|
Glycogen Body
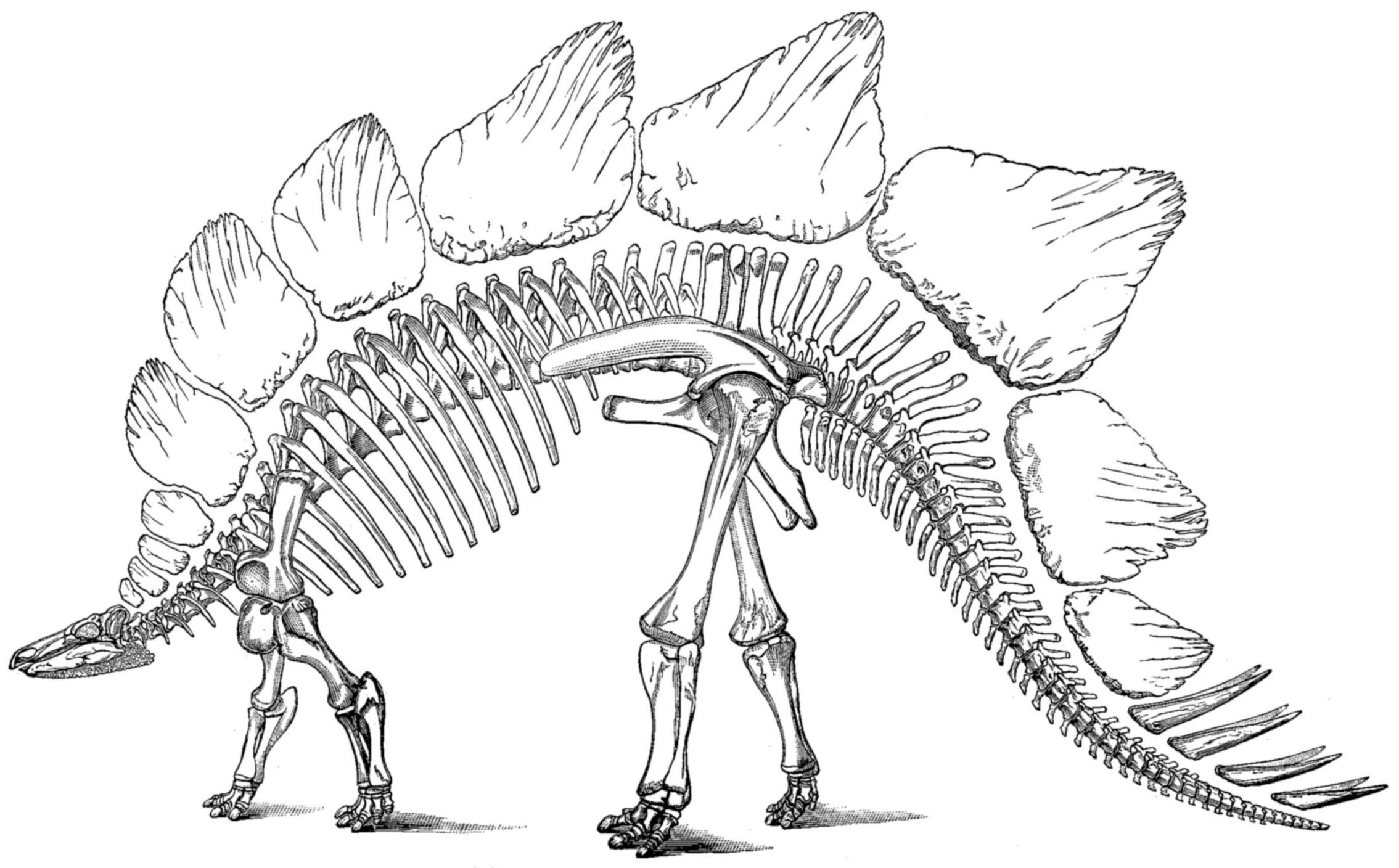
A glycogen body is an oval structure in the spinal cord of birds that is made of specialized cells that contain large amounts of glycogen. Housed within the synsacrum, the function of this structure is not known, but it does not seem to be related to the normal function of glycogen in animals, which is the storage of energy. Glycogen bodies may also have been present in some non-avian dinosaurs and are possibly the explanation for the structure that was once thought to be a "second brain" in animals such as ''Stegosaurus ''Stegosaurus'' (; ) is a genus of herbivorous, four-legged, armored dinosaur from the Late Jurassic, characterized by the distinctive kite-shaped upright plates along their backs and spikes on their tails. Fossils of the genus have been foun ...''. References {{reflist Bird anatomy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spinal Cord
The spinal cord is a long, thin, tubular structure made up of nervous tissue, which extends from the medulla oblongata in the brainstem to the lumbar region of the vertebral column (backbone). The backbone encloses the central canal of the spinal cord, which contains cerebrospinal fluid. The brain and spinal cord together make up the central nervous system (CNS). In humans, the spinal cord begins at the occipital bone, passing through the foramen magnum and then enters the spinal canal at the beginning of the cervical vertebrae. The spinal cord extends down to between the first and second lumbar vertebrae, where it ends. The enclosing bony vertebral column protects the relatively shorter spinal cord. It is around long in adult men and around long in adult women. The diameter of the spinal cord ranges from in the cervical and lumbar regions to in the thoracic area. The spinal cord functions primarily in the transmission of nerve signals from the motor cortex to the body, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bird
Birds are a group of warm-blooded vertebrates constituting the class Aves (), characterised by feathers, toothless beaked jaws, the laying of hard-shelled eggs, a high metabolic rate, a four-chambered heart, and a strong yet lightweight skeleton. Birds live worldwide and range in size from the bee hummingbird to the ostrich. There are about ten thousand living species, more than half of which are passerine, or "perching" birds. Birds have whose development varies according to species; the only known groups without wings are the extinct moa and elephant birds. Wings, which are modified forelimbs, gave birds the ability to fly, although further evolution has led to the loss of flight in some birds, including ratites, penguins, and diverse endemic island species. The digestive and respiratory systems of birds are also uniquely adapted for flight. Some bird species of aquatic environments, particularly seabirds and some waterbirds, have further evolved for swimming. B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cell (biology)
The cell is the basic structural and functional unit of life forms. Every cell consists of a cytoplasm enclosed within a membrane, and contains many biomolecules such as proteins, DNA and RNA, as well as many small molecules of nutrients and metabolites.Cell Movements and the Shaping of the Vertebrate Body in Chapter 21 of Molecular Biology of the Cell '' fourth edition, edited by Bruce Alberts (2002) published by Garland Science. The Alberts text discusses how the "cellular building blocks" move to shape developing embryos. It is also common to describe small molecules such as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glycogen
Glycogen is a multibranched polysaccharide of glucose that serves as a form of energy storage in animals, fungi, and bacteria. The polysaccharide structure represents the main storage form of glucose in the body. Glycogen functions as one of two forms of energy reserves, glycogen being for short-term and the other form being triglyceride stores in adipose tissue (i.e., body fat) for long-term storage. In humans, glycogen is made and stored primarily in the cells of the liver and skeletal muscle. In the liver, glycogen can make up 5–6% of the organ's fresh weight, and the liver of an adult, weighing 1.5 kg, can store roughly 100–120 grams of glycogen. In skeletal muscle, glycogen is found in a low concentration (1–2% of the muscle mass) and the skeletal muscle of an adult weighing 70 kg stores roughly 400 grams of glycogen. The amount of glycogen stored in the body—particularly within the muscles and liver—mostly depends on physical training, bas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Synsacrum
The synsacrum is a skeletal structure of birds and other dinosaurs, in which the sacrum is extended by incorporation of additional fused or partially fused caudal or lumbar vertebrae and it can only be seen in birds. Some posterior thoracic vertebrae, the lumbar, sacral and a few anterior caudal vertebrae are fused to form a complex bone called synsacrum. The innominate bones are fused with the synsacrum to a greater or lesser extent, according to species, forming an avian pelvis. This forms a more extensive rigid structure than the pelvis of a mammal, fulfilling requirements for flight, locomotion and respiration. Posterior to the synsacrum there are a few free caudal vertebrae, the last of which is the pygostyle to which the long, stiff tail feathers are attached. The central section of the synsacrum is swollen to accommodate the glycogen body, an organ whose function is as yet unclear but which may be associated with balance. In terms of external morphology, the synsacrum cor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Unsolved Problems In Biology
This article lists notable unsolved problems in biology. General biology Evolution and origins of life *Origin of life. Exactly how, where, and when did life on Earth originate? Which, if any, of the many hypotheses is correct? What were the metabolic pathways used by the earliest life forms? * Origins of viruses. Exactly how and when did different groups of viruses originate? *Development and evolution of brain. How and why did the brain evolve? What are the molecular determinants of individual brain development? *Origin of Eukaryotes (Symbiogenesis). How and why did cells combine to form the eukaryotic cell? Did one or more random events lead to the first eukaryotic cells, or can the formation of eukaryotic cells be explained by physical and biological principles? How did the mitochondria's mitosis cycle come in sync with its host cell? Did the mitochondria or the nucleus develop first in eukaryotes? *Last Universal Common Ancestor. What were the characteristics of the Last U ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dinosaur
Dinosaurs are a diverse group of reptiles of the clade Dinosauria. They first appeared during the Triassic period, between 243 and 233.23 million years ago (mya), although the exact origin and timing of the evolution of dinosaurs is the subject of active research. They became the dominant terrestrial vertebrates after the Triassic–Jurassic extinction event 201.3 mya; their dominance continued throughout the Jurassic and Cretaceous periods. The fossil record shows that birds are feathered dinosaurs, having evolved from earlier theropods during the Late Jurassic epoch, and are the only dinosaur lineage known to have survived the Cretaceous–Paleogene extinction event approximately 66 mya. Dinosaurs can therefore be divided into avian dinosaurs—birds—and the extinct non-avian dinosaurs, which are all dinosaurs other than birds. Dinosaurs are varied from taxonomic, morphological and ecological standpoints. Birds, at over 10,700 living species, are among ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stegosaurus
''Stegosaurus'' (; ) is a genus of herbivorous, four-legged, armored dinosaur from the Late Jurassic, characterized by the distinctive kite-shaped upright plates along their backs and spikes on their tails. Fossils of the genus have been found in the western United States and in Portugal, where they are found in Kimmeridgian- to early Tithonian-aged strata, dating to between 155 and 145 million years ago. Of the species that have been classified in the upper Morrison Formation of the western US, only three are universally recognized: ''S. stenops'', ''S. ungulatus'' and ''S. sulcatus''. The remains of over 80 individual animals of this genus have been found. ''Stegosaurus'' would have lived alongside dinosaurs such as ''Apatosaurus'', ''Diplodocus'', ''Brachiosaurus'', ''Ceratosaurus'', and ''Allosaurus''; the latter two may have preyed on it. They were large, heavily built, herbivorous quadrupeds with rounded backs, short fore limbs, long hind limbs, and tails held hi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)