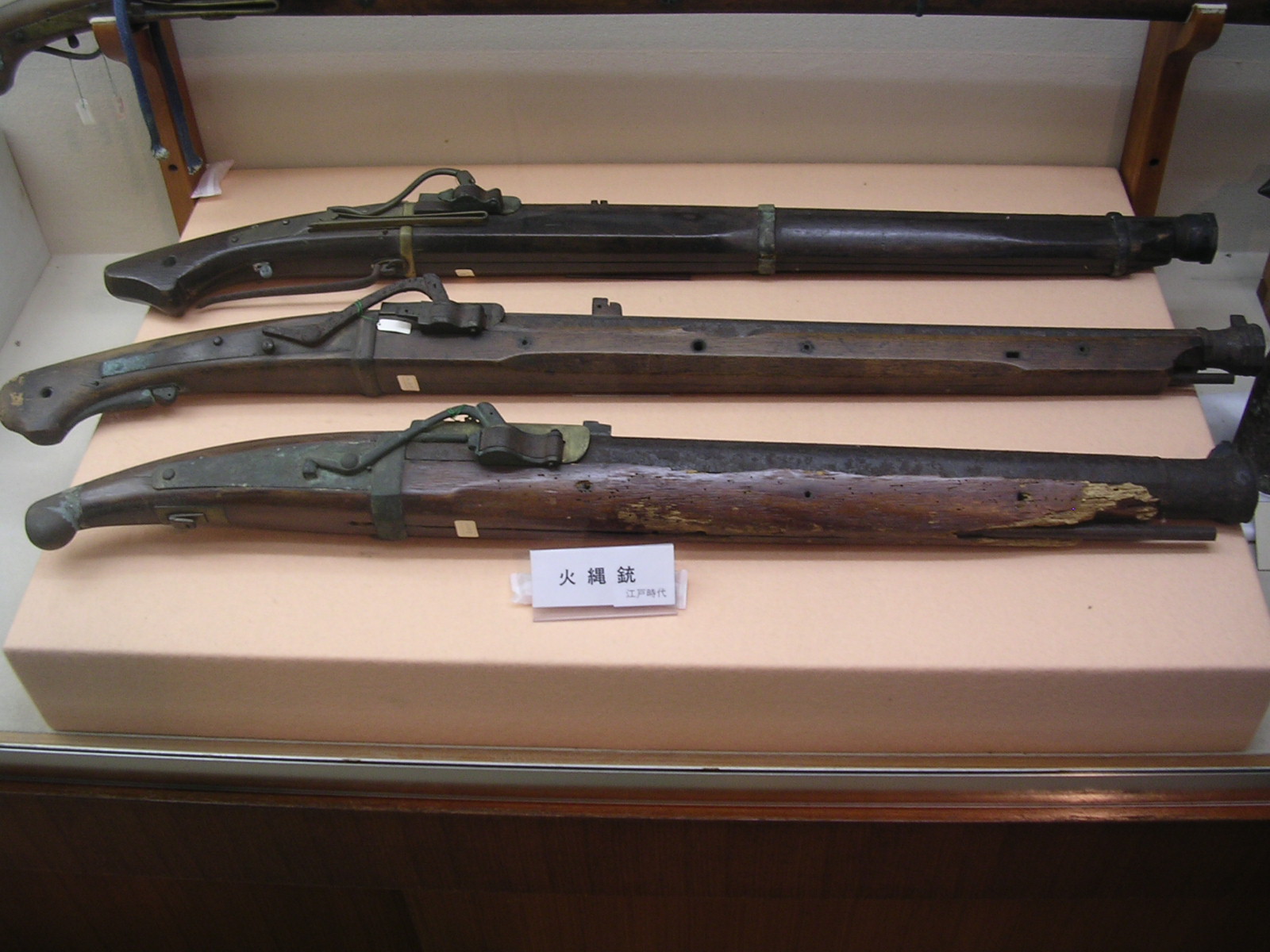
Matchlock
A matchlock or firelock is a historical type of firearm wherein the gunpowder is ignited by a burning piece of rope that is touched to the gunpowder by a mechanism that the musketeer activates by pulling a lever or trigger with his finger. Before the invention of the matchlock mechanism, the musketeer or an assistant had to apply the match directly to gunpowder by hand, much like a cannon. The matchlock mechanism allowed the musketeer to apply the match himself without losing his concentration. Description The classic matchlock gun held a burning slow match in a clamp at the end of a small curved lever known as the ''serpentine''. Upon the pull of a lever (or in later models a trigger) protruding from the bottom of the gun and connected to the serpentine, the clamp dropped down, lowering the smoldering match into the flash pan and igniting the priming powder. The flash from the primer traveled through the touch hole, igniting the main charge of propellant in the gun barrel. On ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arquebus
An arquebus ( ) is a form of long gun that appeared in Europe and the Ottoman Empire during the 15th century. An infantryman armed with an arquebus is called an arquebusier. Although the term ''arquebus'', derived from the Dutch word ''Haakbus'' ("hook gun"), was applied to many different forms of firearms from the 15th to 17th centuries, it originally referred to "a hand-gun with a hook-like projection or lug on its under surface, useful for steadying it against battlements or other objects when firing". These "hook guns" were in their earliest forms of defensive weapons mounted on German city walls in the early 15th century. The addition of a shoulder stock, priming pan, and matchlock mechanism in the late 15th century turned the arquebus into a handheld firearm and also the first firearm equipped with a trigger. The exact dating of the matchlock's appearance is disputed. It could have appeared in the Ottoman Empire as early as 1465 and in Europe a little before 1475. The h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Push Of Pike
The push of pike was a particular feature of late medieval and Early Modern warfare that occurred when two opposing columns of pikemen (often Swiss mercenaries or German Landsknechte) met and became locked in position along a front of interleaved pikes. Shoving match During push of pike, opposing blocks of pikemen would advance with their pikes "charged" horizontally at shoulder level to jab at one another until bodily contact was made. The two sides would then push physically until one or other of them gave way. The push of pike would continue until one of the opposing formations routed or fled, which would generally lead to massive casualties. Each man pressed on the one in front, and so sometimes the formations would crush against each other and many pikemen would have to fight in closer melee combat. The rear ranks would sometimes join the fray but their primary role was to add more weight to the push. Aside from getting impaled by enemy pikes, those in the front ranks died ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)