|
Guanitoxin
Guanitoxin (GNT), formerly known as anatoxin-a(S) "Salivary", is a naturally occurring cyanotoxin commonly isolated from cyanobacteria (specifically of the genus ''Anabaena'') and causes excess salivation in mammals via inhibition of acetylcholinesterase. Guanitoxin was first structurally characterized in 1989, and consists of a cyclic ''N''-hydroxyguanine organophosphate with a phosphate ester moiety. Toxicity and treatment The main mechanism of action for guanitoxin is by irreversibly inhibiting the active site of acetylcholinesterase leading to excess acetylcholine in the parasympathetic and peripheral nervous systems; inducing poisoning via nicotinic and muscarinic cholinergic receptor stimulation. The clinical signs of high level guanitoxin exposure consists mainly of excessive salivation, lacrimation, chromodacryorrhea (in rats), urinary incontinence, muscular weakness, muscle twitching, convulsion, including opisthotonus, and respiratory distress and/or failure. Treatment ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
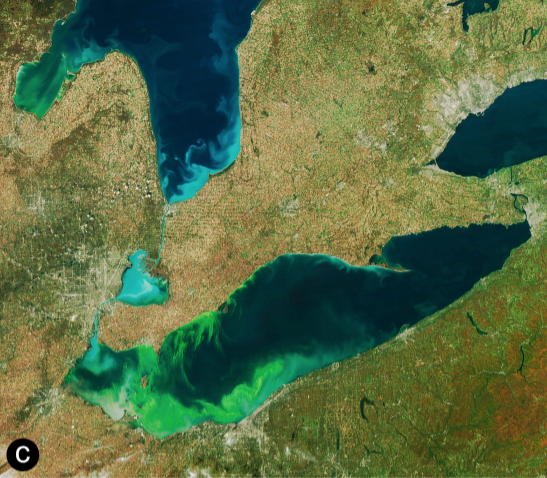
Cyanotoxin
Cyanotoxins are toxins produced by cyanobacteria (also known as blue-green algae). Cyanobacteria are found almost everywhere, but particularly in lakes and in the ocean where, under high concentration of phosphorus conditions, they exponential growth, reproduce exponentially to form Algal bloom, blooms. Blooming cyanobacteria can produce cyanotoxins in such concentrations that they poison and even kill animals and humans. Cyanotoxins can also accumulate in other animals such as fish and shellfish, and cause poisonings such as shellfish poisoning. Some of the most powerful natural poisons known are cyanotoxins. They include potent neurotoxins, hepatotoxins, cytotoxins, and endotoxins. Despite the similarity in name, they are unrelated to cyanides. Exposure to cyanobacteria can result in gastro-intestinal and hayfever symptoms or pruritic skin rashes. Exposure to the cyanobacteria neurotoxin BMAA may be an environmental cause of neurodegenerative diseases such as amyotrophic lateral ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cyanotoxins
Cyanotoxins are toxins produced by cyanobacteria (also known as blue-green algae). Cyanobacteria are found almost everywhere, but particularly in lakes and in the ocean where, under high concentration of phosphorus conditions, they reproduce exponentially to form blooms. Blooming cyanobacteria can produce cyanotoxins in such concentrations that they poison and even kill animals and humans. Cyanotoxins can also accumulate in other animals such as fish and shellfish, and cause poisonings such as shellfish poisoning. Some of the most powerful natural poisons known are cyanotoxins. They include potent neurotoxins, hepatotoxins, cytotoxins, and endotoxins. Despite the similarity in name, they are unrelated to cyanides. Exposure to cyanobacteria can result in gastro-intestinal and hayfever symptoms or pruritic skin rashes. Exposure to the cyanobacteria neurotoxin BMAA may be an environmental cause of neurodegenerative diseases such as amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), Parkinson's d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Organophosphate
In organic chemistry, organophosphates (also known as phosphate esters, or OPEs) are a class of organophosphorus compounds with the general structure , a central phosphate molecule with alkyl or aromatic substituents. They can be considered as esters of phosphoric acid. Like most functional groups, organophosphates occur in a diverse range of forms, with important examples including key biomolecules such as DNA, RNA and ATP, as well as many insecticides, herbicides, nerve agents and flame retardants. OPEs have been widely used in various products as flame retardants, plasticizers, and performance additives to engine oil. The popularity of OPEs as flame retardants came as a substitution for the highly regulated brominated flame retardants. The low cost of production and compatibility to diverse polymers made OPEs to be widely used in industry including textile, furniture, electronics as plasticizers and flame retardants. These compounds are added to the final product physica ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Organophosphates
In organic chemistry, organophosphates (also known as phosphate esters, or OPEs) are a class of organophosphorus compounds with the general structure , a central phosphate molecule with alkyl or aromatic substituents. They can be considered as esters of phosphoric acid. Like most functional groups, organophosphates occur in a diverse range of forms, with important examples including key biomolecules such as DNA, RNA and ATP, as well as many insecticides, herbicides, nerve agents and flame retardants. OPEs have been widely used in various products as flame retardants, plasticizers, and performance additives to engine oil. The popularity of OPEs as flame retardants came as a substitution for the highly regulated brominated flame retardants. The low cost of production and compatibility to diverse polymers made OPEs to be widely used in industry including textile, furniture, electronics as plasticizers and flame retardants. These compounds are added to the final product physi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anatoxin-a
Anatoxin-a, also known as Very Fast Death Factor (VFDF), is a secondary, bicyclic amine alkaloid and cyanotoxin with acute neurotoxicity. It was first discovered in the early 1960s in Canada, and was isolated in 1972. The toxin is produced by multiple genera of cyanobacteria and has been reported in North America, South America, Central America, Europe, Africa, Asia, and Oceania. Symptoms of anatoxin-a toxicity include loss of coordination, muscular fasciculations, convulsions and death by respiratory paralysis. Its mode of action is through the nicotinic acetylcholine receptor (nAchR) where it mimics the binding of the receptor's natural ligand, acetylcholine. As such, anatoxin-a has been used for medicinal purposes to investigate diseases characterized by low acetylcholine levels. Due to its high toxicity and potential presence in drinking water, anatoxin-a poses a threat to animals, including humans. While methods for detection and water treatment exist, scientists have called ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nitrogen Heterocycles
Nitrogen is the chemical element with the symbol N and atomic number 7. Nitrogen is a nonmetal and the lightest member of group 15 of the periodic table, often called the pnictogens. It is a common element in the universe, estimated at seventh in total abundance in the Milky Way and the Solar System. At standard temperature and pressure, two atoms of the element bond to form N2, a colorless and odorless diatomic gas. N2 forms about 78% of Earth's atmosphere, making it the most abundant uncombined element. Nitrogen occurs in all organisms, primarily in amino acids (and thus proteins), in the nucleic acids ( DNA and RNA) and in the energy transfer molecule adenosine triphosphate. The human body contains about 3% nitrogen by mass, the fourth most abundant element in the body after oxygen, carbon, and hydrogen. The nitrogen cycle describes the movement of the element from the air, into the biosphere and organic compounds, then back into the atmosphere. Many industrially importa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Methyl Esters
In organic chemistry, a methyl group is an alkyl derived from methane, containing one carbon atom bonded to three hydrogen atoms, having chemical formula . In formulas, the group is often abbreviated as Me. This hydrocarbon group occurs in many organic compounds. It is a very stable group in most molecules. While the methyl group is usually part of a larger molecule, bounded to the rest of the molecule by a single covalent bond (), it can be found on its own in any of three forms: methanide anion (), methylium cation () or methyl radical (). The anion has eight valence electrons, the radical seven and the cation six. All three forms are highly reactive and rarely observed. Methyl cation, anion, and radical Methyl cation The methylium cation () exists in the gas phase, but is otherwise not encountered. Some compounds are considered to be sources of the cation, and this simplification is used pervasively in organic chemistry. For example, protonation of methanol gives an electr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Guanidine Alkaloids
Guanidine is the compound with the formula HNC(NH2)2. It is a colourless solid that dissolves in polar solvents. It is a strong base that is used in the production of plastics and explosives. It is found in urine predominantly in patients experiencing renal failure. A guanidine moiety also appears in larger organic molecules, including on the side chain of arginine. Structure Guanidine can be thought of as a nitrogenous analogue of carbonic acid. That is, the C=O group in carbonic acid is replaced by a C=NH group, and each OH is replaced by a group. Isobutene can be seen as the carbon analogue in much the same way. A detailed crystallographic analysis of guanidine was elucidated 148 years after its first synthesis, despite the simplicity of the molecule. In 2013, the positions of the hydrogen atoms and their displacement parameters were accurately determined using single-crystal neutron diffraction. Production Guanidine can be obtained from natural sources, being first isolate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neurotoxins
Neurotoxins are toxins that are destructive to nerve tissue (causing neurotoxicity). Neurotoxins are an extensive class of exogenous chemical neurological insultsSpencer 2000 that can adversely affect function in both developing and mature nervous tissue.Olney 2002 The term can also be used to classify endogenous compounds, which, when abnormally contacted, can prove neurologically toxic. Though neurotoxins are often neurologically destructive, their ability to specifically target neural components is important in the study of nervous systems. Common examples of neurotoxins include lead, ethanol (drinking alcohol), glutamate,Choi 1987 nitric oxide, botulinum toxin (e.g. Botox), tetanus toxin,Simpson 1986 and tetrodotoxin. Some substances such as nitric oxide and glutamate are in fact essential for proper function of the body and only exert neurotoxic effects at excessive concentrations. Neurotoxins inhibit neuron control over ion concentrations across the cell membrane, or c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acetylcholinesterase Inhibitors
Acetylcholinesterase inhibitors (AChEIs) also often called cholinesterase inhibitors, inhibit the enzyme acetylcholinesterase from breaking down the neurotransmitter acetylcholine into choline and acetate, thereby increasing both the level and duration of action of acetylcholine in the central nervous system, autonomic ganglia and neuromuscular junctions, which are rich in acetylcholine receptors. Acetylcholinesterase inhibitors are one of two types of cholinesterase inhibitors; the other being butyryl-cholinesterase inhibitors. Acetylcholinesterase is the primary member of the cholinesterase enzyme family. Acetylcholinesterase inhibitors are classified as reversible, irreversible, or quasi-irreversible (also called pseudo-irreversible). Mechanism of action Organophosphates Organophosphates like TEPP and sarin inhibit cholinesterases, enzymes that hydrolyze the neurotransmitter acetylcholine. The active centre of cholinesterases feature two important sites, namely th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paraoxon
Paraoxon is a parasympathomimetic which acts as an cholinesterase inhibitor. It is an organophosphate oxon, and the active metabolite of the insecticide parathion. It is also used as an ophthalmological drug against glaucoma. Paraoxon is one of the most potent acetylcholinesterase-inhibiting insecticides available, around 70% as potent as the nerve agent sarin, and so is now rarely used as an insecticide due to the risk of poisoning to humans and other animals. Paraoxon has been used by scientists to study acute and chronic effects of organophosphate intoxication. It is easily absorbed through skin, and was allegedly used as an assassination weapon by the apartheid-era South African chemical weapons program Project Coast. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scheme For Guanitoxin Degradation
A scheme is a systematic plan for the implementation of a certain idea. Scheme or schemer may refer to: Arts and entertainment * ''The Scheme'' (TV series), a BBC Scotland documentary series * The Scheme (band), an English pop band * ''The Scheme'', an action role-playing video game for the PC-8801, made by Quest Corporation * Schemer (comics), Richard Fisk, a Marvel Comics villain turned antihero * Horace Schemer, a fictional character in the TV series ''Shining Time Station'' * Schemee, a fictional child character and Schemer's nephew in the TV Series ''Shining Time Station'' * ''Schemers'' (film), a Scottish film Other uses * Classification scheme, eg a thesaurus, a taxonomy, a data model, or an ontology * Scheme (programming language), a minimalist dialect of Lisp * Scheme (mathematics), a concept in algebraic geometry * Scheme (linguistics), a figure of speech that changes a sentence's structure * Scam, an attempt to swindle or cheat people through deception **Get-rich-quick ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |