|
Glucagon-like Peptide 1 Receptor
The glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor (GLP1R) is a receptor protein found on beta cells of the pancreas and on neurons of the brain. It is involved in the control of blood sugar level by enhancing insulin secretion. In humans it is synthesised by the gene ''GLP1R'', which is present on chromosome 6. It is a member of the glucagon receptor family of G protein-coupled receptors. GLP1R is composed of two domains, one extracellular (ECD) that binds the C-terminal helix of GLP-1, and one transmembrane (TMD) domain that binds the N-terminal region of GLP-1. In the TMD domain there is a fulcrum of polar residues that regulates the biased signaling of the receptor while the transmembrane helical boundaries and extracellular surface are a trigger for biased agonism. Human receptor ligands GLP1R binds glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP1) and glucagon as its natural endogenous agonists. Receptor agonists: *GLP-1 – endogenous in humans * glucagon – endogenous in humans *Oxyntomodulin * ex ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Receptor (biochemistry)
In biochemistry and pharmacology, receptors are chemical structures, composed of protein, that receive and transduce signals that may be integrated into biological systems. These signals are typically chemical messengers which bind to a receptor and cause some form of cellular/tissue response, e.g. a change in the electrical activity of a cell. There are three main ways the action of the receptor can be classified: relay of signal, amplification, or integration. Relaying sends the signal onward, amplification increases the effect of a single ligand, and integration allows the signal to be incorporated into another biochemical pathway. Receptor proteins can be classified by their location. Transmembrane receptors include ligand-gated ion channels, G protein-coupled receptors, and enzyme-linked hormone receptors. Intracellular receptors are those found inside the cell, and include cytoplasmic receptors and nuclear receptors. A molecule that binds to a receptor is called a ligand ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dulaglutide
Dulaglutide, sold under the brand name Trulicity among others, is a medication used for the treatment of type 2 diabetes in combination with diet and exercise. It is also approved in the United States for the reduction of major adverse cardiovascular events in adults with type 2 diabetes who have established cardiovascular disease or multiple cardiovascular risk factors. It is a once-weekly injection. The most common side effects are nausea, diarrhea, vomiting, abdominal pain, and decreased appetite. It is a glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonist (GLP-1 agonist) consisting of GLP-1(7-37) covalently linked to an Fc fragment of human IgG4. GLP-1 is a hormone that is involved in the normalization of level of glucose in blood (glycemia). The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved dulaglutide for use in the United States in September 2014. It was approved for use in the European Union in November 2014. In 2020, it was the 96th most commonly prescribed medication in the Unit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
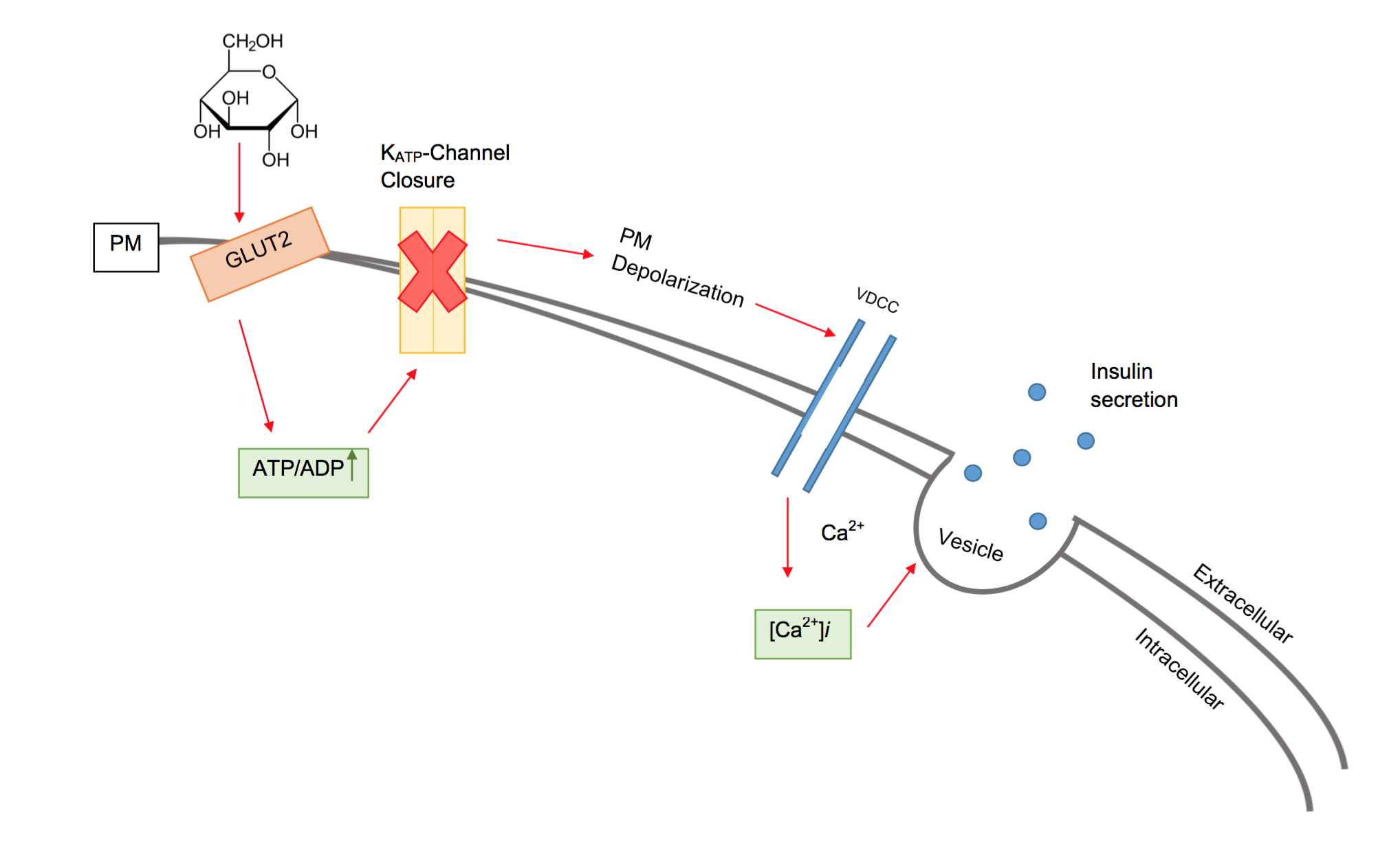
Insulin
Insulin (, from Latin ''insula'', 'island') is a peptide hormone produced by beta cells of the pancreatic islets encoded in humans by the ''INS'' gene. It is considered to be the main anabolic hormone of the body. It regulates the metabolism of carbohydrates, fats and protein by promoting the absorption of glucose from the blood into liver, fat and skeletal muscle cells. In these tissues the absorbed glucose is converted into either glycogen via glycogenesis or fats (triglycerides) via lipogenesis, or, in the case of the liver, into both. Glucose production and secretion by the liver is strongly inhibited by high concentrations of insulin in the blood. Circulating insulin also affects the synthesis of proteins in a wide variety of tissues. It is therefore an anabolic hormone, promoting the conversion of small molecules in the blood into large molecules inside the cells. Low insulin levels in the blood have the opposite effect by promoting widespread catabolism, especially o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adenylyl Cyclase
Adenylate cyclase (EC 4.6.1.1, also commonly known as adenyl cyclase and adenylyl cyclase, abbreviated AC) is an enzyme with systematic name ATP diphosphate-lyase (cyclizing; 3′,5′-cyclic-AMP-forming). It catalyzes the following reaction: :ATP = 3′,5′-cyclic AMP + diphosphate It has key regulatory roles in essentially all cells. It is the most polyphyletic known enzyme: six distinct classes have been described, all catalyzing the same reaction but representing unrelated gene families with no known sequence or structural homology. The best known class of adenylyl cyclases is class III or AC-III (Roman numerals are used for classes). AC-III occurs widely in eukaryotes and has important roles in many human tissues. All classes of adenylyl cyclase catalyse the conversion of adenosine triphosphate (ATP) to 3',5'-cyclic AMP (cAMP) and pyrophosphate.Magnesium ions are generally required and appear to be closely involved in the enzymatic mechanism. The cAMP produced by AC ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beta Cells
Beta cells (β-cells) are a type of cell found in pancreatic islets that synthesize and secrete insulin and amylin. Beta cells make up 50–70% of the cells in human islets. In patients with Type 1 diabetes, beta-cell mass and function are diminished, leading to insufficient insulin secretion and hyperglycemia. Function The primary function of a beta cell is to produce and release insulin and amylin. Both are hormones which reduce blood glucose levels by different mechanisms. Beta cells can respond quickly to spikes in blood glucose concentrations by secreting some of their stored insulin and amylin while simultaneously producing more. Primary cilia on beta cells regulate their function and energy metabolism. Cilia deletion can lead to islet dysfunction and type 2 diabetes. Insulin synthesis Beta cells are the only site of insulin synthesis in mammals. As glucose stimulates insulin secretion, it simultaneously increases proinsulin biosynthesis, mainly through translational cont ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pancreas
The pancreas is an organ of the digestive system and endocrine system of vertebrates. In humans, it is located in the abdomen behind the stomach and functions as a gland. The pancreas is a mixed or heterocrine gland, i.e. it has both an endocrine and a digestive exocrine function. 99% of the pancreas is exocrine and 1% is endocrine. As an endocrine gland, it functions mostly to regulate blood sugar levels, secreting the hormones insulin, glucagon, somatostatin, and pancreatic polypeptide. As a part of the digestive system, it functions as an exocrine gland secreting pancreatic juice into the duodenum through the pancreatic duct. This juice contains bicarbonate, which neutralizes acid entering the duodenum from the stomach; and digestive enzymes, which break down carbohydrates, proteins, and fats in food entering the duodenum from the stomach. Inflammation of the pancreas is known as pancreatitis, with common causes including chronic alcohol use and gallstones. Becaus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Positive Allosteric Modulator
In pharmacology and biochemistry, allosteric modulators are a group of substances that bind to a receptor to change that receptor's response to stimulus. Some of them, like benzodiazepines, are drugs. The site that an allosteric modulator binds to (i.e., an ''allosteric site'') is not the same one to which an endogenous agonist of the receptor would bind (i.e., an ''orthosteric site''). Modulators and agonists can both be called receptor ligands. Allosteric modulators can be 1 of 3 types either: positive, negative or neutral. Positive types increase the response of the receptor by increasing the probability that an agonist will bind to a receptor (i.e. affinity), increasing its ability to activate the receptor (i.e. efficacy), or both. Negative types decrease the agonist affinity and/or efficacy. Neutral types don't affect agonist activity but can stop other modulators from binding to an allosteric site. Some modulators also work as allosteric agonists. The term "allosteric" derive ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Receptor Antagonist
A receptor antagonist is a type of receptor ligand or drug that blocks or dampens a biological response by binding to and blocking a receptor rather than activating it like an agonist. Antagonist drugs interfere in the natural operation of receptor proteins.Pharmacology Guide: In vitro pharmacology: concentration-response curves " '' GlaxoWellcome.'' Retrieved on December 6, 2007. They are sometimes called blockers; examples include alpha blockers, |
Lithium Chloride
Lithium chloride is a chemical compound with the formula Li Cl. The salt is a typical ionic compound (with certain covalent characteristics), although the small size of the Li+ ion gives rise to properties not seen for other alkali metal chlorides, such as extraordinary solubility in polar solvents (83.05 g/100 mL of water at 20 °C) and its hygroscopic properties. Chemical properties The salt forms crystalline hydrates, unlike the other alkali metal chlorides. Mono-, tri-, and pentahydrates are known. The anhydrous salt can be regenerated by heating the hydrates. LiCl also absorbs up to four equivalents of ammonia/mol. As with any other ionic chloride, solutions of lithium chloride can serve as a source of chloride ion, e.g., forming a precipitate upon treatment with silver nitrate: : LiCl + AgNO3 → AgCl + LiNO3 Preparation Lithium chloride is produced by treatment of lithium carbonate with hydrochloric acid. Anhydrous LiCl is prepared from the hydrate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Taspoglutide
Taspoglutide is a former experimental drug, a glucagon-like peptide-1 agonist (GLP-1 agonist), that was under investigation for treatment of type 2 diabetes and being codeveloped by Ipsen and Roche. Initially, phase II trials reported it was effective and well tolerated. Of the eight planned phase III clinical trials of weekly taspoglutide (four against exenatide, sitagliptin, insulin glargine, and pioglitazone), at least five were active in 2009. Preliminary results in early 2010 were favourable. (At least one of the eight planned phase III trials had not started recruiting by end 2009.) In September 2010 Roche halted Phase III clinical trials due to incidences of serious hypersensitivity reactions and gastrointestinal side effects. no new trials have been registered since 2010. Chemistry Taspoglutide is the peptide with the sequence H2N-His-2-methyl-Ala-Glu-Gly-Thr-Phe-Thr-Ser-Asp-Val-Ser-Ser-Tyr-Leu-Glu-Gly-Gln-Ala-Ala-Lys-Glu-Phe-Ile-Ala-Trp-Leu-Val-Lys-2-methyl-Ala-Arg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Semaglutide
Semaglutide, sold under the brand names Ozempic, Wegovy and Rybelsus, is an antidiabetic medication used for the treatment of type 2 diabetes and as anti-obesity medication for long-term weight management, developed by Novo Nordisk in 2012. Semaglutide is a GLP-1 receptor agonist, meaning that it mimics the action of the human incretin glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1), thereby increasing insulin secretion and increasing blood sugar disposal and improving glycemic control. Side effects include nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, abdominal pain, and constipation. In December 2017, the injectable version named Ozempic was approved, in September 2019, a version which can be taken by mouth (Rybelsus) was approved, and in June 2021, a higher-dose injection sold under the brand name Wegovy for long-term weight management in adults was approved by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA). In 2020, semaglutide was the 129th most commonly prescribed medication in the United States, with m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |