|
Hafnium Controversy
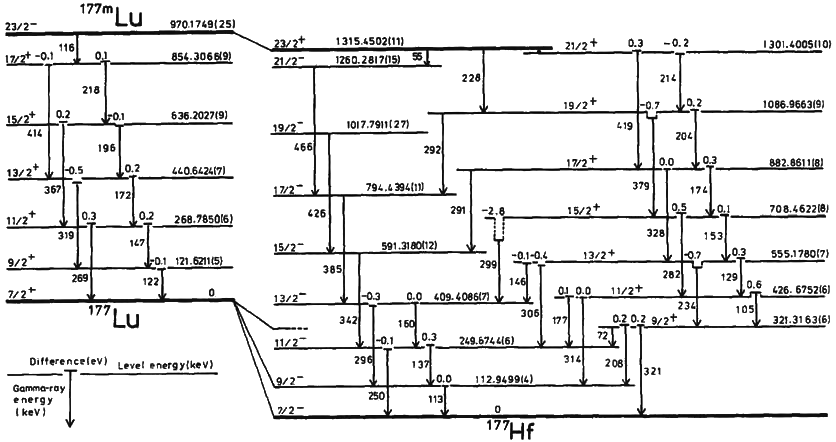
The hafnium controversy is a debate over the possibility of 'triggering' rapid energy releases, via gamma ray emission, from a nuclear isomer of hafnium, 178m2Hf. The energy release is potentially 5 orders of magnitude (100,000 times) more energetic than a chemical reaction, but 2 orders of magnitude less than a nuclear fission reaction. In 1998, a group led by Carl Collins of the University of Texas at Dallas reported having successfully initiated such a trigger. Signal-to-noise ratios were small in those first experiments, and to date no other group has been able to duplicate these results. Peter Zimmerman described claims of weaponization potential as having been based on " very bad science". Background 178m2Hf is a particularly attractive candidate for induced gamma emission (IGE) experiments, because of its high density of stored energy, 2.5 MeV per nucleus, and long 31-year half life for storing that energy. If radiation from some agent could "trigger" a release of that sto ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nuclear Isomer
A nuclear isomer is a metastable state of an atomic nucleus, in which one or more nucleons (protons or neutrons) occupy excited state, higher energy levels than in the ground state of the same nucleus. "Metastable" describes nuclei whose excited states have Half-life, half-lives 100 to 1000 times longer than the half-lives of the excited nuclear states that decay with a "prompt" half life (ordinarily on the order of 10−12 seconds). The term "metastable" is usually restricted to isomers with half-lives of 10−9 seconds or longer. Some references recommend 5 × 10−9 seconds to distinguish the metastable half life from the normal "prompt" Induced gamma emission, gamma-emission half-life. Occasionally the half-lives are far longer than this and can last minutes, hours, or years. For example, the Isotopes of tantalum#Tantalum-180m, nuclear isomer survives so long (at least 1015 years) that it has never been observed to decay spontaneously. The half-life of a nuclear isomer can eve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Megajoule
The joule ( , ; symbol: J) is the unit of energy in the International System of Units (SI). It is equal to the amount of work done when a force of 1 newton displaces a mass through a distance of 1 metre in the direction of the force applied. It is also the energy dissipated as heat when an electric current of one ampere passes through a resistance of one ohm for one second. It is named after the English physicist James Prescott Joule (1818–1889). Definition In terms of SI base units and in terms of SI derived units with special names, the joule is defined as One joule can also be defined by any of the following: * The work required to move an electric charge of one coulomb through an electrical potential difference of one volt, or one coulomb-volt (C⋅V). This relationship can be used to define the volt. * The work required to produce one watt of power for one second, or one watt-second (W⋅s) (compare kilowatt-hour, which is 3.6 megajoules). This relationship can be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hafnium
Hafnium is a chemical element with the symbol Hf and atomic number 72. A lustrous, silvery gray, tetravalent transition metal, hafnium chemically resembles zirconium and is found in many zirconium minerals. Its existence was predicted by Dmitri Mendeleev in 1869, though it was not identified until 1923, by Dirk Coster and George de Hevesy, making it the penultimate stable element to be discovered (the last being rhenium in 1925). Hafnium is named after , the Latin name for Copenhagen, where it was discovered. Hafnium is used in filaments and electrodes. Some semiconductor fabrication processes use its oxide for integrated circuits at 45 nanometers and smaller feature lengths. Some superalloys used for special applications contain hafnium in combination with niobium, titanium, or tungsten. Hafnium's large neutron capture cross section makes it a good material for neutron absorption in control rods in nuclear power plants, but at the same time requires that it be removed from th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nuclear Interdisciplinary Topics
*
*
{{Di ...
Nuclear may refer to: Physics Relating to the nucleus of the atom: * Nuclear engineering *Nuclear physics *Nuclear power *Nuclear reactor *Nuclear weapon *Nuclear medicine *Radiation therapy *Nuclear warfare Mathematics *Nuclear space *Nuclear operator *Nuclear congruence *Nuclear C*-algebra Biology Relating to the nucleus of the cell: * Nuclear DNA Society * Nuclear family, a family consisting of a pair of adults and their children Music * "Nuclear" (band), group music. * "Nuclear" (Ryan Adams song), 2002 *"Nuclear", a song by Mike Oldfield from his ''Man on the Rocks'' album * ''Nu.Clear'' (EP) by South Korean girl group CLC See also *Nucleus (other) *Nucleolus * Nucleation * Nucleic acid *Nucular ''Nucular'' is a common, proscribed pronunciation of the word "nuclear". It is a rough phonetic spelling of . The ''Oxford English Dictionary''s entry dates the word's first published appearance to 1943. Dictionary notes This is one of two con ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nation Books
Type Media Center (formerly The Nation Institute) is a nonprofit media organization that was previously associated with ''The Nation'' magazine. It sponsors fellows, hosts forums, publishes books and investigative reporting, and awards several annual journalism prizes. Orville Schell worked for the organization, and Katrina vanden Heuvel is currently a member of their board of trustees. Type Media Center fellows have included Naomi Klein, Wayne Barrett, Chris Hedges, David Moberg, Jeremy Scahill, and Chris Hayes. The organization has also funded podcasts, short-form broadcast media, and documentaries, including several by Habiba Nosheen. Type is one of the presenters of the Ridenhour Prizes. It collaborates on the Puffin Prize for Creative Citizenship with the Puffin Foundation. Tom Engelhardt is the creator of the organization's TomDispatch.com, a widely syndicated online blog. Type started its publishing imprint Bold Type Books (formerly Nation Books) in 2000, in partnershi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cyclotron
A cyclotron is a type of particle accelerator invented by Ernest O. Lawrence in 1929–1930 at the University of California, Berkeley, and patented in 1932. Lawrence, Ernest O. ''Method and apparatus for the acceleration of ions'', filed: January 26, 1932, granted: February 20, 1934 A cyclotron accelerates charged particles outwards from the center of a flat cylindrical vacuum chamber along a spiral path. The particles are held to a spiral trajectory by a static magnetic field and accelerated by a rapidly varying electric field. Lawrence was awarded the 1939 Nobel Prize in Physics for this invention. The cyclotron was the first "cyclical" accelerator. The primary accelerators before the development of the cyclotron were electrostatic accelerators, such as the Cockcroft–Walton accelerator and Van de Graaff generator. In these accelerators, particles would cross an accelerating electric field only once. Thus, the energy gained by the particles was limited by the maximum elec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
LLNL
Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) is a federal research facility in Livermore, California, United States. The lab was originally established as the University of California Radiation Laboratory, Livermore Branch in 1952 in response to the detonation of the first atomic bomb by the Soviet Union during the Cold War. It later became autonomous in 1971 and was designated a national laboratory in 1981. A federally funded research and development center, Lawrence Livermore Lab is primarily funded by the U.S. Department of Energy and it is managed privately and operated by Lawrence Livermore National Security, LLC (a partnership of the University of California), Bechtel, BWX Technologies, AECOM, and Battelle Memorial Institute in affiliation with the Texas A&M University System. In 2012, the laboratory had the synthetic chemical element livermorium (element 116) named after it. Overview LLNL is self-described as a "premier research and development institution for scie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Synchrotron Light
Synchrotron radiation (also known as magnetobremsstrahlung radiation) is the electromagnetic radiation emitted when relativistic charged particles are subject to an acceleration perpendicular to their velocity (). It is produced artificially in some types of particle accelerators, or naturally by fast electrons moving through magnetic fields. The radiation produced in this way has a characteristic polarization and the frequencies generated can range over a large portion of the electromagnetic spectrum. Synchrotron radiation is similar to bremsstrahlung radiation, which is emitted by a charged particle when the acceleration is parallel to the direction of motion. The general term for radiation emitted by particles in a magnetic field is ''gyromagnetic radiation'', for which synchrotron radiation is the ultra-relativistic special case. Radiation emitted by charged particles moving non-relativistically in a magnetic field is called cyclotron emission. For particles in the mildly ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DARPA
The Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency (DARPA) is a research and development agency of the United States Department of Defense responsible for the development of emerging technologies for use by the military. Originally known as the Advanced Research Projects Agency (ARPA), the agency was created on February 7, 1958, by President Dwight D. Eisenhower in response to the Soviet Union, Soviet launching of Sputnik 1 in 1957. By collaborating with academia, industry, and government partners, DARPA formulates and executes research and development projects to expand the frontiers of technology and science, often beyond immediate U.S. military requirements.Dwight D. Eisenhower and Science & Technology, (2008). Dwight D. Eisenhower Memorial CommissionSource ''The Economist'' has called DARPA the agency "that shaped the modern world," and pointed out that "Moderna COVID-19 vaccine, Moderna's COVID-19 vaccine sits alongside weather satellites, Global Positioning System, GPS, Unmann ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SPring-8 Synchrotron SP8 BL01B1
SPring-8 (an acronym of Super Photon Ring – 8 GeV) is a synchrotron radiation facility located in Sayo Town, Sayo District, Hyōgo Prefecture, Japan, which is the main facility of Harima Science Garden City. It was developed jointly by RIKEN and the Japan Atomic Energy Research Institute, and is owned and managed by RIKEN, and run under commission by the Japan Synchrotron Radiation Research Institute. The machine consists of a storage ring containing an 8 GeV electron beam. On its path around the storage ring, the beam passes through insertion devices to produce synchrotron radiation with energies ranging from soft X-rays (300 eV) up to hard X-rays (300 keV). The synchrotron radiation produced at SPring-8 is used for materials analysis and biochemical protein characterization by many Japanese manufacturers and universities. Together with the Advanced Photon Source at Argonne National Laboratory and the Cornell High Energy Synchrotron Source at Cornell University ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
JASON Defense Advisory Group
JASON is an independent group of elite scientists which advises the United States government on matters of science and technology, mostly of a sensitive nature. The group was created in the aftermath of the Sputnik launch as a way to reinvigorate the idea of having the nation's preeminent scientists help the government with defense problems, similar to the way that scientists helped in World War II but with a new and younger generation. It was established in 1960 and has somewhere between 30 and 60 members. Its work first gained public notoriety as the source of the Vietnam War's McNamara Line electronic barrier. Although most of its research is military-focused, JASON also produced early work on the science of global warming and acid rain. Current unclassified research interests include health informatics, cyberwarfare, and renewable energy. Activities For administrative purposes, JASON's activities are run through the MITRE Corporation, a not-for-profit corporation in McLe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
X-ray Burst
An X-ray, or, much less commonly, X-radiation, is a penetrating form of high-energy electromagnetic radiation. Most X-rays have a wavelength ranging from 10 picometers to 10 nanometers, corresponding to frequencies in the range 30 petahertz to 30 exahertz ( to ) and energies in the range 145 eV to 124 keV. X-ray wavelengths are shorter than those of UV rays and typically longer than those of gamma rays. In many languages, X-radiation is referred to as Röntgen radiation, after the German scientist Wilhelm Conrad Röntgen, who discovered it on November 8, 1895. He named it ''X-radiation'' to signify an unknown type of radiation.Novelline, Robert (1997). ''Squire's Fundamentals of Radiology''. Harvard University Press. 5th edition. . Spellings of ''X-ray(s)'' in English include the variants ''x-ray(s)'', ''xray(s)'', and ''X ray(s)''. The most familiar use of X-rays is checking for fractures (broken bones), but X-rays are also used in other ways. For ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |