|
Gravitational Drag
In astrophysics, dynamical friction or Chandrasekhar friction, sometimes called ''gravitational drag'', is loss of momentum and kinetic energy of moving bodies through gravitational interactions with surrounding matter in space. It was first discussed in detail by Subrahmanyan Chandrasekhar in 1943. Intuitive account An intuition for the effect can be obtained by thinking of a massive object moving through a cloud of smaller lighter bodies. The effect of gravity causes the light bodies to accelerate and gain momentum and kinetic energy (see slingshot effect). By conservation of energy and momentum, we may conclude that the heavier body will be slowed by an amount to compensate. Since there is a loss of momentum and kinetic energy for the body under consideration, the effect is called ''dynamical friction''. Another equivalent way of thinking about this process is that as a large object moves through a cloud of smaller objects, the gravitational effect of the larger object pulls ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Astrophysics
Astrophysics is a science that employs the methods and principles of physics and chemistry in the study of astronomical objects and phenomena. As one of the founders of the discipline said, Astrophysics "seeks to ascertain the nature of the heavenly bodies, rather than their positions or motions in space–''what'' they are, rather than ''where'' they are." Among the subjects studied are the Sun, other stars, galaxies, extrasolar planets, the interstellar medium and the cosmic microwave background. Emissions from these objects are examined across all parts of the electromagnetic spectrum, and the properties examined include luminosity, density, temperature, and chemical composition. Because astrophysics is a very broad subject, ''astrophysicists'' apply concepts and methods from many disciplines of physics, including classical mechanics, electromagnetism, statistical mechanics, thermodynamics, quantum mechanics, relativity, nuclear and particle physics, and atomic and m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Weber State University
Weber State University (pronounced ) is a public university in Ogden, Utah. It was founded in 1889 as Weber Stake Academy. It is accredited by the Northwest Commission on Colleges and Universities. History Weber State University was founded by the Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints as the Weber Stake Academy in 1889. "Weber" comes from the name of the county where the university is located. Weber County was named after John Henry Weber, an early fur trader. The university opened for students in 1889 with 98 students enrolled for classes The first principal of Weber Stake Academy was Louis F. Moench; he served from 1889 to 1892 and again from 1894 to 1902. In the latter year, Moench was succeeded as principal by David O. McKay, who served in that position until 1908. From 1914 to 1917, James L. Barker was the principal of the Weber Stake Academy. In the early 20th century, the school underwent multiple name changes: Weber Stake Academy from its founding in 1889, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Astrophysics
Astrophysics is a science that employs the methods and principles of physics and chemistry in the study of astronomical objects and phenomena. As one of the founders of the discipline said, Astrophysics "seeks to ascertain the nature of the heavenly bodies, rather than their positions or motions in space–''what'' they are, rather than ''where'' they are." Among the subjects studied are the Sun, other stars, galaxies, extrasolar planets, the interstellar medium and the cosmic microwave background. Emissions from these objects are examined across all parts of the electromagnetic spectrum, and the properties examined include luminosity, density, temperature, and chemical composition. Because astrophysics is a very broad subject, ''astrophysicists'' apply concepts and methods from many disciplines of physics, including classical mechanics, electromagnetism, statistical mechanics, thermodynamics, quantum mechanics, relativity, nuclear and particle physics, and atomic and m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Friction
Friction is the force resisting the relative motion of solid surfaces, fluid layers, and material elements sliding against each other. There are several types of friction: *Dry friction is a force that opposes the relative lateral motion of two solid surfaces in contact. Dry friction is subdivided into ''static friction'' ("stiction") between non-moving surfaces, and ''kinetic friction'' between moving surfaces. With the exception of atomic or molecular friction, dry friction generally arises from the interaction of surface features, known as asperities (see Figure 1). *Fluid friction describes the friction between layers of a viscous fluid that are moving relative to each other. *Lubricated friction is a case of fluid friction where a lubricant fluid separates two solid surfaces. *Skin friction is a component of drag, the force resisting the motion of a fluid across the surface of a body. *Internal friction is the force resisting motion between the elements making up a so ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metric Expansion Of Space
The expansion of the universe is the increase in distance between any two given gravitationally unbound parts of the observable universe with time. It is an intrinsic expansion whereby the scale of space itself changes. The universe does not expand "into" anything and does not require space to exist "outside" it. This expansion involves neither space nor objects in space "moving" in a traditional sense, but rather it is the metric (which governs the size and geometry of spacetime itself) that changes in scale. As the spatial part of the universe's spacetime metric increases in scale, objects become more distant from one another at ever-increasing speeds. To any observer in the universe, it appears that all of space is expanding, and that all but the nearest galaxies (which are bound by gravity) recede at speeds that are proportional to their distance from the observer. While objects within space cannot travel faster than light, this limitation does not apply to the effects of ch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arthur Stanley Eddington
Sir Arthur Stanley Eddington (28 December 1882 – 22 November 1944) was an English astronomer, physicist, and mathematician. He was also a philosopher of science and a populariser of science. The Eddington limit, the natural limit to the luminosity of stars, or the radiation generated by accretion onto a compact object, is named in his honour. Around 1920, he foreshadowed the discovery and mechanism of nuclear fusion processes in stars, in his paper "The Internal Constitution of the Stars".The Internal Constitution of the Stars A. S. Eddington The Scientific Monthly Vol. 11, No. 4 (Oct., 1920), pp. 297–303 At that time, the source of stellar energy was a complete mystery; Eddington was the first to correctly speculate that the source was fusion of hydrogen into helium. Eddington wrote a number of articles that announced and explained Einstein's theory of general relativity to the English-speaking world. World War I had severed many lines of scientific communication, and ne ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
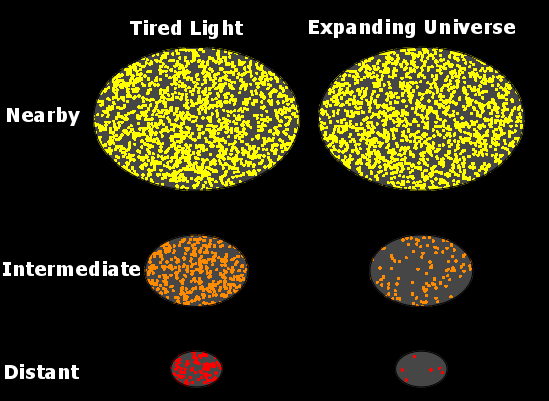
Tired Light
Tired light is a class of hypothetical redshift mechanisms that was proposed as an alternative explanation for the redshift-distance relationship. These models have been proposed as alternatives to the models that require metric expansion of space of which the Big Bang and the Steady State cosmologies are the most famous examples. The concept was first proposed in 1929 by Fritz Zwicky, who suggested that if photons lost energy over time through collisions with other particles in a regular way, the more distant objects would appear redder than more nearby ones. Zwicky himself acknowledged that any sort of scattering of light would blur the images of distant objects more than what is seen. Additionally, the surface brightness of galaxies evolving with time, time dilation of cosmological sources, and a thermal spectrum of the cosmic microwave background have been observed—these effects should not be present if the cosmological redshift was due to any tired light scattering mec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cosmological Redshift
Hubble's law, also known as the Hubble–Lemaître law, is the observation in physical cosmology that galaxies are moving away from Earth at speeds proportional to their distance. In other words, the farther they are, the faster they are moving away from Earth. The velocity of the galaxies has been determined by their redshift, a shift of the light they emit toward the red end of the visible spectrum. Hubble's law is considered the first observational basis for the expansion of the universe, and today it serves as one of the pieces of evidence most often cited in support of the Big Bang model. The motion of astronomical objects due solely to this expansion is known as the Hubble flow. It is described by the equation , with ''H''0 the constant of proportionality—the Hubble constant—between the "proper distance" ''D'' to a galaxy, which can change over time, unlike the comoving distance, and its speed of separation ''v'', i.e. the derivative of proper distance with respect to t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fritz Zwicky
Fritz Zwicky (; ; February 14, 1898 – February 8, 1974) was a Swiss astronomer. He worked most of his life at the California Institute of Technology in the United States of America, where he made many important contributions in theoretical and observational astronomy. In 1933, Zwicky was the first to use the virial theorem to infer the existence of unseen dark matter, describing it as "'". From p 125: ''"Um, wie beobachtet, einen mittleren Dopplereffekt von 1000 km/sek oder mehr zu erhalten, müsste also die mittlere Dichte im Comasystem mindestens 400 mal grösser sein als die auf Grund von Beobachtungen an leuchtender Materie abgeleitete. Falls sich dies bewahrheiten sollte, würde sich also das überraschende Resultat ergeben, dass dunkle Materie in sehr viel grösserer Dichte vorhanden ist als leuchtende Materie."'' (In order to obtain an average Doppler effect of 1000 km/s or more, as observed, the average density in the Coma system would thus have to be at least 400 time ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
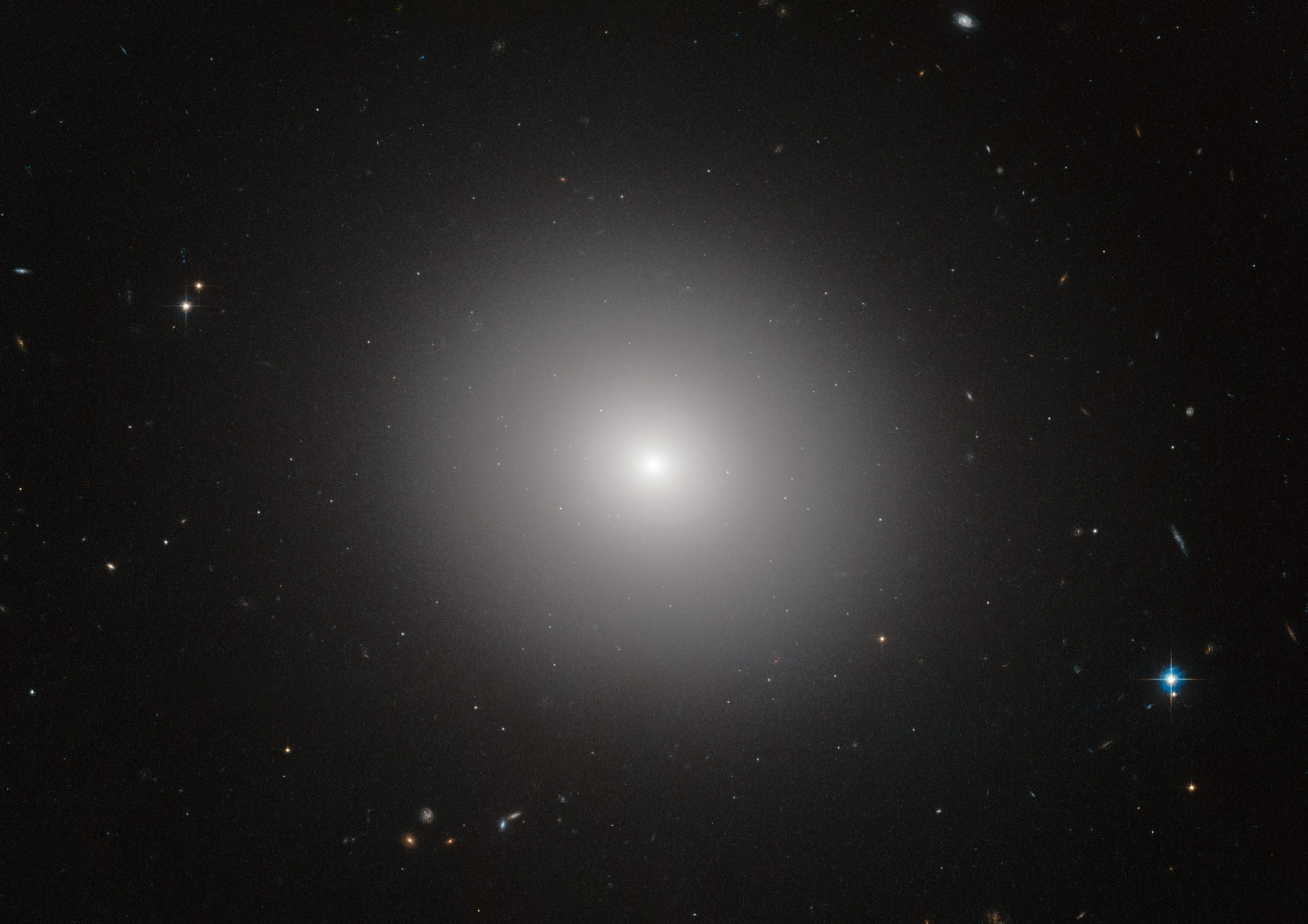
Elliptical Galaxy
An elliptical galaxy is a type of galaxy with an approximately ellipsoidal shape and a smooth, nearly featureless image. They are one of the four main classes of galaxy described by Edwin Hubble in his Hubble sequence and 1936 work ''The Realm of the Nebulae'', with their intermediate scale disks, a subset of the "early-type" galaxy population. Most elliptical galaxies are composed of older, low-mass stars, with a sparse interstellar medium and minimal star formation activity, and they tend to be surrounded by large numbers of globular clusters. Elliptical galaxies are believed to make up approximately 10–15% of galaxies in the Virgo Supercluster, and they are not the dominant type of galaxy in the universe overall. They are preferentially found close to the centers of galaxy clusters. Elliptical galaxies range in size from dwarf ellipticals with tens of millions of stars, to supergiants of over one hundred trillion stars that dominate their galaxy clusters. Original ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spiral Galaxies
Spiral galaxies form a class of galaxy originally described by Edwin Hubble in his 1936 work ''The Realm of the Nebulae''Alt URL pp. 124–151) and, as such, form part of the . Most spiral galaxies consist of a flat, rotating containing s, gas and dust, and a central concentration of stars known as the |
Protoplanetary Disk
A protoplanetary disk is a rotating circumstellar disc of dense gas and dust surrounding a young newly formed star, a T Tauri star, or Herbig Ae/Be star. The protoplanetary disk may also be considered an accretion disk for the star itself, because gases or other material may be falling from the inner edge of the disk onto the surface of the star. This process should not be confused with the accretion process thought to build up the planets themselves. Externally illuminated photo-evaporating protoplanetary disks are called proplyds. Formation Protostars form from molecular clouds consisting primarily of molecular hydrogen. When a portion of a molecular cloud reaches a critical size, mass, or density, it begins to collapse under its own gravity. As this collapsing cloud, called a solar nebula, becomes denser, random gas motions originally present in the cloud average out in favor of the direction of the nebula's net angular momentum. Conservation of angular momentum causes t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |