|
Grand Duke Of Luxembourg
The Grand Duke of Luxembourg ( lb, Groussherzog vu Lëtzebuerg, french: Grand-duc de Luxembourg, german: Großherzog von Luxemburg) is the monarchical head of state of Luxembourg. Luxembourg has been a grand duchy since 15 March 1815, when it was created from territory of the former Duchy of Luxembourg. It was in personal union with the United Kingdom of the Netherlands until 1890 under the House of Orange-Nassau. Luxembourg is the world's only sovereign grand duchy and since 1815, there have been nine monarchs, including the incumbent, Henri. Constitutional role The constitution of Luxembourg defines the grand duke's position: :The grand duke is the head of state, symbol of its unity, and guarantor of national independence. He exercises executive power in accordance with the constitution and the laws of the country. After a constitutional change (to article 34) in December 2008 resulting from Henri's refusal to assent to a law legalizing euthanasia, laws now no longer req ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
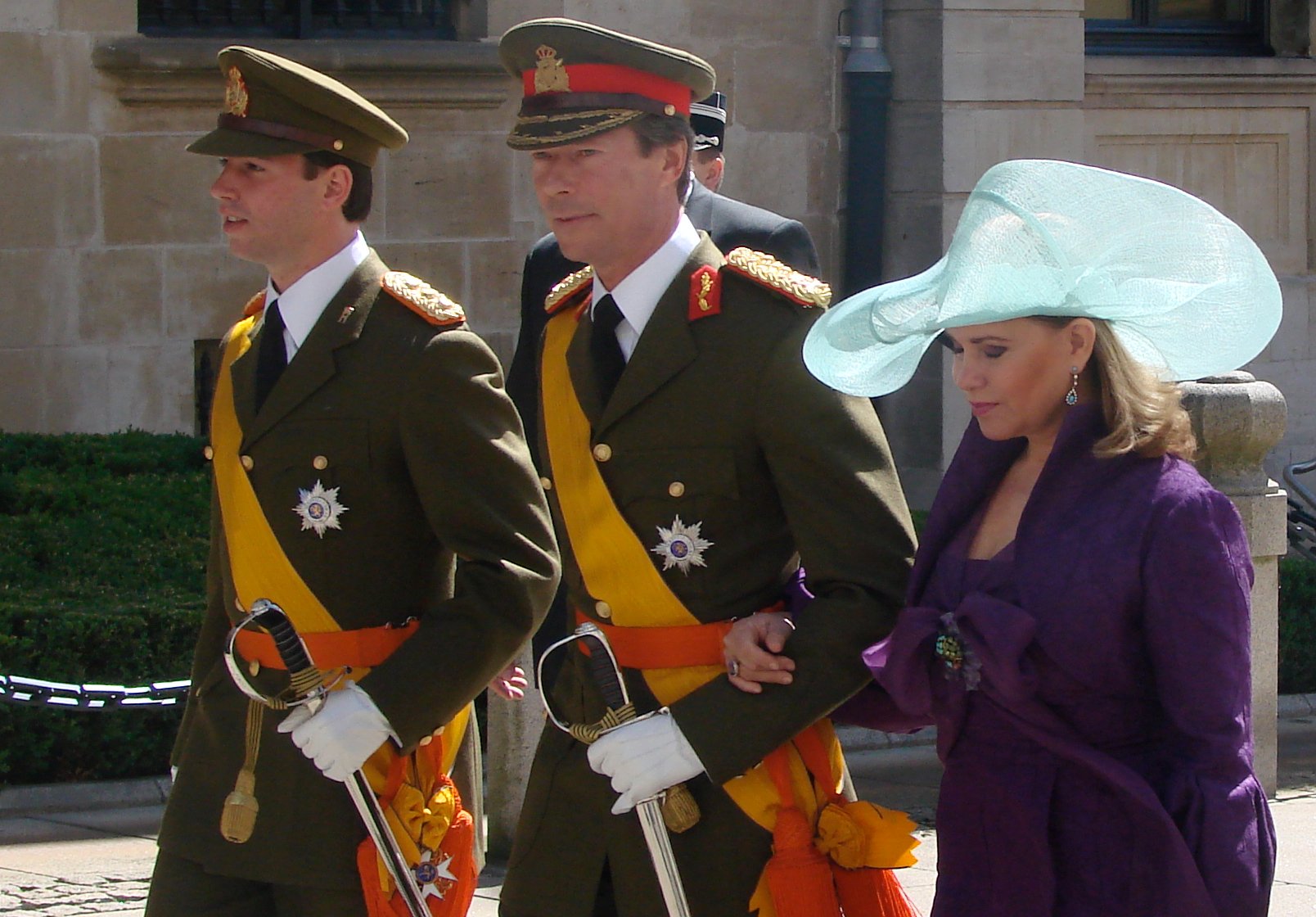
Henri, Grand Duke Of Luxembourg
Henri (french: Henri Albert Gabriel Félix Marie Guillaume, ; born 16 April 1955) is the Grand Duke of Luxembourg. He has reigned since 7 October 2000. Henri, the eldest son of Grand Duke Jean and Princess Joséphine-Charlotte of Belgium, is a first cousin of King Philippe of Belgium. In 2019, Henri's net worth was estimated around US$4 billion. Childhood Prince Henri was born on 16 April 1955, at the Betzdorf Castle in Luxembourg as the second child and first son of Hereditary Grand Duke Jean of Luxembourg and his wife, Princess Joséphine-Charlotte of Belgium. His father was the eldest son of Grand Duchess Charlotte of Luxembourg by her husband, Prince Félix of Bourbon-Parma. His mother was the only daughter of King Leopold III of Belgium by his first wife, Princess Astrid of Sweden. The prince's godparents were the Prince of Liège (his maternal uncle) and Princess Marie Gabriele (his paternal aunt). Henri has four siblings: Archduchess Marie Astrid of Austria (born 1954), ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Executive (government)
The Executive, also referred as the Executive branch or Executive power, is the term commonly used to describe that part of government which enforces the law, and has overall responsibility for the governance of a state. In political systems based on the separation of powers, such as the USA, government authority is distributed between several branches in order to prevent power being concentrated in the hands of a single person or group. To achieve this, each branch is subject to checks by the other two; in general, the role of the Legislature is to pass laws, which are then enforced by the Executive, and interpreted by the Judiciary. The Executive can be also be the source of certain types of law, such as a decree or executive order. In those that use fusion of powers, typically Parliamentary systems, the Executive forms the government and its members generally belong to the political party that controls the legislature or "Parliament". Since the Executive requires the suppor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heir Apparent
An heir apparent, often shortened to heir, is a person who is first in an order of succession and cannot be displaced from inheriting by the birth of another person; a person who is first in the order of succession but can be displaced by the birth of a more eligible heir is known as heir presumptive. Today these terms most commonly describe heirs to hereditary titles (e.g. titles of nobility) or offices, especially when only inheritable by a single person. Most monarchies refer to the heir apparent of their thrones with the descriptive term of ''crown prince'' or ''crown princess'', but they may also be accorded with a more specific substantive title: such as Prince of Orange in the Netherlands, Duke of Brabant in Belgium, Prince of Asturias in Spain (also granted to heirs presumptive), or the Prince of Wales in the United Kingdom; former titles include Dauphin in the Kingdom of France, and Tsesarevich in Imperial Russia. The term is also used metaphorically to indicate a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Morganatic Marriage
Morganatic marriage, sometimes called a left-handed marriage, is a marriage between people of unequal social rank, which in the context of royalty or other inherited title prevents the principal's position or privileges being passed to the spouse, or any children born of the marriage. The concept is most prevalent in German-speaking territories and countries most influenced by the customs of the German-speaking realms. Generally, this is a marriage between a man of high birth (such as from a reigning, deposed or mediatised dynasty) and a woman of lesser status (such as a daughter of a low-ranked noble family or a commoner).Webster's Online Dictionary . Retrieved 2008-07-10. Diesbach, Ghislain de. ''S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Count Of Merenberg
Count of Merenberg (German: ''Graf von Merenberg'') is a hereditary title of nobility that was bestowed in 1868 by the reigning Prince of Waldeck and Pyrmont, George Victor, upon the morganatic wife and male-line descendants of Prince Nikolaus Wilhelm of Nassau (1832–1905), who married Natalia Alexandrovna Pushkina (1836–1913), former wife of Russian general Mikhail Leontievich von Dubelt. Background Nikolaus was a son of William, Duke of Nassau, and his second wife, Princess Pauline of Württemberg. He was also a younger half-brother of Adolphe, who was deposed by Prussia as last reigning Duke of Nassau in 1866 but succeeded as Grand Duke of Luxembourg in 1890. Natalia was a daughter of Alexander Pushkin, the most renowned Russian writer. However, he ranked only as a ''dvoryanin'', an untitled member of the lower nobility. As such, she was not legally permitted to share her husband's princely title or rank, even though his family had ceased to be hereditary rulers when the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Treaty Of London (1867)
The Treaty of London (french: Traité de Londres), often called the Second Treaty of London after the Treaty of London (1839), 1839 Treaty, granted Luxembourg full independence and neutrality. It was signed on 11 May 1867 in the aftermath of the Austro-Prussian War and the Luxembourg Crisis. It had wide-reaching consequences for Luxembourg and for relations among Europe's great powers. Effects The immediate effect of the treaty, established in Article I, was the reaffirmation of the personal union between the Netherlands and Luxembourg under the House of Orange-Nassau. It lasted until 1890, when Wilhelmina ascended the Dutch throne. As a form of Patrilineality#Agnatic succession, agnatic succession was then in effect in Luxembourg (under the Nassau Family Pact of 1783), the Grand Duchy could not pass in the female line. Instead it was the older branch of the House of Nassau (Nassau-Weilburg, now called Luxembourg-Nassau) that inherited that dignity, giving Luxembourg its own e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Congress Of Vienna
The Congress of Vienna (, ) of 1814–1815 was a series of international diplomatic meetings to discuss and agree upon a possible new layout of the European political and constitutional order after the downfall of the French Emperor Napoleon Bonaparte. Participants were representatives of all European powers and other stakeholders, chaired by Austrian statesman Klemens von Metternich, and held in Vienna from September 1814 to June 1815. The objective of the Congress was to provide a long-term peace plan for Europe by settling critical issues arising from the French Revolutionary Wars and the Napoleonic Wars without the use of (military) violence. The goal was not simply to restore old boundaries, but to resize the main powers so they could balance each other and remain at peace, being at the same time shepherds for the smaller powers. More fundamentally, strongly generalising, conservative thinking leaders like Von Metternich also sought to restrain or eliminate republicanism, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
House Of Nassau
The House of Nassau is a diversified aristocratic dynasty in Europe. It is named after the lordship associated with Nassau Castle, located in present-day Nassau, Rhineland-Palatinate, Germany. The lords of Nassau were originally titled "Count of Nassau", then elevated to the princely class as "Princely Counts". Early on they divided into two main branches: the elder (Walramian) branch, that gave rise to the German king Adolf, and the younger (Ottonian) branch, that gave rise to the Princes of Orange and the monarchs of the Netherlands. At the end of the Holy Roman Empire and the Napoleonic Wars, the Walramian branch had inherited or acquired all the Nassau ancestral lands and proclaimed themselves, with the permission of the Congress of Vienna, the "Dukes of Nassau", forming the independent state of Nassau with its capital at Wiesbaden; this territory today mainly lies in the German Federal State of Hesse, and partially in the neighbouring State of Rhineland-Palatinate. The D ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Agnatic-cognatic Primogeniture
Primogeniture ( ) is the right, by law or custom, of the firstborn legitimate child to inherit the parent's entire or main estate in preference to shared inheritance among all or some children, any illegitimate child or any collateral relative. In most contexts, it means the inheritance of the firstborn son (agnatic primogeniture); it can also mean by the firstborn daughter (matrilineal primogeniture). Description The common definition given is also known as male-line primogeniture, the classical form popular in European jurisdictions among others until into the 20th century. In the absence of male-line offspring, variations were expounded to entitle a daughter or a brother or, in the absence of either, to another collateral relative, in a specified order (e.g. male-preference primogeniture, Salic primogeniture, semi-Salic primogeniture). Variations have tempered the traditional, sole-beneficiary, right (such as French appanage) or, in the West since World War II, eliminate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nassau Family Pact
The Nassau Family Pact was a mutual pact of inheritance and succession made in 1783 by princes of the House of Nassau. It confirmed that Salic Law was to operate in favor of all the agnatic lines of the family, specifically the two senior surviving lines which had originated in the Middle Ages, the Walramian and the Ottonian. The pact chiefly provided that in case of one of these lines becoming extinct, the other would succeed in its hereditary Nassau lands ("the main concept of the pact was that if either the Ottonian or Walramian male line would become extinct the other line would succeed"). There was a clause to provide for a so-called Semi-Salic continuation to the dynasty in an undefined way if both the lines were to die out in the male line ("also arranged for that in the absence of all male successors, females could succeed"). In case of the extinction of all male lines, the closest heir to the last male will succeed and in turn will be succeeded by the heirs of that closes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Salic Law
The Salic law ( or ; la, Lex salica), also called the was the ancient Frankish civil law code compiled around AD 500 by the first Frankish King, Clovis. The written text is in Latin and contains some of the earliest known instances of Old Dutch. It remained the basis of Frankish law throughout the early Medieval period, and influenced future European legal systems. The best-known tenet of the old law is the principle of exclusion of women from inheritance of thrones, fiefs, and other property. The Salic laws were arbitrated by a committee appointed and empowered by the King of the Franks. Dozens of manuscripts dating from the sixth to eighth centuries and three emendations as late as the ninth century have survived. Salic law provided written codification of both civil law, such as the statutes governing inheritance, and criminal law, such as the punishment for murder. Although it was originally intended as the law of the Franks, it has had a formative influence on the trad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Business Insider
''Insider'', previously named ''Business Insider'' (''BI''), is an American financial and business news website founded in 2007. Since 2015, a majority stake in ''Business Insider''s parent company Insider Inc. has been owned by the German publishing house Axel Springer. It operates several international editions, including one in the United Kingdom. ''Insider'' publishes original reporting and aggregates material from other outlets. , it maintained a liberal policy on the use of anonymous sources. It has also published native advertising and granted sponsors editorial control of its content. The outlet has been nominated for several awards, but is criticized for using factually incorrect clickbait headlines to attract viewership. In 2015, Axel Springer SE acquired 88 percent of the stake in Insider Inc. for $343 million (€306 million), implying a total valuation of $442 million. In February 2021, the brand was renamed simply ''Insider''. History ''Busi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |