|
Gyrostigma
''Gyrostigma'' is a genus of botfly which parasitize rhinoceroses. The best-known species is ''Gyrostigma rhinocerontis'', the rhinoceros stomach botfly, which develops in the stomach lining of the Black Rhinoceros and White Rhinoceros of Africa, and the adult of which is the largest fly known in Africa. Two other species are known. ''G. conjungens'' was discovered in the stomach of a Kenyan Black Rhinoceros in 1901, but has not been observed since 1961. The other is ''G. sumatrensis'', which was found in a captive Sumatran Rhinoceros The Sumatran rhinoceros (''Dicerorhinus sumatrensis''), also known as the Sumatran rhino, hairy rhinoceros or Asian two-horned rhinoceros, is a rare member of the family Rhinocerotidae and one of five extant species of rhinoceros. It is the o ... in 1884 but has not been observed since. Due to the difficulty of observing these short-lived flies, it is possible that there are other species corresponding to the other species of rhinoceros, but th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sumatran Rhinoceros
The Sumatran rhinoceros (''Dicerorhinus sumatrensis''), also known as the Sumatran rhino, hairy rhinoceros or Asian two-horned rhinoceros, is a rare member of the family Rhinocerotidae and one of five extant species of rhinoceros. It is the only extant species of the genus ''Dicerorhinus''. It is the smallest rhinoceros, although it is still a large mammal; it stands high at the shoulder, with a head-and-body length of and a tail of . The weight is reported to range from , averaging . Like both African species, it has two horns; the larger is the nasal horn, typically , while the other horn is typically a stub. A coat of reddish-brown hair covers most of the Sumatran rhino's body. The Sumatran rhinoceros once inhabited rainforests, swamps and cloud forests in India, Bhutan, Bangladesh, Myanmar, Laos, Thailand, Malaysia, Indonesia and southwestern China, particularly in Sichuan. It is now critically endangered, with only five substantial populations in the wild: four in Suma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frederick William Hope
Frederick William Hope (3 January 1797 – 15 April 1862) was an English clergyman, naturalist, collector, and entomologist, who founded a professorship at the University of Oxford to which he gave his entire collections of insects in 1849 (now known as the Hope Collection or in expanded form the Hope Entomological Collections, with around 3.5 million specimens). He described numerous species and was a founder of the Entomological Society of London in 1833 along with John Obadiah Westwood. Biography Frederick was the second son of John Thomas Hope of Netley Hall, Shrewsbury, and Ellen Hester Mary, only child and heiress of Sir Thomas Edwardes, and was born at their home in 37 Upper Seymour Street, London. He studied under the private tutor Reverend Delafosse and joined Christ Church, Oxford in 1817 and graduated with a BA in 1820. Presented to the curacy of Frodesley in Shropshire, he quickly retired as a result of ill health. Hope married, in 1835, the wealthy Ellen Meredith, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gyrostigma Rhinocerontis
''Gyrostigma rhinocerontis'' (also known as the Rhinoceros stomach botfly) is the largest fly species known in Africa. It is a parasite of the Black Rhinoceros and the White Rhinoceros. Because the fly depends on the rhinoceros for reproduction, its numbers declined steeply as the black and white rhinos faced extinction. Like the rhinoceros, it was presumably once widespread across much of sub-Saharan Africa (outside of the Congo Basin), but is today restricted to the savannas of southern and eastern Africa. Taxonomy The fly was originally described by English naturalist Sir Richard Owen in 1830 under the name of ''Oestrus rhinocerontis''.Neal L. Evenhuis. 2012Sir Richard Owen’s fly, ''Gyrostigma rhinocerontis'' (Diptera: Oestridae): correction of the authorship and date, with a list of animal names newly proposed by Owen in his little-known 1830 catalogue ''Zootaxa'' 3501:74-82. The description was made from larvae within the stomach of a rhinoceros. A fuller explanation was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gyrostigma Conjungens
''Gyrostigma'' is a genus of botfly which parasitize rhinoceroses. The best-known species is ''Gyrostigma rhinocerontis'', the rhinoceros stomach botfly, which develops in the stomach lining of the Black Rhinoceros and White Rhinoceros of Africa, and the adult of which is the largest fly known in Africa. Two other species are known. ''G. conjungens'' was discovered in the stomach of a Kenyan Black Rhinoceros in 1901, but has not been observed since 1961. The other is ''G. sumatrensis'', which was found in a captive Sumatran Rhinoceros The Sumatran rhinoceros (''Dicerorhinus sumatrensis''), also known as the Sumatran rhino, hairy rhinoceros or Asian two-horned rhinoceros, is a rare member of the family Rhinocerotidae and one of five extant species of rhinoceros. It is the o ... in 1884 but has not been observed since. Due to the difficulty of observing these short-lived flies, it is possible that there are other species corresponding to the other species of rhinoceros, but th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gyrostigma Sumatrensis
''Gyrostigma'' is a genus of botfly which parasitize rhinoceroses. The best-known species is ''Gyrostigma rhinocerontis'', the rhinoceros stomach botfly, which develops in the stomach lining of the Black Rhinoceros and White Rhinoceros of Africa, and the adult of which is the largest fly known in Africa. Two other species are known. ''G. conjungens'' was discovered in the stomach of a Kenyan Black Rhinoceros in 1901, but has not been observed since 1961. The other is ''G. sumatrensis'', which was found in a captive Sumatran Rhinoceros The Sumatran rhinoceros (''Dicerorhinus sumatrensis''), also known as the Sumatran rhino, hairy rhinoceros or Asian two-horned rhinoceros, is a rare member of the family Rhinocerotidae and one of five extant species of rhinoceros. It is the o ... in 1884 but has not been observed since. Due to the difficulty of observing these short-lived flies, it is possible that there are other species corresponding to the other species of rhinoceros, but th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Botfly
Botflies, also known as warble flies, heel flies, and gadflies, are a family of flies known as the Oestridae. Their larvae are internal parasites of mammals, some species growing in the host's flesh and others within the gut. ''Dermatobia hominis'' is the only species of botfly known to parasitize humans routinely, though other species of flies cause myiasis in humans. General A botfly, also written bot fly, bott fly or bot-fly in various combinations, is any fly in the family Oestridae. Their life cycles vary greatly according to species, but the larvae of all species are internal parasites of mammals. Largely according to species, they also are known variously as warble flies, heel flies, and gadflies. The larvae of some species grow in the flesh of their hosts, while others grow within the hosts' alimentary tracts. The word "bot" in this sense means a maggot. A warble is a skin lump or callus such as might be caused by an ill-fitting harness, or by the presence of a warble ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
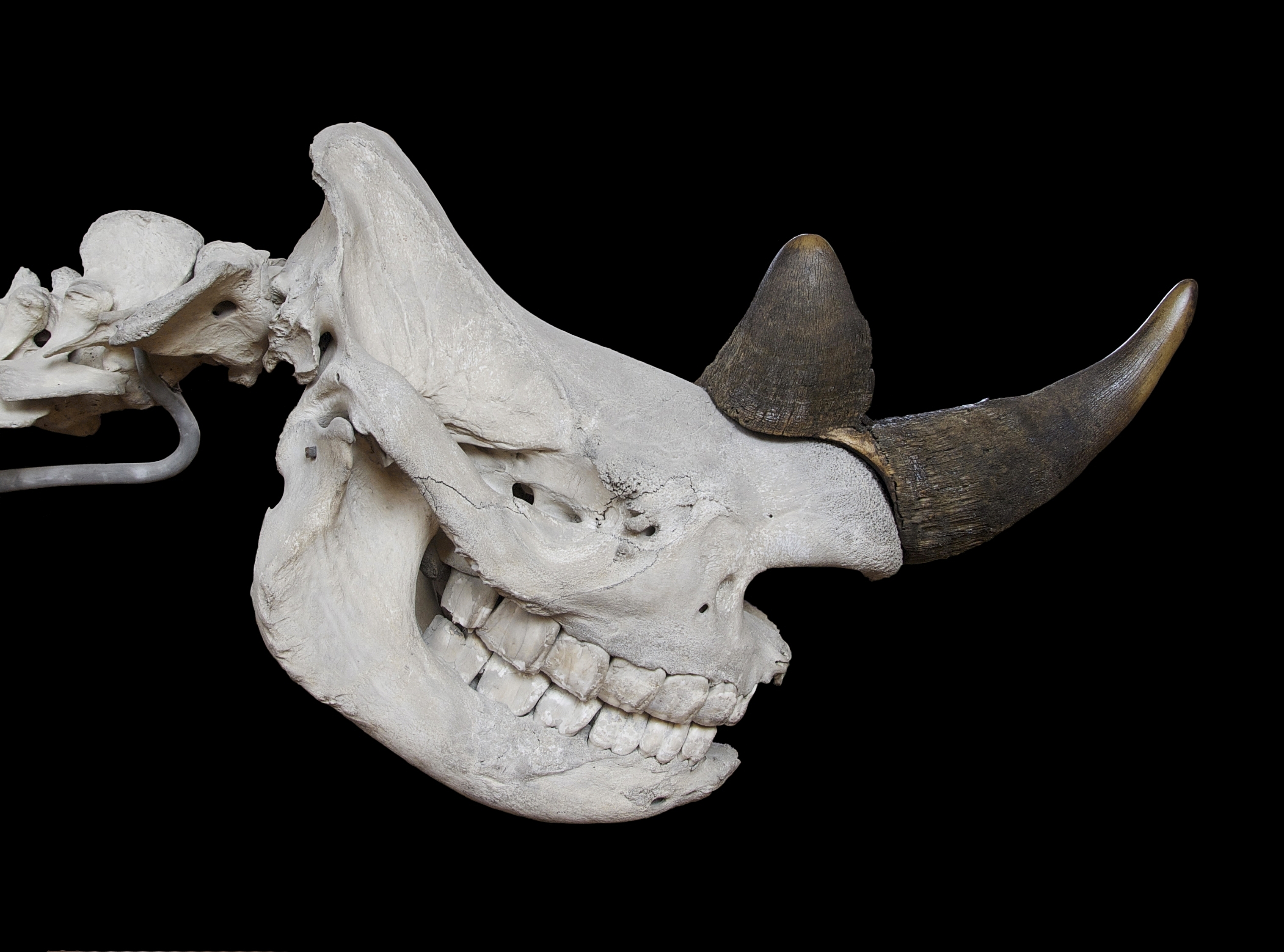
Rhinoceros
A rhinoceros (; ; ), commonly abbreviated to rhino, is a member of any of the five extant species (or numerous extinct species) of odd-toed ungulates in the family Rhinocerotidae. (It can also refer to a member of any of the extinct species of the superfamily Rhinocerotoidea.) Two of the extant species are native to Africa, and three to South and Southeast Asia. Rhinoceroses are some of the largest remaining megafauna: all weigh at least one tonne in adulthood. They have a herbivorous diet, small brains (400–600 g) for mammals of their size, one or two horns, and a thick (1.5–5 cm), protective skin formed from layers of collagen positioned in a lattice structure. They generally eat leafy material, although their ability to ferment food in their hindgut allows them to subsist on more fibrous plant matter when necessary. Unlike other perissodactyls, the two African species of rhinoceros lack teeth at the front of their mouths; they rely instead on their lips to pl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Black Rhinoceros
The black rhinoceros, black rhino or hook-lipped rhinoceros (''Diceros bicornis'') is a species of rhinoceros, native to eastern and southern Africa including Angola, Botswana, Kenya, Malawi, Mozambique, Namibia, South Africa, Eswatini, Tanzania, Zambia, and Zimbabwe. Although the rhinoceros is referred to as ''black'', its colours vary from brown to grey. The other African rhinoceros is the white rhinoceros (''Ceratotherium simum''). The word "white" in the name "white rhinoceros" is often said to be a misinterpretation of the Afrikaans word ' (Dutch ') meaning wide, referring to its square upper lip, as opposed to the pointed or hooked lip of the black rhinoceros. These species are now sometimes referred to as the square-lipped (for white) or hook-lipped (for black) rhinoceros. The species overall is classified as critically endangered (even though the south-western black rhinoceros is classified as near threatened). Three subspecies have been declared extinct, including the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
White Rhinoceros
The white rhinoceros, white rhino or square-lipped rhinoceros (''Ceratotherium simum'') is the largest extant species of rhinoceros. It has a wide mouth used for grazing (behaviour), grazing and is the most social of all rhino species. The white rhinoceros consists of two subspecies: the southern white rhinoceros, with an estimated 19,682–21,077 wild-living animals in the year 2015, and the much rarer northern white rhinoceros. The northern subspecies has very few remaining individuals, with only two confirmed left in 2018 (two females: Fatu, 18 and Najin, 29), both in captivity. Sudan (rhinoceros), Sudan, the world's last known male Northern white rhinoceros, died in Kenya on 19 March 2018 at age 45. Naming A popular albeit widely discredited theory of the origins of the name "white rhinoceros" is a mistranslation from Dutch to English. The English word "white" is said to have been derived by mistranslation of the Dutch word "wijd", which means "wide" in English. The word " ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Natural History (magazine)
''Natural History'' is a natural history magazine published in the United States. The stated mission of the magazine is to promote public understanding and appreciation of nature and science. History Founded in 1900 by the American Museum of Natural History, ''Natural History'' was first titled ''The American Museum Journal''. In 2002, the magazine was purchased from the Museum by a new company, headed at the time by Charles Harris. As of 2013 the magazine is published in North Carolina by Howard Richman. There are 10 issues published annually. Since its founding, ''Natural History'' has chronicled the major expeditions and research findings by curators at the American Museum of Natural History and at other natural history museums and science centers. Stephen Jay Gould's column, "This View of Life," was a regular feature of the magazine from 1974 until he retired the column in 2001. Other regular columnists and contributing authors include Neil deGrasse Tyson, Jared Diamond, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oestridae
Botflies, also known as warble flies, heel flies, and gadflies, are a family of flies known as the Oestridae. Their larvae are internal parasites of mammals, some species growing in the host's flesh and others within the gut. ''Dermatobia hominis'' is the only species of botfly known to parasitize humans routinely, though other species of flies cause myiasis in humans. General A botfly, also written bot fly, bott fly or bot-fly in various combinations, is any fly in the family Oestridae. Their life cycles vary greatly according to species, but the larvae of all species are internal parasites of mammals. Largely according to species, they also are known variously as warble flies, heel flies, and gadflies. The larvae of some species grow in the flesh of their hosts, while others grow within the hosts' alimentary tracts. The word "bot" in this sense means a maggot. A warble is a skin lump or callus such as might be caused by an ill-fitting harness, or by the presence of a warble ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parasitic Flies
Parasitism is a close relationship between species, where one organism, the parasite, lives on or inside another organism, the host, causing it some harm, and is adapted structurally to this way of life. The entomologist E. O. Wilson has characterised parasites as "predators that eat prey in units of less than one". Parasites include single-celled protozoans such as the agents of malaria, sleeping sickness, and amoebic dysentery; animals such as hookworms, lice, mosquitoes, and vampire bats; fungi such as honey fungus and the agents of ringworm; and plants such as mistletoe, dodder, and the broomrapes. There are six major parasitic strategies of exploitation of animal hosts, namely parasitic castration, directly transmitted parasitism (by contact), trophicallytransmitted parasitism (by being eaten), vector-transmitted parasitism, parasitoidism, and micropredation. One major axis of classification concerns invasiveness: an endoparasite lives inside the host's body; an ect ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |