|
Glycolate Dehydrogenase
In enzymology, a glycolate dehydrogenase () is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction :glycolate + acceptor \rightleftharpoons glyoxylate + reduced acceptor Thus, the two substrates of this enzyme are glycolate and acceptor, whereas its two products are glyoxylate and reduced acceptor. This enzyme belongs to the family of oxidoreductases, specifically those acting on the CH-OH group of donor with other acceptors. The systematic name of this enzyme class is glycolate:acceptor 2-oxidoreductase. Other names in common use include glycolate oxidoreductase, glycolic acid dehydrogenase, and glycolate:(acceptor) 2-oxidoreductase. This enzyme participates in glyoxylate and dicarboxylate metabolism Glyoxylate and dicarboxylate metabolism describes a variety of reactions involving glyoxylate or dicarboxylates. Glyoxylate is the conjugate base of glyoxylic acid, and within a buffered environment of known pH such as the cell cytoplasm these t .... References * EC 1.1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enzymology
Enzymes () are proteins that act as biological catalysts by accelerating chemical reactions. The molecules upon which enzymes may act are called substrates, and the enzyme converts the substrates into different molecules known as products. Almost all metabolic processes in the cell need enzyme catalysis in order to occur at rates fast enough to sustain life. Metabolic pathways depend upon enzymes to catalyze individual steps. The study of enzymes is called ''enzymology'' and the field of pseudoenzyme analysis recognizes that during evolution, some enzymes have lost the ability to carry out biological catalysis, which is often reflected in their amino acid sequences and unusual 'pseudocatalytic' properties. Enzymes are known to catalyze more than 5,000 biochemical reaction types. Other biocatalysts are catalytic RNA molecules, called ribozymes. Enzymes' specificity comes from their unique three-dimensional structures. Like all catalysts, enzymes increase the reaction ra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enzyme
Enzymes () are proteins that act as biological catalysts by accelerating chemical reactions. The molecules upon which enzymes may act are called substrates, and the enzyme converts the substrates into different molecules known as products. Almost all metabolic processes in the cell need enzyme catalysis in order to occur at rates fast enough to sustain life. Metabolic pathways depend upon enzymes to catalyze individual steps. The study of enzymes is called ''enzymology'' and the field of pseudoenzyme analysis recognizes that during evolution, some enzymes have lost the ability to carry out biological catalysis, which is often reflected in their amino acid sequences and unusual 'pseudocatalytic' properties. Enzymes are known to catalyze more than 5,000 biochemical reaction types. Other biocatalysts are catalytic RNA molecules, called ribozymes. Enzymes' specificity comes from their unique three-dimensional structures. Like all catalysts, enzymes increase the reaction ra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Catalysis
Catalysis () is the process of increasing the rate of a chemical reaction by adding a substance known as a catalyst (). Catalysts are not consumed in the reaction and remain unchanged after it. If the reaction is rapid and the catalyst recycles quickly, very small amounts of catalyst often suffice; mixing, surface area, and temperature are important factors in reaction rate. Catalysts generally react with one or more reactants to form intermediates that subsequently give the final reaction product, in the process of regenerating the catalyst. Catalysis may be classified as either homogeneous, whose components are dispersed in the same phase (usually gaseous or liquid) as the reactant, or heterogeneous, whose components are not in the same phase. Enzymes and other biocatalysts are often considered as a third category. Catalysis is ubiquitous in chemical industry of all kinds. Estimates are that 90% of all commercially produced chemical products involve catalysts at some s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chemical Reaction
A chemical reaction is a process that leads to the IUPAC nomenclature for organic transformations, chemical transformation of one set of chemical substances to another. Classically, chemical reactions encompass changes that only involve the positions of electrons in the forming and breaking of chemical bonds between atoms, with no change to the Atomic nucleus, nuclei (no change to the elements present), and can often be described by a chemical equation. Nuclear chemistry is a sub-discipline of chemistry that involves the chemical reactions of unstable and radioactive Chemical element, elements where both electronic and nuclear changes can occur. The substance (or substances) initially involved in a chemical reaction are called reagent, reactants or reagents. Chemical reactions are usually characterized by a chemical change, and they yield one or more Product (chemistry), products, which usually have properties different from the reactants. Reactions often consist of a sequence o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Substrate (biochemistry)
In chemistry, the term substrate is highly context-dependent. Broadly speaking, it can refer either to a chemical species being observed in a chemical reaction, or to a surface on which other chemical reactions or microscopy are performed. In the former sense, a reagent is added to the ''substrate'' to generate a product through a chemical reaction. The term is used in a similar sense in synthetic and organic chemistry, where the substrate is the chemical of interest that is being modified. In biochemistry, an enzyme substrate is the material upon which an enzyme acts. When referring to Le Chatelier's principle, the substrate is the reagent whose concentration is changed. ;Spontaneous reaction : :*Where S is substrate and P is product. ;Catalysed reaction : :*Where S is substrate, P is product and C is catalyst. In the latter sense, it may refer to a surface on which other chemical reactions are performed or play a supporting role in a variety of spectroscopic and microscop ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glycolate
Glycolic acid (or hydroxyacetic acid; chemical formula HOCH2CO2H) is a colorless, odorless and hygroscopic crystalline solid, highly soluble in water. It is used in various skin-care products. Glycolic acid is widespread in nature. A glycolate (sometimes spelled "glycollate") is a salt or ester of glycolic acid. History The name "glycolic acid" was coined in 1848 by French chemist Auguste Laurent (1807–1853). He proposed that the amino acid glycine—which was then called ''glycocolle''—might be the amine of a hypothetical acid, which he called "glycolic acid" (''acide glycolique''). Glycolic acid was first prepared in 1851 by German chemist Adolph Strecker (1822–1871) and Russian chemist Nikolai Nikolaevich Sokolov (1826–1877). They produced it by treating hippuric acid with nitric acid and nitrogen dioxide to form an ester of benzoic acid and glycolic acid (C6H5C(=O)OCH2COOH), which they called "benzoglycolic acid" (''Benzoglykolsäure''; also benzoyl glycolic acid). ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electron Acceptor
An electron acceptor is a chemical entity that accepts electrons transferred to it from another compound. It is an oxidizing agent that, by virtue of its accepting electrons, is itself reduced in the process. Electron acceptors are sometimes mistakenly called electron receptors. Typical oxidizing agents undergo permanent chemical alteration through covalent or ionic reaction chemistry, resulting in the complete and irreversible transfer of one or more electrons. In many chemical circumstances, however, the transfer of electronic charge from an electron donor may be only fractional, meaning an electron is not completely transferred, but results in an electron resonance between the donor and acceptor. This leads to the formation of charge transfer complexes in which the components largely retain their chemical identities. The electron accepting power of an acceptor molecule is measured by its electron affinity which is the energy released when filling the lowest unoccupied molecul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Product (chemistry)
Products are the species formed from chemical reactions. During a chemical reaction, reactants are transformed into products after passing through a high energy transition state. This process results in the consumption of the reactants. It can be a spontaneous reaction or mediated by catalysts which lower the energy of the transition state, and by solvents which provide the chemical environment necessary for the reaction to take place. When represented in chemical equations, products are by convention drawn on the right-hand side, even in the case of reversible reactions. The properties of products such as their energies help determine several characteristics of a chemical reaction, such as whether the reaction is exergonic or endergonic. Additionally, the properties of a product can make it easier to extract and purify following a chemical reaction, especially if the product has a different state of matter than the reactants. Spontaneous reaction : R \rightarrow P *Where R is r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
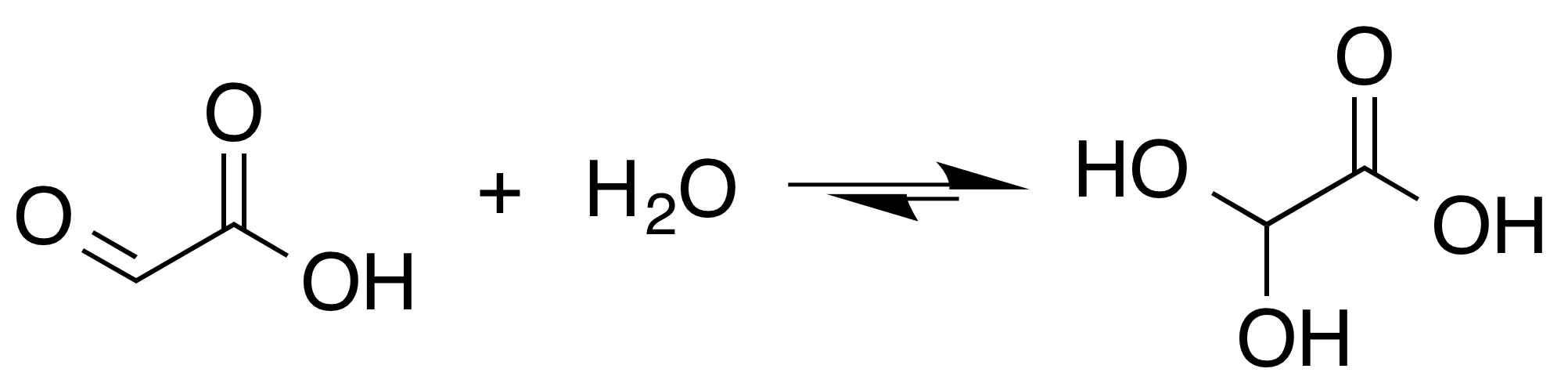
Glyoxylate
Glyoxylic acid or oxoacetic acid is an organic compound. Together with acetic acid, glycolic acid, and oxalic acid, glyoxylic acid is one of the C2 carboxylic acids. It is a colourless solid that occurs naturally and is useful industrially. Structure and nomenclature Although the structure of glyoxylic acid is described as having an aldehyde functional group, the aldehyde is only a minor component of the form most prevalent in some situations. Instead, it often exists as a hydrate or a cyclic dimer. For example, in the presence of water, the carbonyl rapidly converts to a geminal diol (described as the "monohydrate"). The equilibrium constant (''K'') is 300 for the formation of dihydroxyacetic acid at room temperature: : In solution, the monohydrate exists in equilibrium with a hemi acylal dimer form:Georges Mattioda and Yani Christidis “Glyoxylic Acid” Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry, 2002, Wiley-VCH, Weinheim. : In isolation, the aldehyde structure ha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reduced Acceptor
An electron acceptor is a chemical entity that accepts electrons transferred to it from another compound. It is an oxidizing agent that, by virtue of its accepting electrons, is itself reduced in the process. Electron acceptors are sometimes mistakenly called electron receptors. Typical oxidizing agents undergo permanent chemical alteration through covalent or ionic reaction chemistry, resulting in the complete and irreversible transfer of one or more electrons. In many chemical circumstances, however, the transfer of electronic charge from an electron donor may be only fractional, meaning an electron is not completely transferred, but results in an electron resonance between the donor and acceptor. This leads to the formation of charge transfer complexes in which the components largely retain their chemical identities. The electron accepting power of an acceptor molecule is measured by its electron affinity which is the energy released when filling the lowest unoccupied molecul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oxidoreductase
In biochemistry, an oxidoreductase is an enzyme that catalyzes the transfer of electrons from one molecule, the reductant, also called the electron donor, to another, the oxidant, also called the electron acceptor. This group of enzymes usually utilizes NADP+ or NAD+ as cofactors. Transmembrane oxidoreductases create electron transport chains in bacteria, chloroplasts and mitochondria, including respiratory complexes I, II and III. Some others can associate with biological membranes as peripheral membrane proteins or be anchored to the membranes through a single transmembrane helix. in ...
|
List Of Enzymes
This article lists enzymes by their classification in the International Union of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology's Enzyme Commission (EC) numbering system. * List of EC numbers (EC 5) * List of EC numbers (EC 6) :Oxidoreductases (EC 1) (Oxidoreductase) *Dehydrogenase * Luciferase *DMSO reductase :EC 1.1 (act on the CH-OH group of donors) * :EC 1.1.1 (with NAD+ or NADP+ as acceptor) ** Alcohol dehydrogenase (NAD) ** Alcohol dehydrogenase (NADP) **Homoserine dehydrogenase ** Aminopropanol oxidoreductase **Diacetyl reductase **Glycerol dehydrogenase **Propanediol-phosphate dehydrogenase ** glycerol-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (NAD+) ** D-xylulose reductase **L-xylulose reductase **Lactate dehydrogenase **Malate dehydrogenase **Isocitrate dehydrogenase ** HMG-CoA reductase * :EC 1.1.2 (with a cytochrome as acceptor) * :EC 1.1.3 (with oxygen as acceptor) **Glucose oxidase **L-gulonolactone oxidase **Thiamine oxidase **Xanthine oxidase * :EC 1.1.4 (with a disul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |