|
Halazepam
Halazepam is a benzodiazepine derivative that was marketed under the brand names Paxipam in the United States, Alapryl in Spain, and Pacinone in Portugal. Medical uses Halazepam was used for the treatment of anxiety. Adverse effects Adverse effects include drowsiness, confusion, dizziness, and sedation. Gastrointestinal side effects have also been reported including dry mouth and nausea. Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics were listed in ''Current Psychotherapeutic Drugs'' published on June 15, 1998 as follows: Regulatory Information Halazepam is classified as a schedule 4 controlled substance with a corresponding code 2762 by the Drug Enforcement Administration (DEA). Commercial production Halazepam was invented by Schlesinger Walter in the U.S. It was marketed as an anti-anxiety agent in 1981. However, Halazepam is not commercially available in the United States because it was withdrawn by its manufacturer for poor sales. See ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Liver
The liver is a major Organ (anatomy), organ only found in vertebrates which performs many essential biological functions such as detoxification of the organism, and the Protein biosynthesis, synthesis of proteins and biochemicals necessary for digestion and growth. In humans, it is located in the quadrant (anatomy), right upper quadrant of the abdomen, below the thoracic diaphragm, diaphragm. Its other roles in metabolism include the regulation of Glycogen, glycogen storage, decomposition of red blood cells, and the production of hormones. The liver is an accessory digestive organ that produces bile, an alkaline fluid containing cholesterol and bile acids, which helps the fatty acid degradation, breakdown of fat. The gallbladder, a small pouch that sits just under the liver, stores bile produced by the liver which is later moved to the small intestine to complete digestion. The liver's highly specialized biological tissue, tissue, consisting mostly of hepatocytes, regulates a w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quazepam
Quazepam, sold under brand name Doral among others, is a relatively long-acting benzodiazepine derivative drug developed by the Schering Corporation in the 1970s. Quazepam is used for the treatment of insomnia including sleep induction and sleep maintenance. Quazepam induces impairment of motor function and has relatively (and uniquely) selective hypnotic and anticonvulsant properties with considerably less overdose potential than other benzodiazepines (due to its novel receptor-subtype selectively). Quazepam is an effective hypnotic which induces and maintains sleep without disruption of the sleep architecture. It was patented in 1970 and came into medical use in 1985. Medical uses Quazepam is used for short-term treatment of insomnia related to sleep induction or sleep maintenance problems and has demonstrated superiority over other benzodiazepines such as temazepam. It had a fewer incidence of side effects than temazepam, including less sedation, amnesia, and less motor-impa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
GABAA Receptor Positive Allosteric Modulators
In pharmacology, GABAA receptor positive allosteric modulators are positive allosteric modulator (PAM) molecules that increase the activity of the GABAA receptor protein in the vertebrate central nervous system. GABA is a major inhibitory neurotransmitter in the central nervous system. Upon binding, it triggers the GABAA receptor to open its chloride channel to allow chloride ions into the neuron, making the cell hyperpolarized and less likely to fire. GABAA PAMs increase the effect of GABA by making the channel open more frequently or for longer periods. However, they have no effect if GABA or another agonist is not present. Unlike GABAA receptor agonists, GABAA PAMs do not bind at the same active site as the γ-Aminobutyric acid (GABA) neurotransmitter molecule: they affect the receptor by binding at a different site on the protein. This is called allosteric modulation. In psychopharmacology, GABAA receptor PAMs used as drugs have mainly sedative and anxiolytic effects. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chloroarenes
In organic chemistry, an aryl halide (also known as haloarene) is an aromatic compound in which one or more hydrogen atoms, directly bonded to an aromatic ring are replaced by a halide. The haloarene are different from haloalkanes because they exhibit many differences in methods of preparation and properties. The most important members are the aryl chlorides, but the class of compounds is so broad that there are many derivatives and applications. Preparation The two main preparatory routes to aryl halides are direct halogenation and via diazonium salts. Direct halogenation In the Friedel-Crafts halogenation, Lewis acids serve as catalysts. Many metal chlorides are used, examples include iron(III) chloride or aluminium chloride. The most important aryl halide, chlorobenzene is produced by this route. Monochlorination of benzene is always accompanied by formation of the dichlorobenzene derivatives. Arenes with electron donating groups react with halogens even in the absence of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Benzodiazepines
Benzodiazepines (BZD, BDZ, BZs), sometimes called "benzos", are a class of depressant drugs whose core chemical structure is the fusion of a benzene ring and a diazepine ring. They are prescribed to treat conditions such as anxiety disorders, insomnia, and seizures. The first benzodiazepine, chlordiazepoxide (Librium), was discovered accidentally by Leo Sternbach in 1955 and was made available in 1960 by Hoffmann–La Roche, who soon followed with diazepam (Valium) in 1963. By 1977, benzodiazepines were the most prescribed medications globally; the introduction of selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), among other factors, decreased rates of prescription, but they remain frequently used worldwide. Benzodiazepines are depressants that enhance the effect of the neurotransmitter gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) at the GABAA receptor, resulting in sedative, hypnotic ( sleep-inducing), anxiolytic (anti-anxiety), anticonvulsant, and muscle relaxant properties. High doses of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abandoned Drugs
Abandon, abandoned, or abandonment may refer to: Common uses * Abandonment (emotional), a subjective emotional state in which people feel undesired, left behind, insecure, or discarded * Abandonment (legal), a legal term regarding property ** Child abandonment, the extralegal abandonment of children ** Lost, mislaid, and abandoned property, legal status of property after abandonment and rediscovery * Abandonment (mysticism) Art, entertainment, and media Film * ''Abandon'' (film), a 2002 film starring Katie Holmes * ''Abandoned'' (1949 film), starring Dennis O'Keefe * ''Abandoned'' (1955 film), the English language title of the Italian war film ''Gli Sbandati'' * ''Abandoned'' (2001 film), a Hungarian film * ''Abandoned'' (2010 film), starring Brittany Murphy * ''Abandoned'' (2015 film), a television movie about the shipwreck of the ''Rose-Noëlle'' in 1989 * ''Abandoned'' (2022 film), starring Emma Roberts * ''The Abandoned'' (1945 film), a 1945 Mexican film * ''The Aban ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
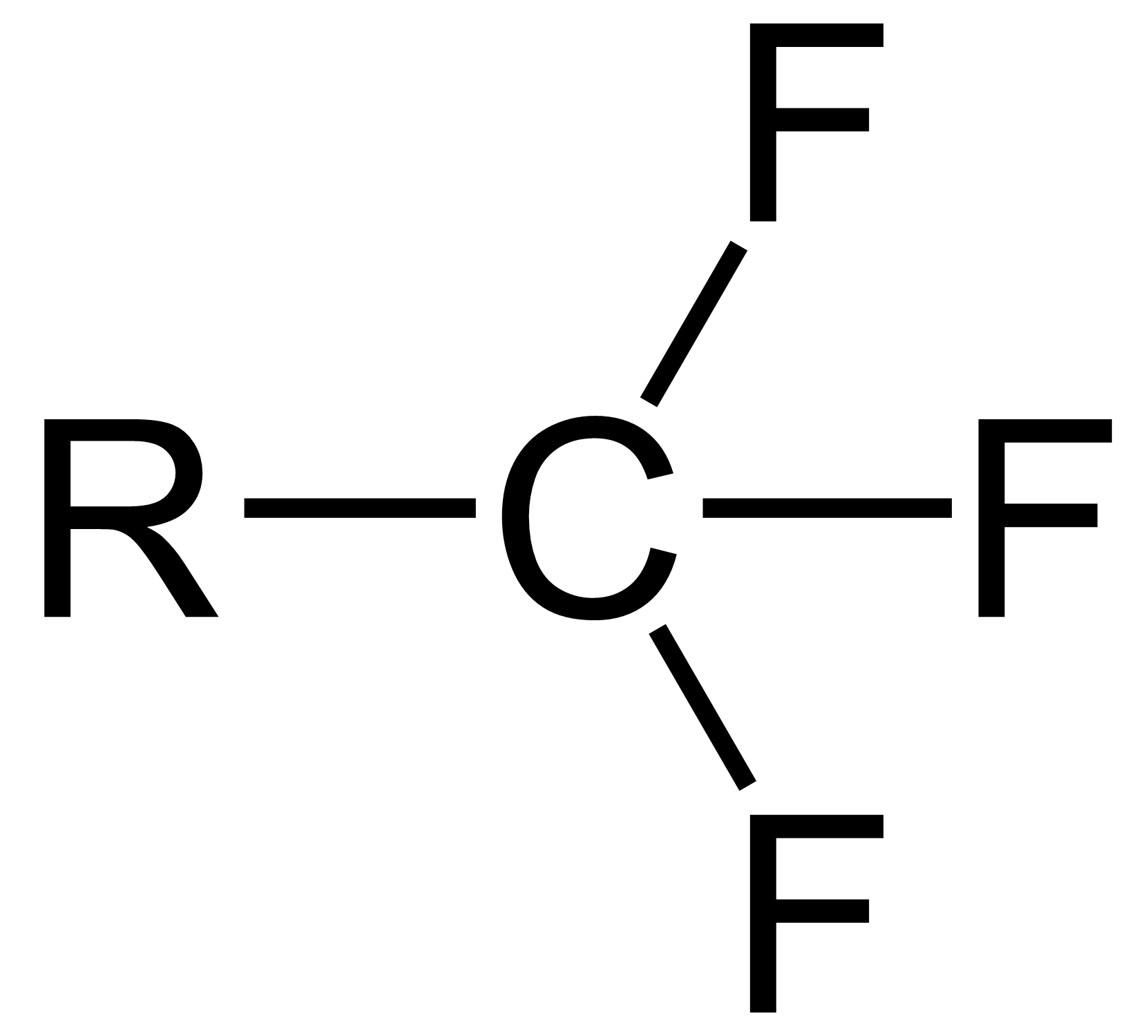
Trifluoromethyl Group
The trifluoromethyl group is a functional group that has the formula -CF3. The naming of is group is derived from the methyl group (which has the formula -CH3), by replacing each hydrogen atom by a fluorine atom. Some common examples are trifluoromethane H–, 1,1,1-trifluoroethane –, and hexafluoroacetone –CO–. Compounds with this group are a subclass of the organofluorines. Properties The trifluoromethyl group has a significant electronegativity that is often described as being intermediate between the electronegativities of fluorine and chlorine. For this reason, trifluoromethyl-substituted compounds are often strong acids, such as trifluoromethanesulfonic acid and trifluoroacetic acid. Conversely, the trifluoromethyl group lowers the basicity of compounds like trifluoroethanol. Uses The trifluoromethyl group occurs in certain pharmaceuticals, drugs, and abiotically synthesized natural fluorocarbon based compounds. The medicinal use of the trifloromethyl group dates from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Triflubazam
Triflubazam is a drug which is a 1,5- benzodiazepine derivative, related to clobazam. It has sedative and anxiolytic effects, with a long half-life and duration of action. See also * Benzodiazepine *Clobazam Clobazam, sold under the brand names Frisium, Onfi and others, is a benzodiazepine class medication that was patented in 1968. Clobazam was first synthesized in 1966 and first published in 1969. Clobazam was originally marketed as an anxioselect ... * CP-1414S * Triflunordazepam References Benzodiazepines GABAA receptor positive allosteric modulators Lactams Trifluoromethyl compounds {{sedative-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fletazepam
Fletazepam is a drug which is a benzodiazepine derivative. It has sedative and anxiolytic effects similar to those produced by other benzodiazepine derivatives, but is mainly notable for its strong muscle relaxant properties. Fletazepam is most closely related to other ''N''-trifluoroethyl substituted benzodiazepines such as halazepam and quazepam Quazepam, sold under brand name Doral among others, is a relatively long-acting benzodiazepine derivative drug developed by the Schering Corporation in the 1970s. Quazepam is used for the treatment of insomnia including sleep induction and sleep .... See also * Benzodiazepine References Benzodiazepines Chloroarenes GABAA receptor positive allosteric modulators Trifluoromethyl compounds Fluoroarenes {{sedative-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chlordiazepoxide
Chlordiazepoxide, trade name Librium among others, is a sedative and hypnotic medication of the benzodiazepine class; it is used to treat anxiety, insomnia and symptoms of Drug withdrawal, withdrawal from Alcohol (drug), alcohol and other drugs. Chlordiazepoxide has a medium to long half-life but its active metabolite has a very long half-life. The drug has amnesic, anticonvulsant, anxiolytic, hypnotic, sedative and skeletal muscle relaxant properties. Chlordiazepoxide was patented in 1958 and approved for medical use in 1960. It was the first benzodiazepine to be synthesized and the discovery of chlordiazepoxide was by pure chance. Chlordiazepoxide and other benzodiazepines were initially accepted with widespread public approval but were followed with widespread public disapproval and recommendations for more restrictive medical guidelines for its use. Medical uses Chlordiazepoxide is indicated for the short-term (2–4 weeks) treatment of anxiety that is severe and disab ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kidney
The kidneys are two reddish-brown bean-shaped organs found in vertebrates. They are located on the left and right in the retroperitoneal space, and in adult humans are about in length. They receive blood from the paired renal arteries; blood exits into the paired renal veins. Each kidney is attached to a ureter, a tube that carries excreted urine to the bladder. The kidney participates in the control of the volume of various body fluids, fluid osmolality, acid–base balance, various electrolyte concentrations, and removal of toxins. Filtration occurs in the glomerulus: one-fifth of the blood volume that enters the kidneys is filtered. Examples of substances reabsorbed are solute-free water, sodium, bicarbonate, glucose, and amino acids. Examples of substances secreted are hydrogen, ammonium, potassium and uric acid. The nephron is the structural and functional unit of the kidney. Each adult human kidney contains around 1 million nephrons, while a mouse kidney contains on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diazepam
Diazepam, first marketed as Valium, is a medicine of the benzodiazepine family that acts as an anxiolytic. It is commonly used to treat a range of conditions, including anxiety, seizures, alcohol withdrawal syndrome, muscle spasms, insomnia, and restless legs syndrome. It may also be used to cause memory loss during certain medical procedures. It can be taken by mouth, inserted into the rectum, injected into muscle, injected into a vein or used as a nasal spray. When given into a vein, effects begin in one to five minutes and last up to an hour. By mouth, effects begin after 15 to 60 minutes. Common side-effects include sleepiness and trouble with coordination. Serious side effects are rare. They include increased risk of suicide, decreased breathing, and an increased risk of seizures if used too frequently in those with epilepsy. Occasionally, excitement or agitation may occur. Long-term use can result in tolerance, dependence, and withdrawal symptoms on dose reduction ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




_DOJ.jpg)